Green Investors Were Crushed. Now It’s Time to Make Money.
The lessons have been hard, and are a reminder of the basic facts of investing
Invest according to your political views, and you’re unlikely to make money. Companies that appeal to left-wingers or to right-wingers might be good or bad investments, but the fact of being, on current politics, clean and union-friendly for the left or oily and gun-friendly for the right is neither here nor there. What matters is their ability to make money and how highly they are valued.
This has been rammed home for environmentally-minded investors in the past year, as a coordinated selloff in anything with green credentials crushed the idea of making money while doing good.
It turns out that the real world is tougher than advocates of ESG—environmental, social and governance—investing claimed. The lessons have been hard, but should remind investors in the sector of some of the basic facts of investing. The fall in prices has improved the outlook for the stocks.
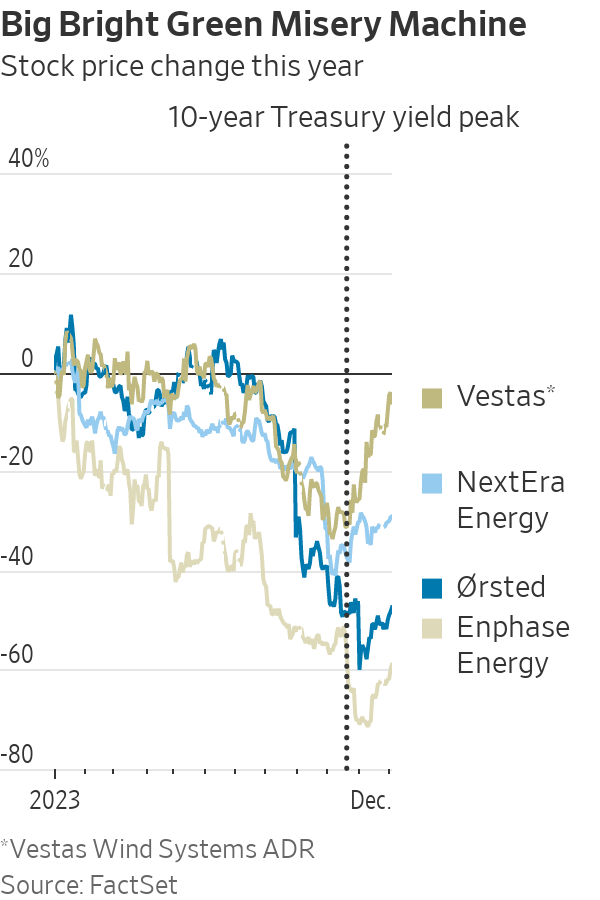
This year has been almost universally bad for clean investments. The two worst performers still in the S&P 500 are solar companies Enphase Energy and SolarEdge Technologies, down 60% and 70%, respectively. Hydrogen stocks have fallen sharply, led by Plug Power, which warned it might not survive. Wind-farm developers have been doing so badly they have pulled out of some contracts, with Denmark’s Ørsted off 48% in dollar terms and Florida-based NextEra Energy off 29%.
Electric cars have disappointed too, hitting startups and suppliers and pushing the price of lithium ores, used to produce the battery metal, down by three-quarters or more, although market-leader Tesla’s stock has been an exception.
Just as there was a coordinated green selloff, there has been a coordinated partial rebound in the past month or so.
This provides the first lesson: debt. The clean-energy sector is dependent on vast amounts of borrowing, so high interest rates really hurt. Roman Boner, who runs a clean-energy fund at Dutch fund manager Robeco, points out that major projects are typically financed with 80% debt, so rises in financing costs have a big impact on competitiveness.
Investors who bought into green stocks probably didn’t think they were making a leveraged bet on Treasurys, but that is what they ended up with. It isn’t only about corporate financing costs, either. High borrowing costs hit consumer demand for rooftop solar and for electric cars, both of which are often leased, since leasing costs depend on the cost of debt.
At a very high level, this is about long-term thinking. Low rates encourage investors to think long term, because they make future profits almost as valuable as current profits, and encourage borrowing to try to secure those future profits.
High rates encourage short-term thinking, by making profits today far more valuable than future profits—why bet on the future when you can earn 5% from Treasury bills? Short-term we get fossil-fuel profits, while long-term we get either clean energy or global warming; recently investors have been encouraged by rising rates to think short term.
The second lesson: government. Ronald Reagan overstated it when he said: “The nine most terrifying words in the English language are: ‘I’m from the government, and I’m here to help.’” But investors who rely on state subsidies to ensure profits leave themselves at the mercy of both fickle politicians and the bureaucrats Reagan was concerned about. This year’s selloff has been worsened by the bureaucrats and their failure to provide the details of many of the subsidies promised in last year’s badly named Inflation Reduction Act.
“We’re still hoping to get them by year end,” says Ed Lees, co-head of the environmental strategies group at BNP Paribas Asset Management. The next problem might be the politicians, at least if Donald Trump wins the presidency and torches the IRA. Lees thinks this will be hard, because so many IRA-subsidised projects are heading for Republican states. But Trump certainly has no sympathy for environmental causes.
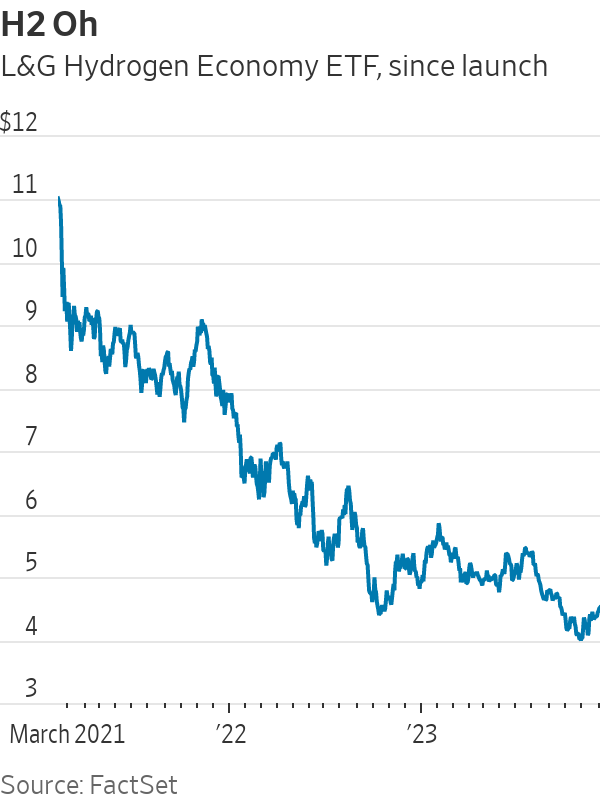
The third lesson is the one most relevant to buying today: valuation. Buying stocks when they are trendy and wildly overpriced is a recipe for disaster. Perhaps the most extreme example of late is the L&G Hydrogen Economy ETF, launched in London at the height of clean-energy excitement in February 2021. It plummeted from day one, never regained its launch price, and is down 55% since then.
“We’ve seen a very harsh reality check,” said Sonja Laud, chief investment officer of L&G Investment Management.
The question is whether the hype has left. Laud worries that one year of high rates won’t have crushed all the excesses built up in 12 years of near-zero rates. But clearly valuations are much lower than they were, and she is hopeful there are opportunities to be found now.
“The huge green premium you had previously is no longer there,” says Velislava Dimitrova, who runs sustainable funds at Fidelity International. Clean-energy stocks are “much more interesting than they used to be—I don’t believe that renewables are dead.”
In the bond market, investors are no longer paying much if any “greenium,” or extra price for green bonds. In stocks, it is harder to judge: The S&P Global Clean Energy index trades at a discount to the global market on some measures, but not others, making it difficult to conclude that the sector as a whole is a wonderful bargain.
Still, it is good news for buyers that the hype has evaporated. Investors who care about profits more than purpose can finally consider clean-energy stocks again.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
Continued stagflation and cost of living pressures are causing couples to think twice about starting a family, new data has revealed, with long term impacts expected
Australia is in the midst of a ‘baby recession’ with preliminary estimates showing the number of births in 2023 fell by more than four percent to the lowest level since 2006, according to KPMG. The consultancy firm says this reflects the impact of cost-of-living pressures on the feasibility of younger Australians starting a family.
KPMG estimates that 289,100 babies were born in 2023. This compares to 300,684 babies in 2022 and 309,996 in 2021, according to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS). KPMG urban economist Terry Rawnsley said weak economic growth often leads to a reduced number of births. In 2023, ABS data shows gross domestic product (GDP) fell to 1.5 percent. Despite the population growing by 2.5 percent in 2023, GDP on a per capita basis went into negative territory, down one percent over the 12 months.
“Birth rates provide insight into long-term population growth as well as the current confidence of Australian families,” said Mr Rawnsley. “We haven’t seen such a sharp drop in births in Australia since the period of economic stagflation in the 1970s, which coincided with the initial widespread adoption of the contraceptive pill.”
Mr Rawnsley said many Australian couples delayed starting a family while the pandemic played out in 2020. The number of births fell from 305,832 in 2019 to 294,369 in 2020. Then in 2021, strong employment and vast amounts of stimulus money, along with high household savings due to lockdowns, gave couples better financial means to have a baby. This led to a rebound in births.
However, the re-opening of the global economy in 2022 led to soaring inflation. By the start of 2023, the Australian consumer price index (CPI) had risen to its highest level since 1990 at 7.8 percent per annum. By that stage, the Reserve Bank had already commenced an aggressive rate-hiking strategy to fight inflation and had raised the cash rate every month between May and December 2022.
Five more rate hikes during 2023 put further pressure on couples with mortgages and put the brakes on family formation. “This combination of the pandemic and rapid economic changes explains the spike and subsequent sharp decline in birth rates we have observed over the past four years,” Mr Rawnsley said.
The impact of high costs of living on couples’ decision to have a baby is highlighted in births data for the capital cities. KPMG estimates there were 60,860 births in Sydney in 2023, down 8.6 percent from 2019. There were 56,270 births in Melbourne, down 7.3 percent. In Perth, there were 25,020 births, down 6 percent, while in Brisbane there were 30,250 births, down 4.3 percent. Canberra was the only capital city where there was no fall in the number of births in 2023 compared to 2019.
“CPI growth in Canberra has been slightly subdued compared to that in other major cities, and the economic outlook has remained strong,” Mr Rawnsley said. “This means families have not been hurting as much as those in other capital cities, and in turn, we’ve seen a stabilisation of births in the ACT.”
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.






















