China’s Punishment for People With Bad Debts: No Fast Trains or Nice Hotels
Beijing’s crackdown on millions of delinquent debtors makes catching up on unpaid bills a slog
FOSHAN, China—Qin Huangsheng once imagined a better life in the city when she left her home village to become a factory worker at age 16.
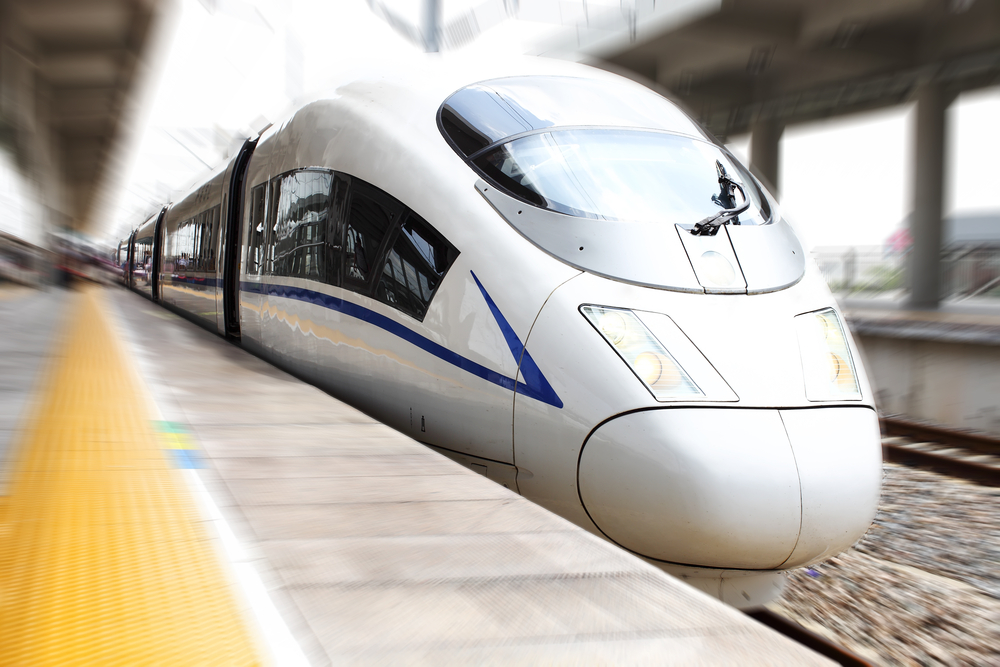
Now, in her early 40s, she has $40,000 in personal debt and a base salary of $400 a month. Debt collectors are hounding her. She is blocked from buying tickets on China’s high-speed rail, just one of the penalties the government is increasingly imposing on people who don’t pay their bills.
On the ageing slow trains she is left to ride, Qin sometimes looks at the other passengers and thinks: “I wonder if they’re all bad debtors like me.”
People across China are being weighed down by their debts and a system that penalises them for not paying the money back. Beijing is cracking down on delinquent debtors by seizing their salaries or restricting them from getting government jobs, as well as curbing their access to high-speed trains and air travel. Many are forbidden from buying expensive insurance policies and told they aren’t allowed to go on vacation or stay in nice hotels. Authorities can detain them if they don’t comply.
The number of people on a publicly available government delinquency blacklist has jumped by nearly 50% since late 2019 to 8.3 million today. Courts can put people on the blacklist when they don’t fulfil judgments against them to pay money back or are deemed to be not cooperating with legal proceedings.
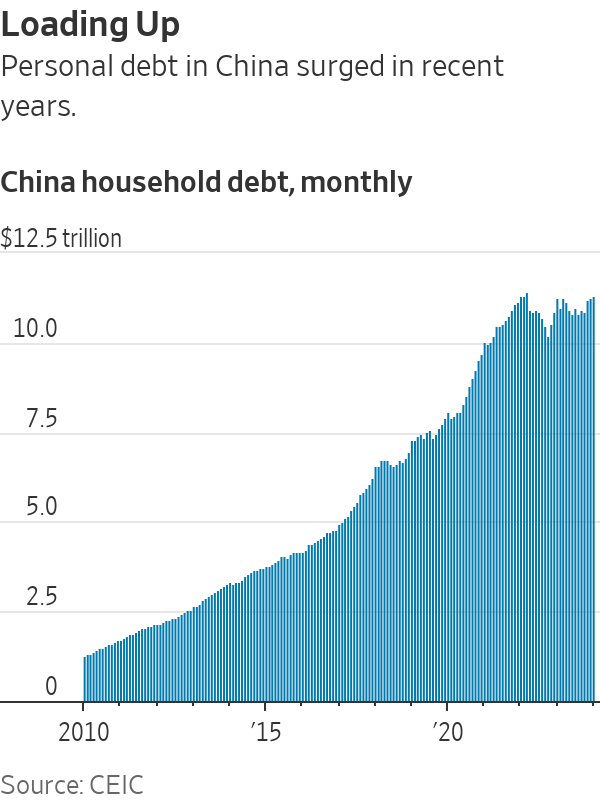
Unlike in the U.S., China doesn’t allow most people—including those who had a run of bad luck—to declare bankruptcy to write off bad debts and move on with their lives, a policy some Chinese scholars are criticising as unfair.
Household debt has surged by 50% in the past five years to around $11 trillion today. While that is lower than the $17.5 trillion Americans owe, it is a huge sum in a country where people earn far less.
With home prices falling, deflation risks becoming entrenched and unemployment a persistent challenge , Chinese leaders are eager to get people spending more. But each additional dollar going to pay for debt is taking away one that could be used to splurge on new clothes or pay for a vacation. The threat of punishment for falling behind on debt is making many families more conservative with their money.
Retail sales of consumer goods in China rose 4.7% year-over-year in the first quarter, the government said Tuesday, lagging behind total economic growth of 5.3%. As many in China curtail spending, the government is giving priority to turbocharging manufacturing and exports, a strategy that is exacerbating trade tensions with the West.
With so many Chinese consumers under financial pressure, Western companies including Apple , Estée Lauder and General Motors have reported weaker sales in China .
Chinese officials didn’t respond to questions about the blacklisting system. The government has said previously it only seeks to target those who have the ability to repay their debts but refuse to do so.
Behind China’s personal-debt surge
China’s long housing boom was a significant cause of the rise in personal debts, because many people had to borrow more to afford homes. Some buyers took on extra debt to buy more properties for investment purposes, sometimes letting them sit empty. Now that the boom is over and prices are falling , many are stuck with debts they can’t handle.
The number of foreclosed homes listed for sale rose 43% in 2023 to roughly 400,000 properties, according to real-estate research firm China Index Academy.
The increase in personal debts is also partly a result of more people using credit cards or tapping personal credit lines to handle expenses as the economy stagnates.
Many economists say a U.S.-style financial crisis is unlikely in China soon. State control of the banking system means the government can absorb losses and inject capital in an emergency. Household debts have also largely plateaued over the past two years, as many people give priority to using extra cash to pay down liabilities rather than shopping or investing in stocks.
Still, the prevalence of large personal debts is a problem for China’s leadership.
“Household debt booms tend to lead to bad macroeconomic outcomes, even in the absence of a financial crisis,” said Amir Sufi, a University of Chicago economist. China has no simple fix. “Once the cycle starts, it’s usually one in which it’s painful, long and difficult to predict when it will end,” Sufi said.
A tough system for borrowers
China has tried for years to lift personal spending to ease its economy’s traditional reliance on infrastructure and real-estate growth. Its banks issued tens of millions of new credit cards each year, with outstanding balances jumping 50% between 2018 and 2023 to well over $1 trillion. Private technology apps such as Alipay and WeChat also started helping consumers secure loans as their digital payment systems soared in popularity.
But when debts go unpaid, a person’s income can be seized by the state to cover their liabilities, leaving debtors with a small allowance to scrape by.
A 38-year-old man petitioned courts in the southern city of Guangzhou to raise his monthly allowance to 12,000 yuan, equivalent to around $1,600, from 9,500 yuan to help pay for a newborn child. Judges denied his request late last year, and instead concluded that his allowance should be cut by nearly 40% because he was already getting too much, court records show.
A black market has emerged to serve people on the blacklist. In one case, Shanghai authorities busted a ring of scalpers who were booking high-speed rail tickets on behalf of debtors who were barred from doing so themselves. In early 2021, authorities tracked down a debtor who had been using the service and took him into custody, according to a local court.
The current system gives priority to protecting creditors—often powerful, state-owned institutions—at the expense of helping struggling individuals. Scholars who study the issue say China urgently needs a nationwide personal-bankruptcy system to achieve leader Xi Jinping’s goal of making the country more equitable , by forcing creditors and debtors to share the costs of soured loans.
“A personal-bankruptcy system is a mechanism for the redistribution of wealth,” Li Shuguang, a scholar who has advised the government on bankruptcy policy, wrote in a Chinese magazine commentary online last summer.
Movement on the issue has been stymied in part by opponents who believe such a system would only encourage more people to shirk their debts.
One woman’s saga
For Qin, the former factory worker, easy access to credit backfired badly.
As a 16-year-old in 1999, Qin boarded an overnight bus from her home in rural southern China to the grimy manufacturing hub of Dongguan, north of Hong Kong.
Her parents, who are farmers, couldn’t afford a payment of less than $15 needed for her to take a high-school entrance exam. She vowed to make it on her own, and found work in factories producing slippers and golden jewellery.
A few years later, Qin secured her first credit card. With it, she bought a computer to teach herself to type so she could land a better job.
When the bill was paid, Qin said she tried to cancel the card. “Keep it for an emergency,” the bank clerk told her.
Qin’s career flourished and she eventually moved to the metropolis of Guangzhou. By 2010, she said, she was managing bidding for a company that supplied fire-safety equipment to real-estate projects. Her nest egg steadily grew from the lucrative commissions she earned in the property boom.
When the property sector slowed, she jumped industries. An acquaintance had been involved in a startup that was developing software to help small-business owners collect WeChat data to generate more foot traffic and aid marketing efforts.
Qin said she invested the equivalent of around $150,000 of her savings into the venture.
The startup burned through her initial investment as it tried to get the software up and running. Qin said she then agreed to start putting some of its expenses, including office supplies, rent and employee salaries, on her credit cards, and to tap personal credit lines she had obtained via WeChat and Alipay.
A roadshow by the company was warmly received, she said. But its prospects dimmed after the Covid pandemic hit.
The company’s struggles left Qin with the equivalent of tens of thousands of dollars of debt. Phone calls from debt collectors have become a daily occurrence.
With no option of bankruptcy, Qin concluded that a new job was her only way out of trouble.
“As long as I’m still living and have a life, I can work hard to earn the money back,” she said.
That path has faced unexpected difficulties. In 2021, while preparing for a business trip to Shanghai, more than 700 miles northeast of Guangzhou, Qin realized that she had lost her access to high-speed rail, where a government I.D. is required to buy a ticket. She took the slow train—and later quit that job in part because the travel restrictions were making it impossible.
Local officials didn’t respond to questions about Qin’s case and The Wall Street Journal wasn’t able to verify some details of her account.
Today, Qin is working in a shop in Foshan, south of Guangzhou, selling traditional Chinese medicines. With a base salary of about $400 a month, she has found it tough to put a dent in her debts, but said she has managed to pay back two of her credit cards so far, with about $40,000 still to go.
Qin is trying to stay optimistic, hoping that medicine will be in high demand as China’s population ages, opening the door to bonuses and potentially even running her own shop. Still, she has had to get creative to earn the cash to pay her debts.
Her current role requires Qin to collect payments from customers using a digital wallet on WeChat. But she said that function on her account has been frozen several times since 2022, leaving Qin to seek help from her family.
She decided not to tell her parents about the full scale of her troubles, however.
If they knew the truth, Qin said, they “wouldn’t be able to sleep.”
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
Continued stagflation and cost of living pressures are causing couples to think twice about starting a family, new data has revealed, with long term impacts expected
Australia is in the midst of a ‘baby recession’ with preliminary estimates showing the number of births in 2023 fell by more than four percent to the lowest level since 2006, according to KPMG. The consultancy firm says this reflects the impact of cost-of-living pressures on the feasibility of younger Australians starting a family.
KPMG estimates that 289,100 babies were born in 2023. This compares to 300,684 babies in 2022 and 309,996 in 2021, according to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS). KPMG urban economist Terry Rawnsley said weak economic growth often leads to a reduced number of births. In 2023, ABS data shows gross domestic product (GDP) fell to 1.5 percent. Despite the population growing by 2.5 percent in 2023, GDP on a per capita basis went into negative territory, down one percent over the 12 months.
“Birth rates provide insight into long-term population growth as well as the current confidence of Australian families,” said Mr Rawnsley. “We haven’t seen such a sharp drop in births in Australia since the period of economic stagflation in the 1970s, which coincided with the initial widespread adoption of the contraceptive pill.”
Mr Rawnsley said many Australian couples delayed starting a family while the pandemic played out in 2020. The number of births fell from 305,832 in 2019 to 294,369 in 2020. Then in 2021, strong employment and vast amounts of stimulus money, along with high household savings due to lockdowns, gave couples better financial means to have a baby. This led to a rebound in births.
However, the re-opening of the global economy in 2022 led to soaring inflation. By the start of 2023, the Australian consumer price index (CPI) had risen to its highest level since 1990 at 7.8 percent per annum. By that stage, the Reserve Bank had already commenced an aggressive rate-hiking strategy to fight inflation and had raised the cash rate every month between May and December 2022.
Five more rate hikes during 2023 put further pressure on couples with mortgages and put the brakes on family formation. “This combination of the pandemic and rapid economic changes explains the spike and subsequent sharp decline in birth rates we have observed over the past four years,” Mr Rawnsley said.
The impact of high costs of living on couples’ decision to have a baby is highlighted in births data for the capital cities. KPMG estimates there were 60,860 births in Sydney in 2023, down 8.6 percent from 2019. There were 56,270 births in Melbourne, down 7.3 percent. In Perth, there were 25,020 births, down 6 percent, while in Brisbane there were 30,250 births, down 4.3 percent. Canberra was the only capital city where there was no fall in the number of births in 2023 compared to 2019.
“CPI growth in Canberra has been slightly subdued compared to that in other major cities, and the economic outlook has remained strong,” Mr Rawnsley said. “This means families have not been hurting as much as those in other capital cities, and in turn, we’ve seen a stabilisation of births in the ACT.”
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.






















