2023: A Year of Economic Turbulence — and Resilience
OPINION
As 2023 draws to a close, we are presented with an opportune moment to reflect on a year marked by economic resilience and a transformation of our economic environment that has not been seen for decades. We continue to push through the complex circumstances presented by the post-COVID recovery, remaining inflation, and the aggressive array of official interest rate increases during 2023.
Just as we see signs that the fight against global inflation may have finally resolved during an astounding year of economic resilience, there remains the threat of a new set of black swan events lurking in the shadows. We could very well see both global and local economic indicators deteriorating well into 2024. In addition, there remains the major threat of a disruption to global trade due to the Houthi militants’ interference in the Suez Canal.
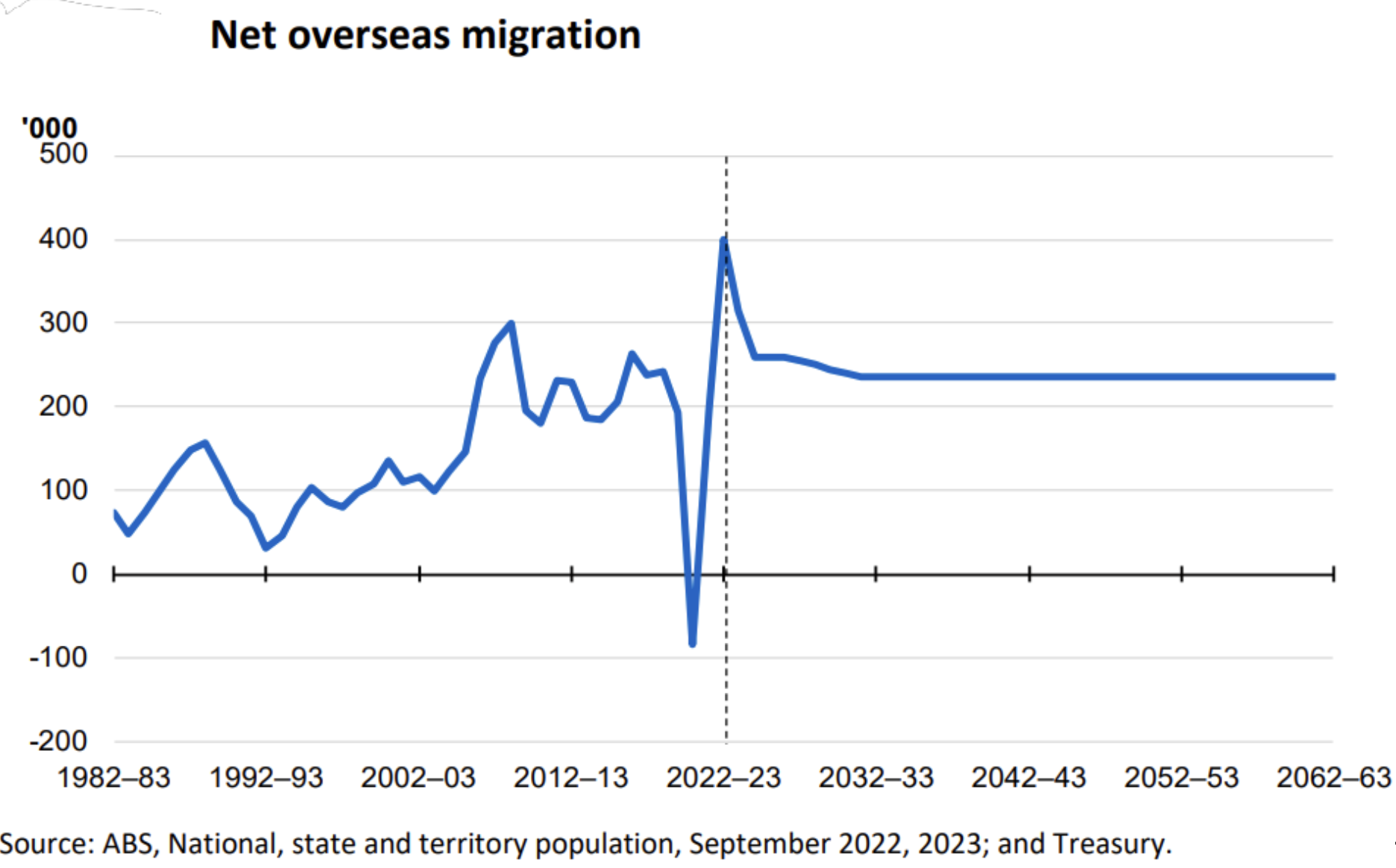
Undoubtedly, the pace of the economic slowdown hastened in the September quarter with unemployment rising, and GDP only barely increasing by 0.2%, falling short of the anticipated 0.5%. If adjusted for immigration, Australia is officially in a per capita recession.
Australia’s record net migration of 2.5% for the 2023 calendar year undoubtedly enabled our economy to remain resilient, while also presenting itself as a potential medium to long-term nuisance. Migration helps ease some of the pressure we are currently experiencing in our tight labour market and leads to higher aggregate demand. However, it also places additional inflationary pressure on housing and rent.
Monetary Policy Outlook
The RBA’s approach to monetary policy has been a topic of much debate, with a very direct transmission channel to mortgage holders in Australia, where there is also higher household leverage. Higher rates end up being passed onto renters and mortgage holders, who comprise roughly 70% of the market. This illustrates the blunt aspect of monetary policy and how it disproportionately impacts certain groups, such as young, lower-income mortgagors trying to support their family. On the other hand, self-funded retirees are a group that is generally well-placed in a rising interest rate environment.
The RBA’s cautious stance, including the decision to keep the cash rate on hold in December, was a response to the evolving economic situation and clear signs of the economy cooling, including slower GDP growth, lower inflation, and higher unemployment.
Many economists now predict that in 2024, during the 4th quarter, interest rates will begin to be reduced. The question is what the neutral cash rate is estimated to be – somewhere between 2.75% and 3.75% – where the rate neither increases nor decreases inflationary pressure.
Labour Market and Unemployment
A significant aspect of 2023 was the labour market beginning to loosen as consumer spending softened. The unemployment rate in Australia rose to 3.9% in November, indicating a clear upward trend. This was coupled with an increased underemployment trend which is expected to continue throughout 2024.
While the RBA’s primary mandate is to manage inflation, it also has a key role in achieving full employment. There is a concept relating to a neutral unemployment rate, where any further increase has an inflationary impact on the economy. This is referred to as the Non-Accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment (NAIRU) and is often referred to in the RBA’s statements. They believe that Australia’s natural rate of unemployment should be 4.5%. Moving closer to this rate allows us to see improvements in productivity whilst not incurring significant inflationary pressure or economic weakening. Indeed, such low unemployment during the year has made our economy extraordinarily resilient in the face of adversity.
As the unemployment rate gets closer to the target of 4.5%, it often impels the RBA to cut the official cash rate.
Household and Household Income
The increase in average mortgage rates and the strain on household budgets were notable over the past year. Real household disposable income declined significantly. Interest paid on housing debt and income tax payable increased substantially, further stressing household finances. Despite these adversities, we have witnessed an extraordinary recovery in property prices during the year, which has been rather counterintuitive from a pure economic standpoint.
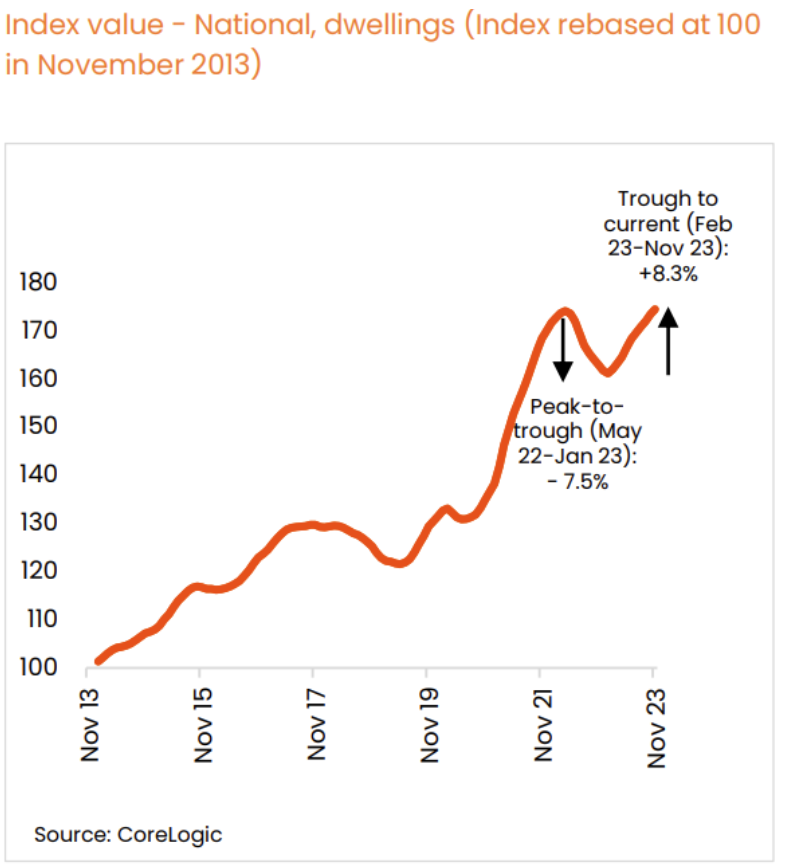
The rationale behind this can be explained by the decade-long chronic shortage of housing supply, combined with high net migration. This reinforces the unrelenting nature of housing demand in Australia. It is also a testament to how families will continue to make sacrifices to enable them to live in their property and avoid renting. As the housing crisis worsens, there is a realisation that residential property is not merely an asset class for investment, but also an essential piece of infrastructure for which all levels of government are responsible to deliver sufficient supply. However, we must remember: there is no immediate or quick fix.
Private Credit’s Role
Private credit, especially secured lending, becomes even more crucial in this uncertain and tumultuous environment. Traditional banks, facing an uncertain economic climate, become more cautious, paving the way for firms like Msquared Capital to provide essential credit to SMEs.
For us at Msquared Capital, our daily interactions with borrowers ensures we are always there to witness and respond to ever-changing conditions. We can see dislocations within the lending market and that is what enables us to find the best risk-rated returns for our investors.
Secured private credit is in high demand as investors navigate uncertain times and move away from riskier assets in which the downside risk is the absolute loss of capital following from heightened market volatility. Investors are seeking a safe haven that provides steady and reliable income, all while being secured by real assets – that is, property – with asset preservation qualities.
Many investors are only now beginning to discover private credit and its benefits. At Msquared Capital we see that there is still a lack of understanding and awareness on the difference between private credit providers and their offerings. Another crucial point to remember is that not all debt, nor fund managers, are the same or of equal quality.
Looking Ahead
2023 was a year of economic turbulence, characterised by slowing growth, a shifting labour market, and evolving monetary policy. For Msquared Capital, this environment necessitates adaptive strategies to navigate the changing landscape. As we look forward to 2024, we remain committed to providing innovative and secure credit solutions, while being mindful of the broader economic context and its implications for our clients and investments.
In our view the RBA will likely continue its inflation-fighting rhetoric, but the need for further rate rises seems to have dissipated given rising unemployment and falling GDP per capita. It is highly unlikely that there will be significant property appreciation in the short-term unless interest rates are reduced more aggressively than anticipated. In addition, some property segments, such as holiday houses, regional areas, and commercial office space, have more inherent downside risk.
Overall, Australia is once again the ‘lucky country’, having been much more resilient than our peers. This is a testament to our resource-rich land, high immigration, farming, stable government, and that we are distanced far enough from other countries so as to not be entangled in their geopolitical mess. This is what allows our lucky country to weather most economic shocks relativity unscathed.
Paul Miron is managing director of Msquared Capital, a private credit provider with investment opportunities backed by quality property located primarily along Australia’s Eastern Seaboard; we ensure that all investment opportunities are based on risk-to-reward as our core offering, coupled with strong performance. Mortgage funds perform well during volatile times, and capital preservation is regular, with a reliable monthly income that gives our investors peace of mind.
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
Impact investing is becoming more mainstream as larger, institutional asset owners drive more money into the sector, according to the nonprofit Global Impact Investing Network in New York.
In the GIIN’s State of the Market 2024 report, published late last month, researchers found that assets allocated to impact-investing strategies by repeat survey responders grew by a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14% over the last five years.
These 71 responders to both the 2019 and 2024 surveys saw their total impact assets under management grow to US$249 billion this year from US$129 billion five years ago.
Medium- and large-size investors were largely responsible for the strong impact returns: Medium-size investors posted a median CAGR of 11% a year over the five-year period, and large-size investors posted a median CAGR of 14% a year.
Interestingly, the CAGR of assets held by small investors dropped by a median of 14% a year.
“When we drill down behind the compound annual growth of the assets that are being allocated to impact investing, it’s largely those larger investors that are actually driving it,” says Dean Hand, the GIIN’s chief research officer.
Overall, the GIIN surveyed 305 investors with a combined US$490 billion under management from 39 countries. Nearly three-quarters of the responders were investment managers, while 10% were foundations, and 3% were family offices. Development finance institutions, institutional asset owners, and companies represented most of the rest.
The majority of impact strategies are executed through private-equity, but public debt and equity have been the fastest-growing asset classes over the past five years, the report said. Public debt is growing at a CAGR of 32%, and public equity is growing at a CAGR of 19%. That compares to a CAGR of 17% for private equity and 7% for private debt.
According to the GIIN, the rise in public impact assets is being driven by larger investors, likely institutions.
Private equity has traditionally served as an ideal way to execute impact strategies, as it allows investors to select vehicles specifically designed to create a positive social or environmental impact by, for example, providing loans to smallholder farmers in Africa or by supporting fledging renewable energy technologies.
Future Returns: Preqin expects managers to rely on family offices, private banks, and individual investors for growth in the next six years
But today, institutional investors are looking across their portfolios—encompassing both private and public assets—to achieve their impact goals.
“Institutional asset owners are saying, ‘In the interests of our ultimate beneficiaries, we probably need to start driving these strategies across our assets,’” Hand says. Instead of carving out a dedicated impact strategy, these investors are taking “a holistic portfolio approach.”
An institutional manager may want to address issues such as climate change, healthcare costs, and local economic growth so it can support a better quality of life for its beneficiaries.
To achieve these goals, the manager could invest across a range of private debt, private equity, and real estate.
But the public markets offer opportunities, too. Using public debt, a manager could, for example, invest in green bonds, regional bank bonds, or healthcare social bonds. In public equity, it could invest in green-power storage technologies, minority-focused real-estate trusts, and in pharmaceutical and medical-care company stocks with the aim of influencing them to lower the costs of care, according to an example the GIIN lays out in a separate report on institutional strategies.
Influencing companies to act in the best interests of society and the environment is increasingly being done through such shareholder advocacy, either directly through ownership in individual stocks or through fund vehicles.
“They’re trying to move their portfolio companies to actually solving some of the challenges that exist,” Hand says.
Although the rate of growth in public strategies for impact is brisk, among survey respondents investments in public debt totaled only 12% of assets and just 7% in public equity. Private equity, however, grabs 43% of these investors’ assets.
Within private equity, Hand also discerns more evidence of maturity in the impact sector. That’s because more impact-oriented asset owners invest in mature and growth-stage companies, which are favored by larger asset owners that have more substantial assets to put to work.
The GIIN State of the Market report also found that impact asset owners are largely happy with both the financial performance and impact results of their holdings.
About three-quarters of those surveyed were seeking risk-adjusted, market-rate returns, although foundations were an exception as 68% sought below-market returns, the report said. Overall, 86% reported their investments were performing in line or above their expectations—even when their targets were not met—and 90% said the same for their impact returns.
Private-equity posted the strongest results, returning 17% on average, although that was less than the 19% targeted return. By contrast, public equity returned 11%, above a 10% target.
The fact some asset classes over performed and others underperformed, shows that “normal economic forces are at play in the market,” Hand says.
Although investors are satisfied with their impact performance, they are still dealing with a fragmented approach for measuring it, the report said. “Despite this, over two-thirds of investors are incorporating impact criteria into their investment governance documents, signalling a significant shift toward formalising impact considerations in decision-making processes,” it said.
Also, more investors are getting third-party verification of their results, which strengthens their accountability in the market.
“The satisfaction with performance is nice to see,” Hand says. “But we do need to see more about what’s happening in terms of investors being able to actually track both the impact performance in real terms as well as the financial performance in real terms.”
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.


















