Trade Woes in Asia Bring Inflation Relief to U.S. Consumers
But slowing exports to Western nations won’t alone stem rapidly rising prices
SINGAPORE—Sinking global trade is pummelling Asian exports, bringing some relief on inflation to U.S. and other Western consumers.
But easing prices for home furnishings, electronics and other manufactured goods don’t signal high inflation will soon be defeated. Wage growth and services price gains are still elevated. And central banks in the U.S. and Europe are warning they aren’t finished raising interest rates in their fight to cool inflation.
Cheap Asian goods helped keep a lid on price growth for decades before the pandemic. Economists say that phenomenon is unlikely to return with the same intensity now that the high-water mark of globalisation has passed.
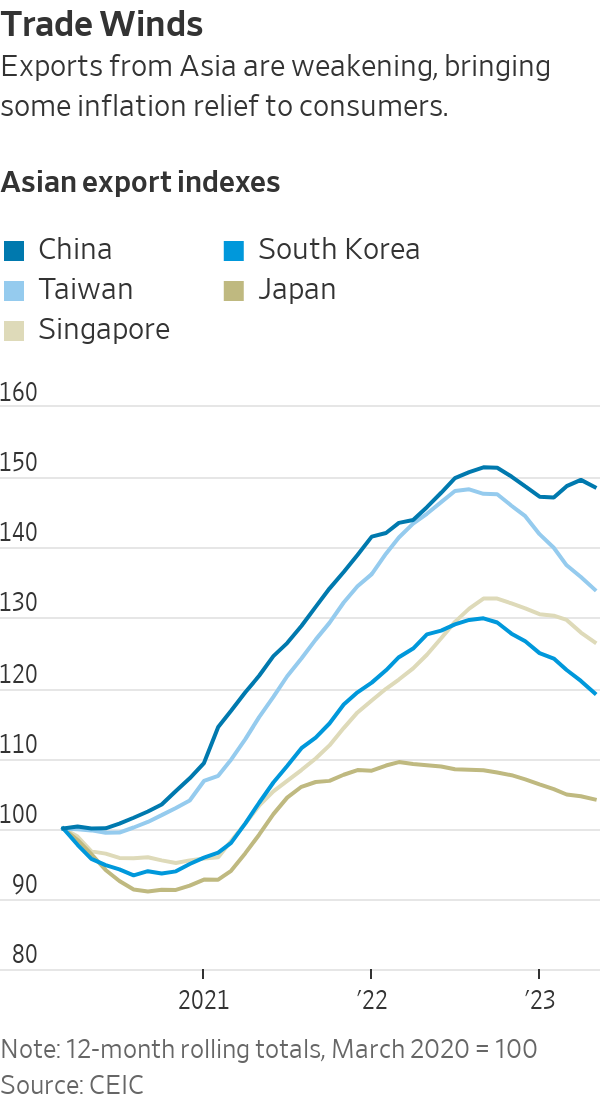
Asia’s powerhouse exporters enjoyed a boom in overseas sales during the pandemic as locked-down consumers splurged on new computers, workout gear and home improvements.
On a rolling 12-month basis, the U.S. dollar value of exports from China, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan and Singapore peaked last year in September at $6.1 trillion. That was 40% higher than recorded over the 12 months through March 2020, when the pandemic began, according to a Wall Street Journal analysis of official figures compiled by data provider CEIC.
Asian exports started sliding late last year as rising interest rates took some heat out of economic growth. Western consumers have slowed spending on goods in favour of eating out, traveling and other services they missed during the pandemic. Hopes that China’s reopening would spur a rebound in trade have fizzled along with the country’s consumer-led recovery.
Exports from South Korea over the 12 months through May were 11% lower than they were in the year through September. Taiwan exports were down 14% over the same period. Singapore’s were down 6%, Japan’s 4% and China’s by 3%.
The weakness in trade is showing up in the prices charged for goods when they leave Asia’s factories. Chinese producer prices fell 4.6% in May compared with a year earlier, the eighth straight month of declining supplier prices in the world’s largest factory floor. Similar gauges of inflation in other Asian exporter economies are weakening, too, as lower commodity prices reduce costs and collapsing demand for goods saps companies’ pricing power.
The effects of cooling Asia trade are starting to be felt in the U.S., where the Federal Reserve signalled it expects to further increase interest rates after holding them steady this month.
U.S. import prices for goods from Hong Kong, Singapore, Taiwan and South Korea were down 6.3% in May compared with a year earlier, according to the Labor Department. Import prices were down 2% from China and 3.7% from the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, a 10-member group that includes Indonesia, Malaysia and Thailand.
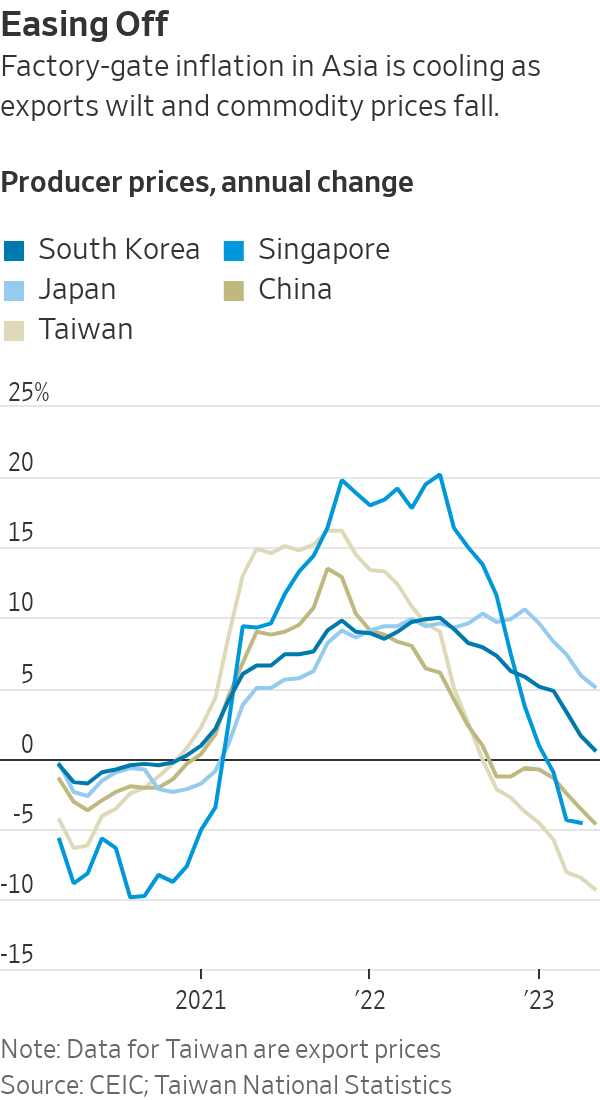
The prices paid by importers don’t quite line up with the prices faced by consumers, as companies need to cover labor, shipping and other costs to get products into stores.
Nonetheless, prices declined in May from a year earlier for a variety of goods in the U.S. that are often sourced from Asia, including furniture, home appliances, televisions, sports equipment, computers and smartphones.
Overall U.S. inflation is proving resilient, though. The consumer-price index, which measures what Americans pay for goods and services, rose 4% in May from a year earlier—twice the Fed’s 2% goal. Core consumer prices, which exclude food and energy, climbed 5.3%.
If surging prices for goods during the pandemic delivered the first burst of inflation, and rocketing energy prices after Russia invaded Ukraine propelled the second, then the current stickiness of inflation is being fuelled by increases in wages and the price of services. So while easing goods-price inflation is welcome, it doesn’t mean central banks have won the battle, economists say.
“The disinflation impulse coming from Asia is not going to be the magic bullet for the West’s inflation problem,” said Frederic Neumann, chief Asia economist at HSBC in Hong Kong, referring to the slowing pace of price increases.
In the decades before the pandemic, the integration of China into the global economy contributed to a long spell of low and stable inflation enjoyed by many Western economies. The broader integration of markets for goods, services, labor and capital under the banner of globalisation meant cheaper goods for consumers and fewer inflation worries for central banks, though economists debate just how big the effects were.
Now, governments and corporations are tiptoeing away from unfettered globalisation in the interests of security and economic resilience. Manufacturers are adding factories in Vietnam or India while reducing their reliance on China, reflecting concern over icy relations between the U.S.-led West and Beijing. Governments are dangling subsidies in strategic industries such as semiconductors and green-technology products to bring investment and jobs home.
Such trade fractures can increase costs for manufacturers, which, alongside healthier global demand, suggests that inflation in the future won’t be as subdued as it was in the recent past, economists say.
That doesn’t mean globalisation is over or that Asia won’t remain a competitive place to manufacture. But it does mean Asia is unlikely to be as potent a force in tempering price gains as it once was.
“The golden era of globalisation—and the disinflationary pressure associated with that—I think that has gone,” said Neil Shearing, group chief economist at Capital Economics in London.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
From warmer neutrals to tactile finishes, Australian homes are moving away from stark minimalism and towards spaces that feel more human.
French luxury-goods giant’s results are a sign that shoppers weren’t splurging on its collections of high-end garments in the run-up to the holiday season.
French luxury-goods giant’s results are a sign that shoppers weren’t splurging on its collections of high-end garments in the run-up to the holiday season.
LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton wrapped up last year’s final quarter with sluggish sales growth, a sign that shoppers weren’t splurging on its collections of high-end garments and handbags in the run-up to the holiday season.
The French luxury-goods giant posted fourth-quarter sales of 22.72 billion euros ($27 billion), up 1% organically. Analysts had forecast €22.59 billion in sales and an organic decline of 0.3%, according to Visible Alpha.
LVMH’s fashion and leather goods division, which houses brands like Louis Vuitton and Dior, contributed €10.16 billion in sales, down 3% organically.
Sales at perfumes and cosmetics declined 1%, while the wines and spirits division reported a 9% contraction in sales. Selective retailing, the unit behind Sephora, fared better, with a 7% increase in sales, while watches and jewelry logged 8% growth.
For LVMH and the wider luxury-goods sector, the final quarter represents a key test of customers’ willingness to indulge on nonessential items in the run-up to Black Friday, Thanksgiving and Christmas.
Earlier this month, British trench-coat maker Burberry Group , Italian luxury-fashion house Brunello Cucinelli and Cartier owner Cie. Financière Richemont all reported higher sales for the quarter, raising the bar for industry bellwether LVMH.
Weak sales growth shows that LVMH’s collections aren’t appealing to clients and that the group is still contending with a slowdown in spending for luxury goods that has plagued the industry for years.
Demand weakened considerably after a postpandemic boom, especially among less affluent shoppers. The downturn has been particularly acute in China—a key market for LVMH and its rivals—as shoppers there have been holding back spending.
Last year brought a dose of uncertainty for LVMH and the sector as it took several months for the European Union to reach a trade deal with the U.S. after President Trump announced his Liberation Day tariffs.
Luxury goods are particularly sensitive to trans-Atlantic trade frictions and the specter of tariffs has never fully disappeared despite that trade deal.
Last week, LVMH and other luxury stocks slumped after Trump threatened 10% levies on various European countries he said were opposed to a U.S. takeover of Greenland. He subsequently called off those tariffs.
LVMH closed 2025 with €80.81 billion in annual sales, down 1% organically. Analysts had forecast €80.65 billion in 2025 sales with a 1.8% organic decline, according to Visible Alpha.
The group said revenue declined in Europe in the second half of the year, while the U.S. benefited from solid demand.
Sales in Japan were down from 2024, but the company said it had seen a noticeable improvement in trends in the rest of Asia, citing a return to growth in the second half of the year.
In an earnings call, executives expressed confidence for 2026 despite an uncertain geopolitical and macroeconomic environment, saying the positive trends they started to see in the second half were still there.
Net profit slid 13% on year to €10.88 billion, while profit from recurring operations fell 9% to nearly €17.76 billion. Analysts had forecast net profit of 10.55 billion euros and profit from recurring operations of €17.15 billion, according to Visible Alpha.
The group said it would propose a dividend of €13 a share at its shareholders’ meeting on April 23, the same as the previous year.
From office parties to NYE fireworks, here are the bottles that deserve pride of place in the ice bucket this season.
On October 2, acclaimed chef Dan Arnold will host an exclusive evening, unveiling a Michelin-inspired menu in a rare masterclass of food, storytelling and flavour.























