The U.S. Economy’s Secret Weapon: Seniors With Money to Spend
Americans 65 and older account for record share of spending and are less susceptible to interest rates
Why has consumer spending proven so resilient as the Federal Reserve has raised interest rates? An important and little-appreciated reason: Consumers are getting older.
In August, 17.7% of the population was 65 or older, according to the Census Bureau, the highest on record going back to 1920 and up sharply from 13% in 2010. The elderly aren’t just more numerous: Their finances are relatively healthy and they have less need to borrow, such as to buy a house, and are less at risk of layoffs than other consumers.
This has made the elderly a spending force to be reckoned with. Americans age 65 and up accounted for 22% of spending last year, the highest share since records began in 1972 and up from 15% in 2010, according to the Labor Department’s survey of consumer expenditures released in September.
“These are the consumers that will matter over the coming year,” said Susan Sterne, chief economist at Economic Analysis Associates.
“Our large share of older consumers provides a consumption base in times like today when job growth slows, interest rates rise and student-debt loan repayments begin again,” she said.
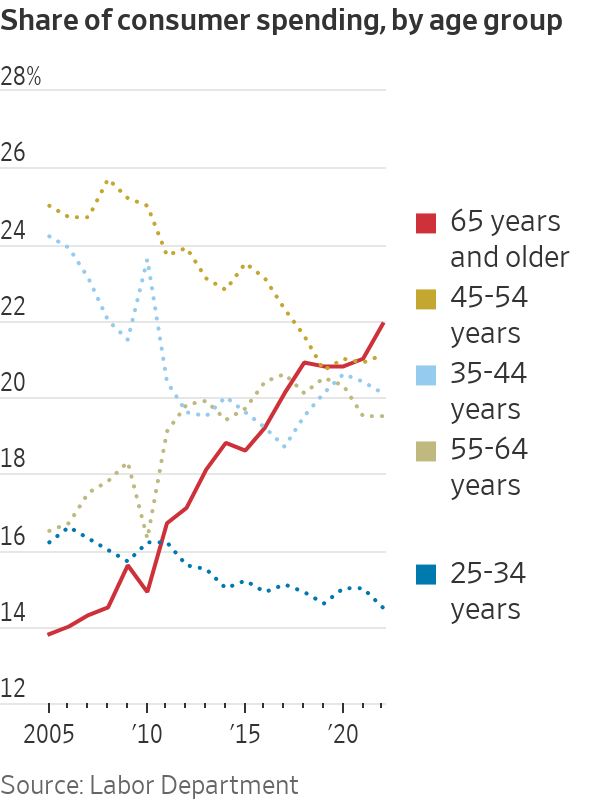
Seniors’ high spending propensities reflect health, wealth and perhaps lingering psychological effects of the pandemic.
“All my life it was, save for this, save for that,” said Maureen Green, 66, of Cape Cod, Mass. “Now there’s money in the bank and I’m spending in ways that bring me closer to friends and family than I did before.”
Green, a real-estate agent with four grown children living across the country, estimated she is spending 25% more and twice as much time traveling now compared with 2019. She recently traveled to Syracuse, N.Y., to catch a photo exhibit with friends, and toured Rhode Island with her son and his girlfriend.
“The one million Americans who didn’t survive Covid—that’s part of it. That taught me not to let time go by because before I know it, that time won’t be there anymore,” she said.
Living better, longer—and larger
“The lifestyle of the senior has changed dramatically—they’re more active than ever,” said Marshal Cohen, chief retail adviser of Circana, a research firm specialising in consumer behavior. That has expanded the menu of recreation on which to spend, he said. “They’re riding e-bikes, they’re hiking, they’re traveling. And they’re doing these things for longer than they’ve ever been done.”
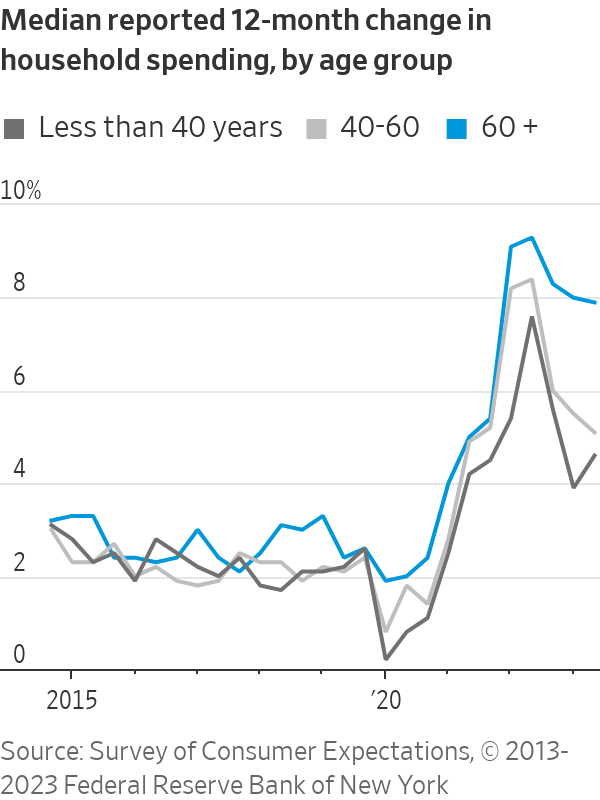
The average household led by someone age 65 and older spent 2.7% more last year than in 2021, adjusted for inflation, according to the Labor Department, compared with 0.7% for under-65 households. Spending by older households is up 34.5% from 1982, compared with 16.5% for younger households.
Comparable data isn’t available for 2023. However, consumers older than 60 reported spending 7.9% more in August than a year earlier, compared with a 5.1% increase among those age 40 to 60 and a 4.6% gain for younger consumers, according to a survey by the New York Fed. The data aren’t adjusted for inflation.
The growing yen to spend by the elderly is amplified by their sheer numbers. The unusually large cohort of baby boomers, the youngest of which are 59, are reaching their retirement years en masse.
American Cruise Lines, which gears its cruises toward older consumers, said it is seeing double-digit sales growth this year, driven largely by boomers. The Guilford, Conn., company this year added three ships to its fleet and expanded its season by a month for some popular routes.
“River cruising has traditionally attracted an older audience, and with more boomers retiring each year, we see both a rapid rate of growth and demand for longer experiences,” said Charles B. Robertson, the company’s president and chief executive.
The economy’s silver bullet
Another factor in the elderly’s favor: relatively strong finances. Americans age 70 and older now hold nearly 26% of household wealth, the highest since records began in 1989, according to the Federal Reserve.
While economists still see a relatively high probability of recession in the coming year, Ed Yardeni, president and chief investment strategist of Yardeni Research, isn’t one of them. An important reason: By the Fed’s reckoning, baby boomers alone have now amassed $77.1 trillion in wealth. “There’s a $77 trillion-wide hole in the theory that consumers’ running out of pandemic savings will sink the economy,” he said.
They have less consumer debt, minimal student debt and are more likely to own their homes outright. Many of those who have mortgages refinanced at the unprecedented low in mortgage rates after the pandemic hit. They are also less likely to need to move due to an expanding family or a new job than Gen Z and Millennials, shielding them from the impact of rising housing costs.
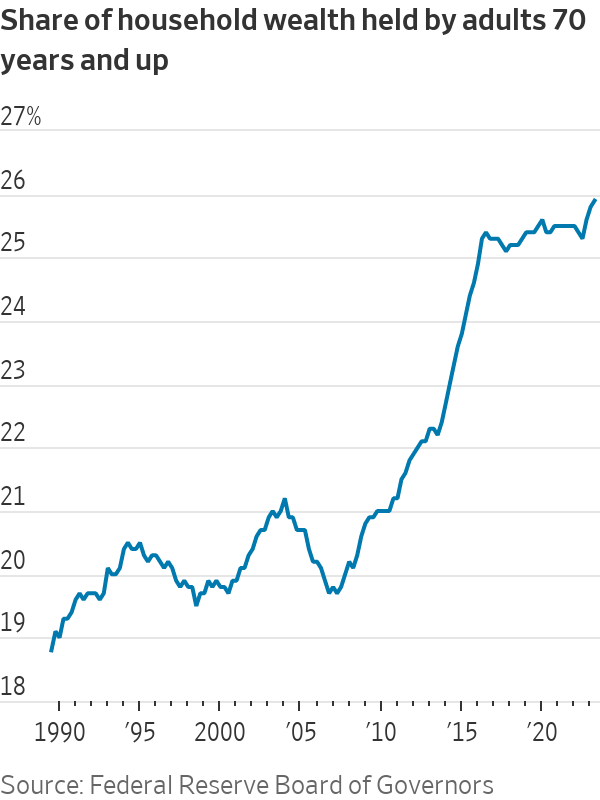
Retirees also received an 8.7% cost-of-living-adjustment bump to Social Security payments in January, the largest single-year increase since 1981, and an automatic adjustment to offset last year’s 9.1% inflation peak.
These factors have cushioned seniors from the twin scourges of inflation and high interest rates. And since most of them are retired, seniors’ spending is less vulnerable to the rise in unemployment that many economists anticipate in coming quarters.
Subscription demand for the Cincinnati Opera’s summer festival this year was surprisingly strong and driven by older patrons, said Todd Bezold, director of marketing.
“Despite the multiyear trend in subscriptions going down, down, down in every art form, we went up this year—by 3%,” he said. That jump in demand came despite a sharp rise in ticket prices to account for several years of inflation. “The vast majority of our subscribers are baby boomers; we know that much.”
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
Continued stagflation and cost of living pressures are causing couples to think twice about starting a family, new data has revealed, with long term impacts expected
Australia is in the midst of a ‘baby recession’ with preliminary estimates showing the number of births in 2023 fell by more than four percent to the lowest level since 2006, according to KPMG. The consultancy firm says this reflects the impact of cost-of-living pressures on the feasibility of younger Australians starting a family.
KPMG estimates that 289,100 babies were born in 2023. This compares to 300,684 babies in 2022 and 309,996 in 2021, according to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS). KPMG urban economist Terry Rawnsley said weak economic growth often leads to a reduced number of births. In 2023, ABS data shows gross domestic product (GDP) fell to 1.5 percent. Despite the population growing by 2.5 percent in 2023, GDP on a per capita basis went into negative territory, down one percent over the 12 months.
“Birth rates provide insight into long-term population growth as well as the current confidence of Australian families,” said Mr Rawnsley. “We haven’t seen such a sharp drop in births in Australia since the period of economic stagflation in the 1970s, which coincided with the initial widespread adoption of the contraceptive pill.”
Mr Rawnsley said many Australian couples delayed starting a family while the pandemic played out in 2020. The number of births fell from 305,832 in 2019 to 294,369 in 2020. Then in 2021, strong employment and vast amounts of stimulus money, along with high household savings due to lockdowns, gave couples better financial means to have a baby. This led to a rebound in births.
However, the re-opening of the global economy in 2022 led to soaring inflation. By the start of 2023, the Australian consumer price index (CPI) had risen to its highest level since 1990 at 7.8 percent per annum. By that stage, the Reserve Bank had already commenced an aggressive rate-hiking strategy to fight inflation and had raised the cash rate every month between May and December 2022.
Five more rate hikes during 2023 put further pressure on couples with mortgages and put the brakes on family formation. “This combination of the pandemic and rapid economic changes explains the spike and subsequent sharp decline in birth rates we have observed over the past four years,” Mr Rawnsley said.
The impact of high costs of living on couples’ decision to have a baby is highlighted in births data for the capital cities. KPMG estimates there were 60,860 births in Sydney in 2023, down 8.6 percent from 2019. There were 56,270 births in Melbourne, down 7.3 percent. In Perth, there were 25,020 births, down 6 percent, while in Brisbane there were 30,250 births, down 4.3 percent. Canberra was the only capital city where there was no fall in the number of births in 2023 compared to 2019.
“CPI growth in Canberra has been slightly subdued compared to that in other major cities, and the economic outlook has remained strong,” Mr Rawnsley said. “This means families have not been hurting as much as those in other capital cities, and in turn, we’ve seen a stabilisation of births in the ACT.”
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.





















