Fed Raises Rate by 0.5 Percentage Point, Signals More Increases Likely
Most officials penciled in plans to raise rates above 5% next year, higher than previously expected
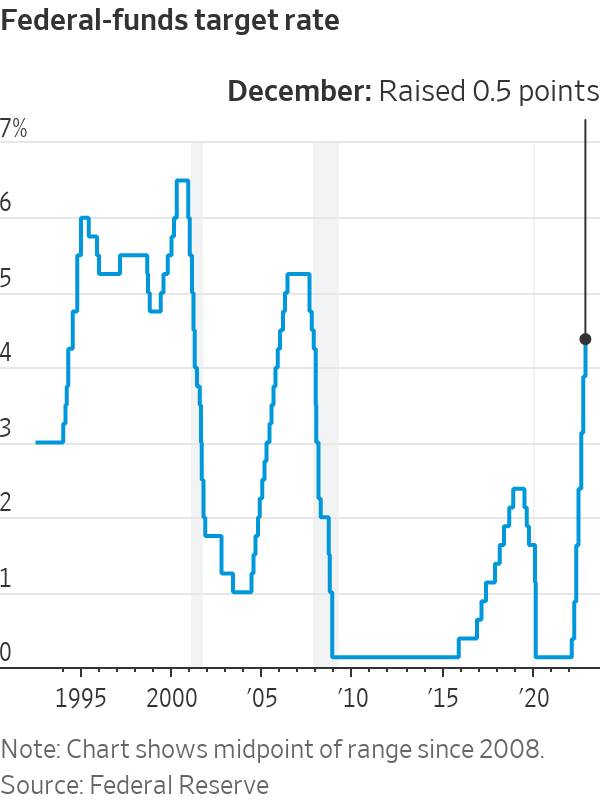
WASHINGTON—The Federal Reserve approved an interest-rate increase of 0.5 percentage point and signalled plans to lift rates through the spring, though likely in smaller increments, to combat high inflation.
The decision Wednesday marked a step down after four consecutive larger increases of 0.75 point and raised the benchmark federal-funds rate to a range between 4.25% and 4.5%, a 15-year high.
Markets retreated slightly after the announcement. The Dow Jones Industrial Average lost 142.29 points, or 0.4%, to 33966.35. The yield on the benchmark 10-year U.S. Treasury note edged up to 3.503% from its Tuesday level of 3.501%. Yields rise as prices fall.
The latest increase capped a year in which the Fed raised rates from near zero at the fastest pace since the early 1980s to fight inflation, which is running near a 40-year high.
Fed policy makers are entering a new phase of policy tightening in which they are trying to determine just how high to raise rates. Fed Chair Jerome Powell said in a news conference it was “broadly right” that slowing rate rises to more traditional quarter-percentage-point increments as soon as the Fed’s next meeting, Jan. 31-Feb. 1, would provide the best way to manage the risk of over-tightening.
“It makes a lot of sense, it seems to me—particularly if you consider how far we’ve come,” Mr. Powell said. But he said twice that the Fed hadn’t made any decisions about upcoming meetings, and that the outcome would depend on the state of the economy and borrowing costs.
Rate increases work with what economists call long and variable lags, which means the central bankers may not know for a year or more if they have tightened too much or not enough.
In new economic projections released after the meeting, most Fed officials penciled in plans to raise the fed-funds rate to a peak level between 5% and 5.5% in 2023 and hold it there until some time in 2024. In September, they anticipated lifting the rate to around 4.6% by the end of next year.
After Wednesday’s press conference, investors in interest-rate futures markets expected the Fed to raise rates to a level just below 5% by March before pausing. Bond markets rallied when Mr. Powell hinted the Fed might raise rates by a smaller step of a quarter-point, or 25 basis points, in February, said Lee Ferridge, a senior economic strategist at State Street Global Markets.
“It’s like the new projections didn’t happen, quite honestly. And I’m surprised the market is shrugging it off so confidently,” said Mr. Ferridge. “The expectation is the economic data will be so poor” by the end of the first quarter “that the Fed will stop hiking.”
Mr. Ferridge said he wasn’t convinced the Fed would dial down the pace of rate rises again in February. “If the data comes in hot, then I think they could still go 50,” he said.
Fed rate increases this year have hit asset prices and are causing a significant slowdown in rate-sensitive sectors of the economy such as housing. But in recent weeks, longer-term bond yields have tumbled as investors anticipate a speedy decline in inflation, possibly due to a recession next year.
The fed-funds rate influences other borrowing costs throughout the economy, including rates on car loans, mortgages and business debt.
Fed officials say they combat inflation primarily by slowing the economy through tighter financial conditions—such as higher borrowing costs, lower stock prices and a stronger dollar—that curb demand. As a result, any easing of financial conditions while the Fed continues to battle inflation could raise the risk of a deeper or longer downturn if it prompts the central bank to keep lifting rates.
Mr. Powell suggested the Fed would raise rates to higher levels for longer if broader financial conditions don’t “reflect the policy restraint that we’re putting in place to bring inflation down.”
The projections released Wednesday showed considerable divergence over what might happen after next year. Around one third of officials expect to hold the fed-funds rate above 4.5% through 2024. Most officials anticipate cutting rates by around 1 percentage point in 2024.
Mr. Powell said no officials had projected rate cuts next year and that they weren’t likely to consider lowering interest rates until policy makers are confident inflation is moving down to the Fed’s 2% goal in a sustained fashion.
Data released since the Fed’s November meeting have provided a mixed picture of the economy. While domestic demand has slowed and the housing market is entering a sharp downturn, the job market has remained strong and declines in gas prices could help sustain consumer spending.
Inflation has also slowed in the past two months. Consumer prices climbed 0.1% in November from the previous month and 7.1% from a year earlier, the Labor Department said Tuesday, both down notably from comparable previous increases.
The Fed pays close attention to so-called core prices, which exclude volatile food and energy categories, as a better predictor of future inflation than overall inflation. Over the past three months, core prices increased at a 4.3% annualised rate, the lowest such reading in more than one year.
Tuesday’s inflation report “provides a compelling case for downshifting to a 25-basis-point increase in February,” said Matthew Luzzetti, chief U.S. economist at Deutsche Bank.
“There are really good reasons for them to slow down if they can,” said Mr. Luzzetti. “I think they want to avoid pausing only to have to re-hike later, and getting down to 25 basis points allows them the best chance of avoiding that possibility.”
Mr. Powell acknowledged the improvement in the inflation rate but warned it might decline to levels that are still uncomfortably high, citing concerns that prices for labor-intensive services might rise if wage growth doesn’t slow down.
Prices of goods such as used cars are declining, a development the Fed has anticipated for more than a year, and there is evidence that rents and other housing costs are set to cool notably amid a sharp slowdown in the growth of new households.
“We welcome these better inflation reports…but I think we’re realistic about the broader project,” Mr. Powell said. Despite progress on goods and housing inflation, “the big story will really be the rest of it, and there’s not much progress there. And that’s going to take time.”
That pessimism was reflected in many Fed officials’ economic projections. Compared with September, they now anticipate a bigger increase in the unemployment rate next year and barely any economic growth.
Those projections offered “the whiff of a bumpy landing on the economic horizon,” said Daleep Singh, a former senior Fed official who is now chief global economist at PGIM Fixed Income.
Most officials expect making somewhat less progress on inflation next year than they had anticipated in September, which is one reason for projecting somewhat higher interest rates. Because central bankers believe inflation-adjusted or “real” policy rates are what matters for slowing the economy, a slower decline in inflation would require higher interest rates to achieve the same degree of economic restrictiveness.
They project core inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy categories, to fall from 5% on an annual basis in October to 3.5% at the end of next year, according to their preferred gauge, the Commerce Department’s personal-consumption expenditures index. That is up from their projection of 3% in September.
Wage growth hasn’t shown meaningful signs of slowing down, particularly as companies offer higher wages to attract new workers than they pay their current workers. Some Fed officials and private-sector economists are concerned that another calendar year of high inflation could lead employees to seek and receive higher pay early next year, which could help fuel more inflation.
Fed policy makers coalesced this spring around plans to raise rates by a half-percentage point at each meeting until they saw evidence inflation was slowing. Almost as soon as those plans came together, Mr. Powell decided to accelerate the increases amid fears that very high inflation would lead consumers and businesses to expect prices to keep climbing rapidly, causing high inflation to persist. The central bank lifted rates by 0.75 percentage point in June, the largest increase in 28 years.
At the time, Mr. Powell said such big moves would be uncommon. But continued high inflation and doubts in financial markets over the Fed’s commitment to fight it led the central bank to make three more increases of that magnitude.
“What’s impressed me to no end is it hasn’t broken anything. For all the talk of crashing the economy and breaking the financial markets, it hasn’t done that,” said Fed governor Christopher Waller last month, referring to the cumulative rate increases.
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
Continued stagflation and cost of living pressures are causing couples to think twice about starting a family, new data has revealed, with long term impacts expected
Australia is in the midst of a ‘baby recession’ with preliminary estimates showing the number of births in 2023 fell by more than four percent to the lowest level since 2006, according to KPMG. The consultancy firm says this reflects the impact of cost-of-living pressures on the feasibility of younger Australians starting a family.
KPMG estimates that 289,100 babies were born in 2023. This compares to 300,684 babies in 2022 and 309,996 in 2021, according to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS). KPMG urban economist Terry Rawnsley said weak economic growth often leads to a reduced number of births. In 2023, ABS data shows gross domestic product (GDP) fell to 1.5 percent. Despite the population growing by 2.5 percent in 2023, GDP on a per capita basis went into negative territory, down one percent over the 12 months.
“Birth rates provide insight into long-term population growth as well as the current confidence of Australian families,” said Mr Rawnsley. “We haven’t seen such a sharp drop in births in Australia since the period of economic stagflation in the 1970s, which coincided with the initial widespread adoption of the contraceptive pill.”
Mr Rawnsley said many Australian couples delayed starting a family while the pandemic played out in 2020. The number of births fell from 305,832 in 2019 to 294,369 in 2020. Then in 2021, strong employment and vast amounts of stimulus money, along with high household savings due to lockdowns, gave couples better financial means to have a baby. This led to a rebound in births.
However, the re-opening of the global economy in 2022 led to soaring inflation. By the start of 2023, the Australian consumer price index (CPI) had risen to its highest level since 1990 at 7.8 percent per annum. By that stage, the Reserve Bank had already commenced an aggressive rate-hiking strategy to fight inflation and had raised the cash rate every month between May and December 2022.
Five more rate hikes during 2023 put further pressure on couples with mortgages and put the brakes on family formation. “This combination of the pandemic and rapid economic changes explains the spike and subsequent sharp decline in birth rates we have observed over the past four years,” Mr Rawnsley said.
The impact of high costs of living on couples’ decision to have a baby is highlighted in births data for the capital cities. KPMG estimates there were 60,860 births in Sydney in 2023, down 8.6 percent from 2019. There were 56,270 births in Melbourne, down 7.3 percent. In Perth, there were 25,020 births, down 6 percent, while in Brisbane there were 30,250 births, down 4.3 percent. Canberra was the only capital city where there was no fall in the number of births in 2023 compared to 2019.
“CPI growth in Canberra has been slightly subdued compared to that in other major cities, and the economic outlook has remained strong,” Mr Rawnsley said. “This means families have not been hurting as much as those in other capital cities, and in turn, we’ve seen a stabilisation of births in the ACT.”
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.