The $65 Million Perk for CEOs: Personal Use of the Corporate Jet Has Soared
Company spending on the benefit has climbed 50% since before the pandemic
One of the flashiest executive perks has roared back since the onset of the pandemic: free personal travel on the company jet.
Companies in the S&P 500 spent $65 million for executives to use corporate jets for personal travel in 2022, up about 50% from prepandemic levelsthree years earlier, a Wall Street Journal analysis found. Early signs suggest the trend continued last year.
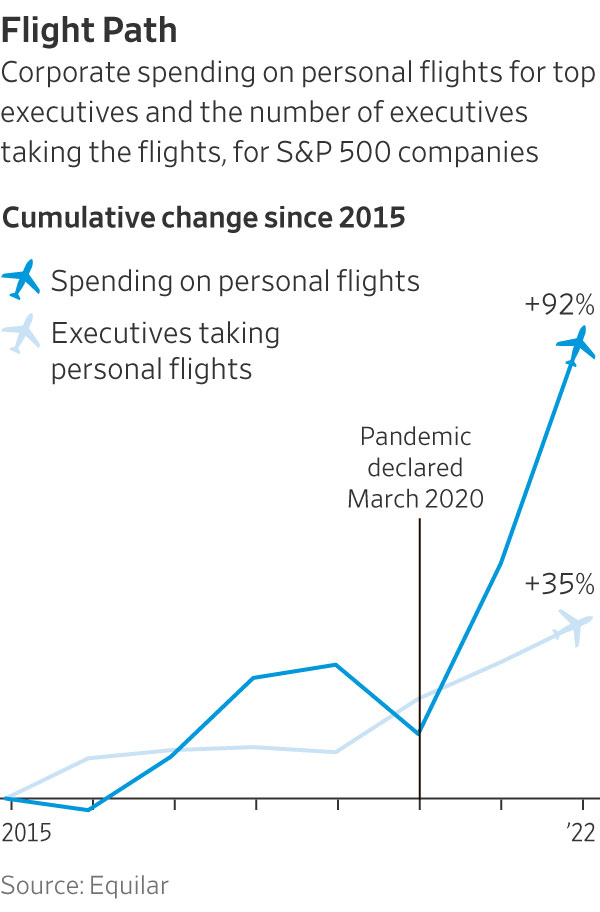
Overall, the number of big companies providing the perk rose about 14% since 2019, to 216 in 2022, figures from executive-data firmEquilar show. The number of executives receiving free flights grew nearly 25%, to 427.
Most companies report executive pay and perks in the spring.
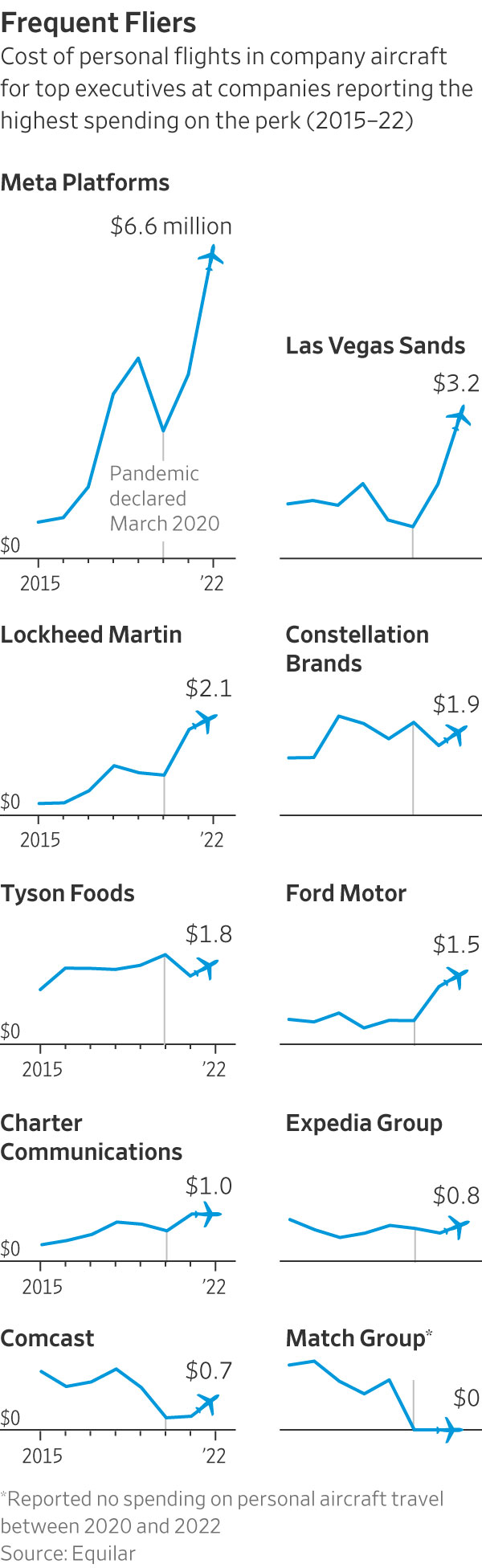
Meta Platforms spent $6.6 million in 2022 on personal flights for Chief Executive Mark Zuckerberg and his then-lieutenant, Sheryl Sandberg—up about 55% from 2019, the Journal found. Casino company Las Vegas Sands spent $3.2 million on flights for four executives, more than double its annual expense in any year since 2015. Exelon, which owns Chicago’s Commonwealth Edison utility, more than tripled its spending on the perk since 2019.
Company jets have long symbolised corporate success and, to critics, excess. Companies typically say flying corporate is safer, healthier and more efficient. Some companies—including Cardinal Health, Raymond James Financial and Hormel Foods—added or expanded the perk in 2020 or 2021, citing pandemic health and safety concerns. Most spending growth came at companies already paying for personal flights in 2019.
Palo Alto Networks began subsidising personal flights for CEO Nikesh Arora in the year ended July 2022, spending about $650,000. That total rose to $1.8 million in its most recent fiscal year, plus a further $286,000 to cover his tax bill for the perk, the cybersecurity company said in an October securities filing.
The company said in filings that its board requires Arora to fly corporate in response to a security consultant’s report. “There was a bona fide, business-related security concern for Mr. Arora and credible threat actors existed with both the willingness and resources necessary for conducting an attack on Mr. Arora,” it said.
Companies report spending on flights they can’t classify as business-related, including trips to board meetings for other companies or commuting from distant residences. Some give executives a fixed personal-flight allowance in hours or dollars, and require reimbursement beyond that.
The sums have little financial impact on most giant corporations, even when annual flight bills exceed a million dollars. Critics say the free flights indicate directors too eager to please top executives.
“The vast majority of S&P 500 companies do not offer this perk,” said Rosanna Landis Weaver, an executive-pay analyst at As You Sow, a nonprofit shareholder-advocacy group that has produced annual lists of CEOs it considers overpaid.
The Journal’s analysis reflects what companies disclose in securities filings, typically in footnotes to annual proxy statements. Federal rules generally require companies to itemize the perk for each top executive if it costs the company $25,000 or more in a year.
PepsiCo spent $776,000 on personal flights for five executives in 2022, double what it paid for the perk in 2019. Two-thirds of the spending subsidized flights by CEO Ramon Laguarta, who is required to use company aircraft for personal flights for safety and efficiency reasons. In an interview last spring, Laguarta said he sometimes ended business trips to Europe by flying to visit his mother in his native Barcelona. She died later in the year, in her 90s.
A PepsiCo spokesman said the company jet allows executives to reach remote facilities.
Personal jet use can draw investor and regulatory scrutiny. It contributed to the ouster of Credit Suisse’s chairman in 2022.
In June, tool maker Stanley Black & Decker settled Securities and Exchange Commission charges that it failed to disclose $1.3 million in perks for four executives and a director, mostly their use of company aircraft, from 2017 through 2020. In 2020, Hilton Worldwide Holdings settled SEC charges that it didn’t disclose $1.7 million in perks over four years, in part by underreporting costs for CEO Christopher Nassetta’s personal flights by 87%in two of those years. Hilton paid a $600,000 penalty.
Both companies settled without admitting or denying wrongdoing.
Stanley Black & Decker said it raised the errors with the SEC and settled without a fine. In 2022, Stanley Black & Decker reported spending nearly $143,500 on personal flights for former CEO James Loree and his successor, Donald Allan Jr., primarily to fly to outside board meetings or from second homes to work.
Hilton cited higher fuel prices in reporting about $500,000 in flights for Nassetta in 2022.
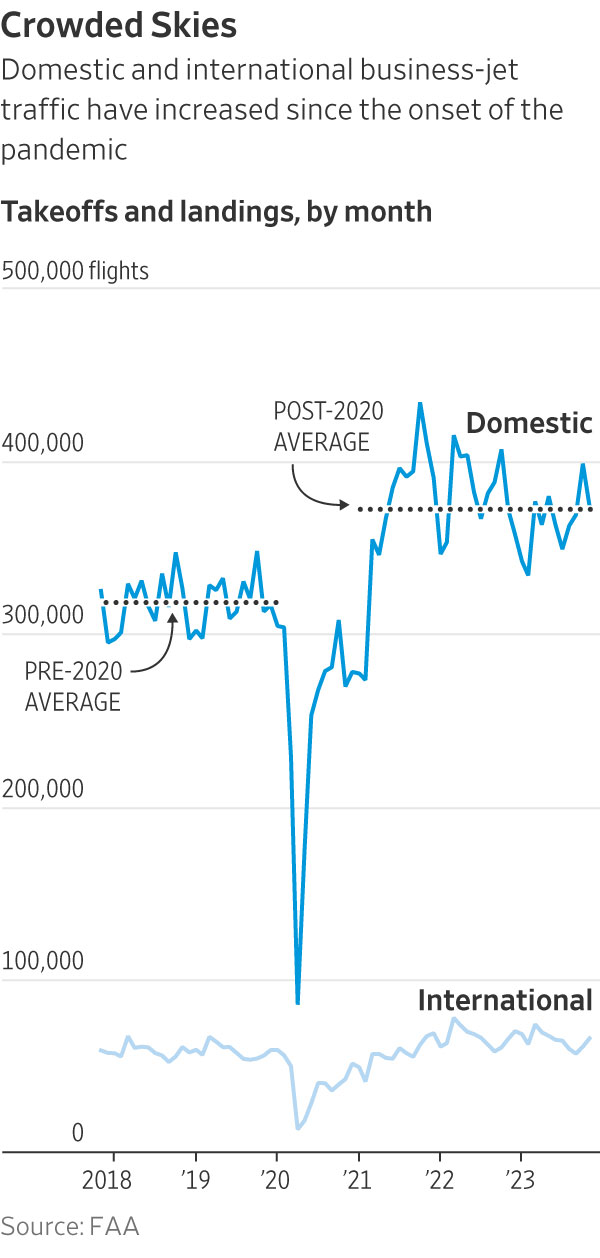
Spending on executives’ personal travel outpaced overall growth in business-jet traffic. Takeoffs and landings are up by about 19% since 2019, after dropping sharply in 2020, Federal Aviation Administration data show. Corporate spending on the perk rose 52%, the Journal found.
Higher fuel costs in 2022 contributed to the increase in spending, and there is little indication of a slowdown last year. Of the 15 S&P 500 companies that have reported spending on the perk in fiscal years ended in the second half of 2023, 10 said they increased spending, including three that didn’t report the perk a year earlier, securities filings show.
Sixteen companies that started paying for personal flights during the pandemic have since stopped. An additional 31 continued spending into 2022, with a median of $124,000. Accenture, Palo Alto Networks and concert promoter Live Nation Entertainment reported spending more than $500,000 apiece.
In 2020, Julie Sweet’s first full year as CEO, Accenture capped annual spending for her personal flights at $200,000, then doubled it the next year. Accenture raised the cap to $600,000 in its year that ended Aug. 31, when it spent about $575,000 on Sweet’s personal flights, the company said in a December securities filing.
In its filings, Accenture said it encourages Sweet to use company aircraft for personal travel, citing a security study the company commissioned.
Companies that provided the perk already in 2019 accounted for most of the recent growth in spending, the Journal found.
Meta, for example, spent nearly $11 million on Zuckerberg and Sandberg’s personal flights from 2015 through 2019, and a further $13.3 million over the next three years. Zuckerberg’s company-paid travel included trips on an aircraft he owns, which Meta charters for business, paying $523,000 in 2022. The Facebook owner stopped paying for Sandberg’s personal flights when she stepped down as a company employee in September 2022. She remains on Meta’s board.
Spokesmen for Meta and Sandberg declined to comment beyond Meta’s securities disclosures.
CEOs incurred most of the personal flight spending, making up half the executives receiving the perk in 2022 and two-thirds of the overall cost, Equilar’s data show.
At some companies, other executives are making up a bigger share of the cost. Four Norfolk Southern executive vice presidents accounted for just over half its roughly $370,000 in spending on personal flights in 2022, securities filings show. CEO Alan Shaw accounted for the rest. By contrast, the railroad reported subsidising flights only for then-CEO James Squires in the five years through 2020.
Shaw may take as many as 60 hours of personal flights on company aircraft before reimbursing Norfolk Southern, the company said in its filings. Personal use of company aircraft by executives other than the CEO was infrequent, it added. Norfolk Southern didn’t respond to requests for comment.
—Jennifer Maloney contributed to this article.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
Impact investing is becoming more mainstream as larger, institutional asset owners drive more money into the sector, according to the nonprofit Global Impact Investing Network in New York.
In the GIIN’s State of the Market 2024 report, published late last month, researchers found that assets allocated to impact-investing strategies by repeat survey responders grew by a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14% over the last five years.
These 71 responders to both the 2019 and 2024 surveys saw their total impact assets under management grow to US$249 billion this year from US$129 billion five years ago.
Medium- and large-size investors were largely responsible for the strong impact returns: Medium-size investors posted a median CAGR of 11% a year over the five-year period, and large-size investors posted a median CAGR of 14% a year.
Interestingly, the CAGR of assets held by small investors dropped by a median of 14% a year.
“When we drill down behind the compound annual growth of the assets that are being allocated to impact investing, it’s largely those larger investors that are actually driving it,” says Dean Hand, the GIIN’s chief research officer.
Overall, the GIIN surveyed 305 investors with a combined US$490 billion under management from 39 countries. Nearly three-quarters of the responders were investment managers, while 10% were foundations, and 3% were family offices. Development finance institutions, institutional asset owners, and companies represented most of the rest.
The majority of impact strategies are executed through private-equity, but public debt and equity have been the fastest-growing asset classes over the past five years, the report said. Public debt is growing at a CAGR of 32%, and public equity is growing at a CAGR of 19%. That compares to a CAGR of 17% for private equity and 7% for private debt.
According to the GIIN, the rise in public impact assets is being driven by larger investors, likely institutions.
Private equity has traditionally served as an ideal way to execute impact strategies, as it allows investors to select vehicles specifically designed to create a positive social or environmental impact by, for example, providing loans to smallholder farmers in Africa or by supporting fledging renewable energy technologies.
Future Returns: Preqin expects managers to rely on family offices, private banks, and individual investors for growth in the next six years
But today, institutional investors are looking across their portfolios—encompassing both private and public assets—to achieve their impact goals.
“Institutional asset owners are saying, ‘In the interests of our ultimate beneficiaries, we probably need to start driving these strategies across our assets,’” Hand says. Instead of carving out a dedicated impact strategy, these investors are taking “a holistic portfolio approach.”
An institutional manager may want to address issues such as climate change, healthcare costs, and local economic growth so it can support a better quality of life for its beneficiaries.
To achieve these goals, the manager could invest across a range of private debt, private equity, and real estate.
But the public markets offer opportunities, too. Using public debt, a manager could, for example, invest in green bonds, regional bank bonds, or healthcare social bonds. In public equity, it could invest in green-power storage technologies, minority-focused real-estate trusts, and in pharmaceutical and medical-care company stocks with the aim of influencing them to lower the costs of care, according to an example the GIIN lays out in a separate report on institutional strategies.
Influencing companies to act in the best interests of society and the environment is increasingly being done through such shareholder advocacy, either directly through ownership in individual stocks or through fund vehicles.
“They’re trying to move their portfolio companies to actually solving some of the challenges that exist,” Hand says.
Although the rate of growth in public strategies for impact is brisk, among survey respondents investments in public debt totaled only 12% of assets and just 7% in public equity. Private equity, however, grabs 43% of these investors’ assets.
Within private equity, Hand also discerns more evidence of maturity in the impact sector. That’s because more impact-oriented asset owners invest in mature and growth-stage companies, which are favored by larger asset owners that have more substantial assets to put to work.
The GIIN State of the Market report also found that impact asset owners are largely happy with both the financial performance and impact results of their holdings.
About three-quarters of those surveyed were seeking risk-adjusted, market-rate returns, although foundations were an exception as 68% sought below-market returns, the report said. Overall, 86% reported their investments were performing in line or above their expectations—even when their targets were not met—and 90% said the same for their impact returns.
Private-equity posted the strongest results, returning 17% on average, although that was less than the 19% targeted return. By contrast, public equity returned 11%, above a 10% target.
The fact some asset classes over performed and others underperformed, shows that “normal economic forces are at play in the market,” Hand says.
Although investors are satisfied with their impact performance, they are still dealing with a fragmented approach for measuring it, the report said. “Despite this, over two-thirds of investors are incorporating impact criteria into their investment governance documents, signalling a significant shift toward formalising impact considerations in decision-making processes,” it said.
Also, more investors are getting third-party verification of their results, which strengthens their accountability in the market.
“The satisfaction with performance is nice to see,” Hand says. “But we do need to see more about what’s happening in terms of investors being able to actually track both the impact performance in real terms as well as the financial performance in real terms.”
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.






















