Luxury Brands Are in a Winner-Takes-All Phase
Hermès captured the lion’s share of growth in luxury-goods spending in the second quarter, while everyone else lagged behind
Louis Vuitton’s owner designed the medals for the Paris Olympic Games. It can’t be easy to see rival Hermès make off with gold in the second-quarter sales heat.
France’s three most powerful luxury-goods companies reported very mixed second-quarter results last week. On Tuesday, LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton said sales in the three months through June rose by a disappointing 1% compared with the same period last year. Gucci owner Kering followed with an 11% fall for the quarter and issued a profit warning. Hermès left its competitors in the dust with a 13% increase in sales over the same period.
Hermès captured more than 100% of the incremental growth in the industry in the latest quarter. Luxury shoppers spent €440 million—equivalent to $477.6 million at current exchange rates—more in the French brand’s stores than they did in the same period of last year. They spent €400 million less on all other luxury brands combined, based on analysis by Bank of America.
This points to a double whammy for high-end brands, which face challenges at both ends of the consumer spectrum they serve.
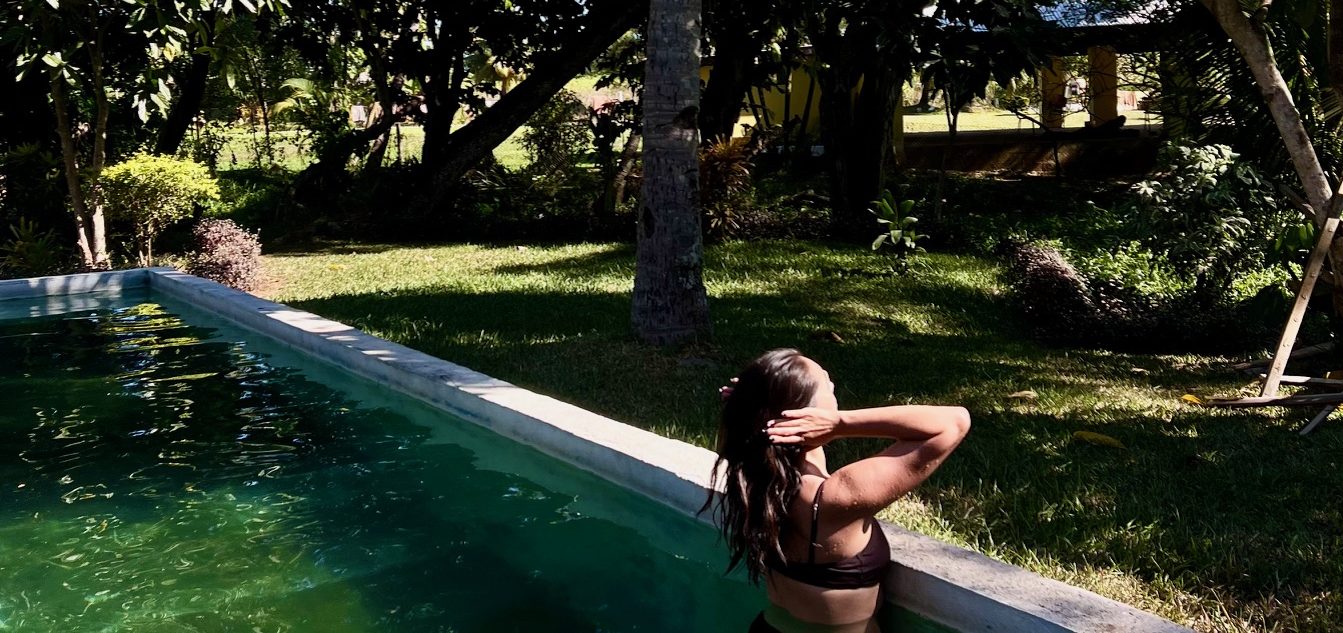
It has been clear for months that middle-class shoppers in the U.S. and China, the luxury industry’s two most important markets, have reined in their purchasing.
Chinese consumers are saving rather than spending because the value of their homes is falling. Lower-income and middle-income Americans who developed a taste for luxury during the pandemic have pulled back sharply as they have burned through excess savings.
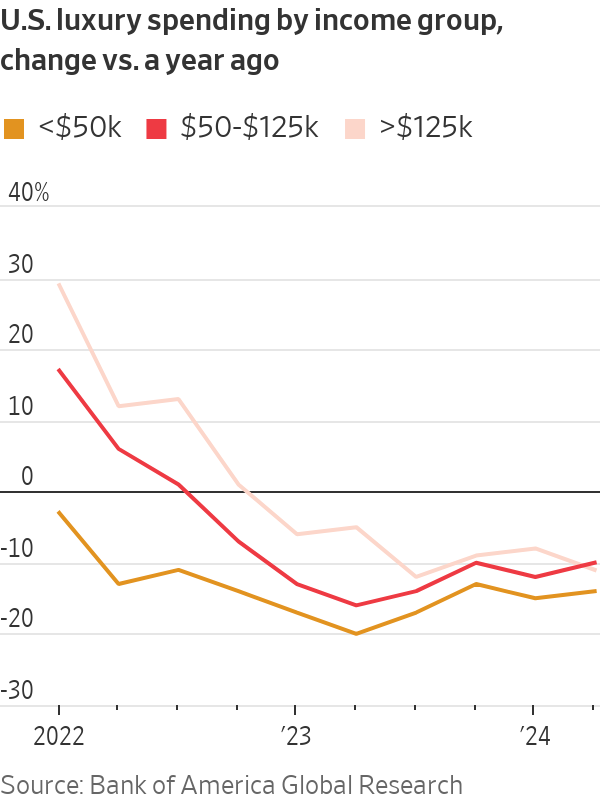
Now, wealthy consumers, too, seem to be getting choosier about which brands they will and won’t buy. Hermès Chief Executive Axel Dumas said there is a “flight to quality” under way in the luxury industry. This shift is benefiting the Birkin handbag maker , which has a reputation for timeless designs.
Chinese buyers in particular are avoiding flashy and logo-heavy brands as worries about the country’s economy and real-estate challenges grow.
Jewellery sales are also holding up as shoppers look for goods that are more likely to hold their value than clothing or handbags. Cartier’s owner Richemont said its jewellery sales rose 4% in the quarter, although the company’s overall sales were weighed down by weak demand for its watch and fashion brands. Kering jewellery labels Boucheron and Pomellato were rare bright spots in its portfolio.
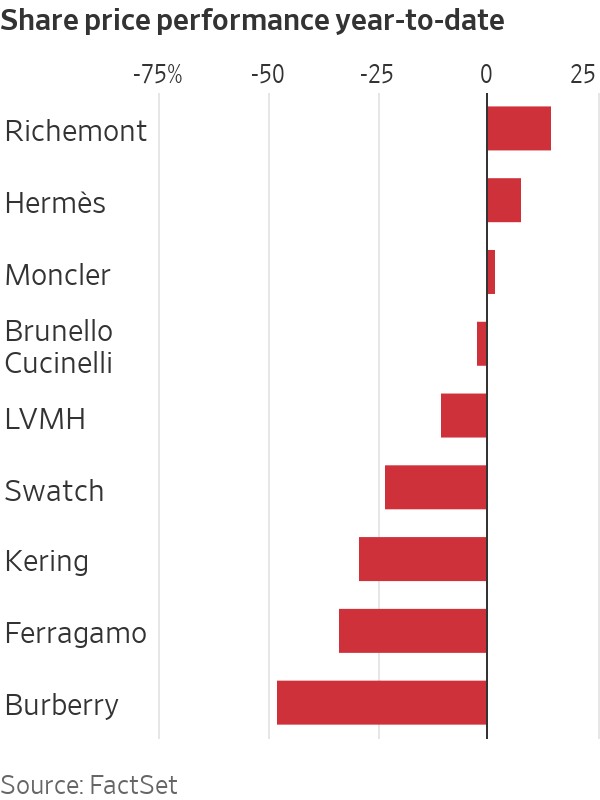
The outlook is harsh for brands such as Gucci and Burberry that are in turnaround mode. The latter issued a profit warning earlier this month and replaced its CEO in an admission that a years-long push to make the British trench-coat maker more exclusive had failed. Its shares have fallen to levels not seen since 2010.
Both brands face an uphill battle to lure shoppers. Neither Gucci nor Burberry is known for the classic designs now in vogue. The labels might also have exacerbated the slump, as the sharp price increases that luxury brands implemented in recent years have sidelined aspirational shoppers.
Luxury stocks are diverging. Shares in Richemont and Hermès have gained 15% and 8% respectively so far this year, with everyone else in the red.
Investors are taking their cue from wealthy shoppers: In troubled times, the most exclusive brands are the safest bet.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
A divide has opened in the tech job market between those with artificial-intelligence skills and everyone else.
A 30-metre masterpiece unveiled in Monaco brings Lamborghini’s supercar drama to the high seas, powered by 7,600 horsepower and unmistakable Italian design.
A divide has opened in the tech job market between those with artificial-intelligence skills and everyone else.
There has rarely, if ever, been so much tech talent available in the job market. Yet many tech companies say good help is hard to find.
What gives?
U.S. colleges more than doubled the number of computer-science degrees awarded from 2013 to 2022, according to federal data. Then came round after round of layoffs at Google, Meta, Amazon, and others.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts businesses will employ 6% fewer computer programmers in 2034 than they did last year.
All of this should, in theory, mean there is an ample supply of eager, capable engineers ready for hire.
But in their feverish pursuit of artificial-intelligence supremacy, employers say there aren’t enough people with the most in-demand skills. The few perceived as AI savants can command multimillion-dollar pay packages. On a second tier of AI savvy, workers can rake in close to $1 million a year .
Landing a job is tough for most everyone else.
Frustrated job seekers contend businesses could expand the AI talent pipeline with a little imagination. The argument is companies should accept that relatively few people have AI-specific experience because the technology is so new. They ought to focus on identifying candidates with transferable skills and let those people learn on the job.
Often, though, companies seem to hold out for dream candidates with deep backgrounds in machine learning. Many AI-related roles go unfilled for weeks or months—or get taken off job boards only to be reposted soon after.
Playing a different game
It is difficult to define what makes an AI all-star, but I’m sorry to report that it’s probably not whatever you’re doing.
Maybe you’re learning how to work more efficiently with the aid of ChatGPT and its robotic brethren. Perhaps you’re taking one of those innumerable AI certificate courses.
You might as well be playing pickup basketball at your local YMCA in hopes of being signed by the Los Angeles Lakers. The AI minds that companies truly covet are almost as rare as professional athletes.
“We’re talking about hundreds of people in the world, at the most,” says Cristóbal Valenzuela, chief executive of Runway, which makes AI image and video tools.
He describes it like this: Picture an AI model as a machine with 1,000 dials. The goal is to train the machine to detect patterns and predict outcomes. To do this, you have to feed it reams of data and know which dials to adjust—and by how much.
The universe of people with the right touch is confined to those with uncanny intuition, genius-level smarts or the foresight (possibly luck) to go into AI many years ago, before it was all the rage.
As a venture-backed startup with about 120 employees, Runway doesn’t necessarily vie with Silicon Valley giants for the AI job market’s version of LeBron James. But when I spoke with Valenzuela recently, his company was advertising base salaries of up to $440,000 for an engineering manager and $490,000 for a director of machine learning.
A job listing like one of these might attract 2,000 applicants in a week, Valenzuela says, and there is a decent chance he won’t pick any of them. A lot of people who claim to be AI literate merely produce “workslop”—generic, low-quality material. He spends a lot of time reading academic journals and browsing GitHub portfolios, and recruiting people whose work impresses him.
In addition to an uncommon skill set, companies trying to win in the hypercompetitive AI arena are scouting for commitment bordering on fanaticism .
Daniel Park is seeking three new members for his nine-person startup. He says he will wait a year or longer if that’s what it takes to fill roles with advertised base salaries of up to $500,000.
He’s looking for “prodigies” willing to work seven days a week. Much of the team lives together in a six-bedroom house in San Francisco.
If this sounds like a lonely existence, Park’s team members may be able to solve their own problem. His company, Pickle, aims to develop personalised AI companions akin to Tony Stark’s Jarvis in “Iron Man.”
Overlooked
James Strawn wasn’t an AI early adopter, and the father of two teenagers doesn’t want to sacrifice his personal life for a job. He is beginning to wonder whether there is still a place for people like him in the tech sector.
He was laid off over the summer after 25 years at Adobe , where he was a senior software quality-assurance engineer. Strawn, 55, started as a contractor and recalls his hiring as a leap of faith by the company.
He had been an artist and graphic designer. The managers who interviewed him figured he could use that background to help make Illustrator and other Adobe software more user-friendly.
Looking for work now, he doesn’t see the same willingness by companies to take a chance on someone whose résumé isn’t a perfect match to the job description. He’s had one interview since his layoff.
“I always thought my years of experience at a high-profile company would at least be enough to get me interviews where I could explain how I could contribute,” says Strawn, who is taking foundational AI courses. “It’s just not like that.”
The trouble for people starting out in AI—whether recent grads or job switchers like Strawn—is that companies see them as a dime a dozen.
“There’s this AI arms race, and the fact of the matter is entry-level people aren’t going to help you win it,” says Matt Massucci, CEO of the tech recruiting firm Hirewell. “There’s this concept of the 10x engineer—the one engineer who can do the work of 10. That’s what companies are really leaning into and paying for.”
He adds that companies can automate some low-level engineering tasks, which frees up more money to throw at high-end talent.
It’s a dynamic that creates a few handsomely paid haves and a lot more have-nots.
ABC Bullion has launched a pioneering investment product that allows Australians to draw regular cashflow from their precious metal holdings.
A luxury lifestyle might cost more than it used to, but how does it compare with cities around the world?























