Is Now the Time to Invest in Emerging Markets?
Emerging-markets stock ETFs offer exposure to higher-growth markets, but they also can be volatile. Here is a look at the pros and cons of these investments.
For some investors seeking to diversify their portfolios, emerging markets are looking increasingly attractive.
There are 169 emerging-markets stock ETFs available to fund investors, with total assets of about $296 billion, according to fund researcher Morningstar Direct.
Some analysts and financial advisers say there is a lot to like about this sector right now. What is the argument for putting money into these exchange-traded funds? And what’s the argument for getting out, or not starting at all? Here’s a look at the pros and cons.
The Pros
One factor driving interest in emerging-markets ETFs is that emerging economies are growing faster than advanced economies, and that isn’t forecast to change soon. The International Monetary Fund forecasts real GDP growth of only 1.4% in advanced economies in 2024 due to inflation, monetary policy and other factors. In contrast, the IMF projects real GDP growth of 4.1% for emerging and developing economies, helped by countries such as India, which is expected to grow at a rate of 6.3%.
“The biggest reason to invest in emerging-markets ETFs today is to gain exposure to high-growth markets with burgeoning middle-class consumers such as China, India, Mexico, Taiwan, South Korea and Vietnam,” says Aniket Ullal, senior vice president and head of ETF data and analytics at CFRA Research. He says emerging markets are home to more than 4.3 billion people, and they account for about half of global GDP.

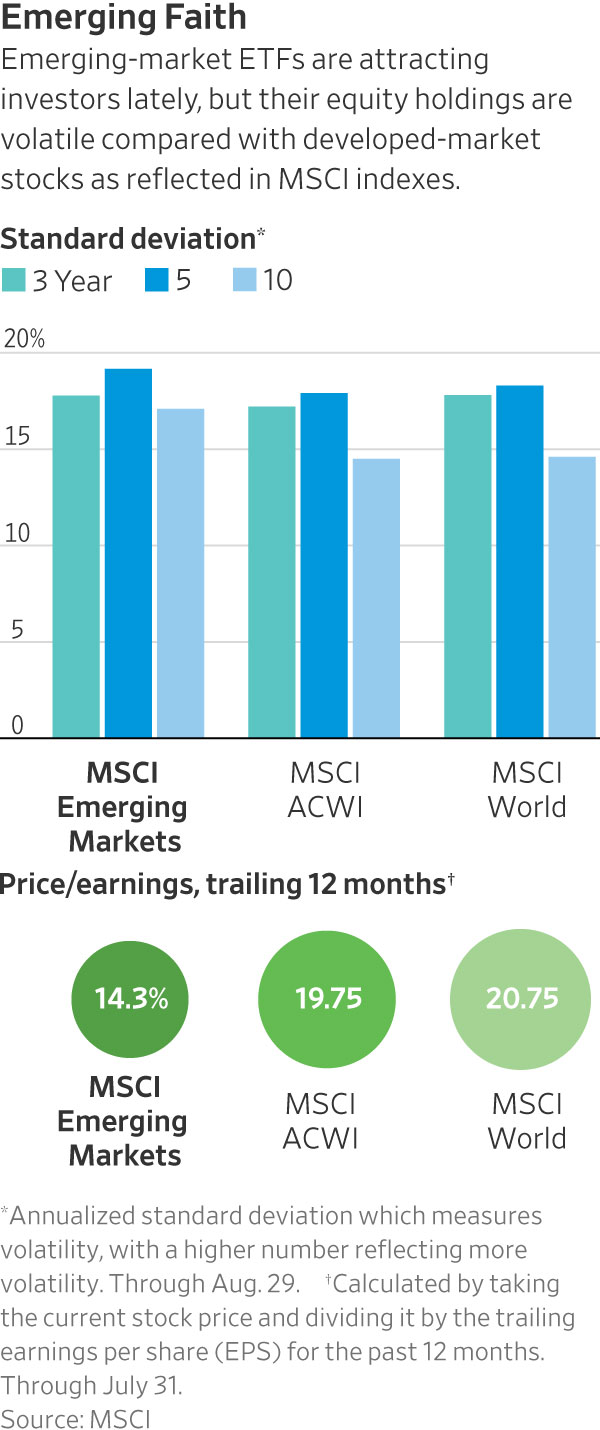
Another attraction is that valuations on emerging-markets stocks are low. While the price-to-earnings ratio of the S&P 500 was 22.4 based on trailing 12-month reported earnings as of July 31, the P/E ratio of the MSCI Emerging Markets—which includes the stock of most liquid large- and midcap companies in 25 emerging-market countries—was 14.13.
“This is a smart contrarian play for investors who want to diversify their portfolios geographically,” says Gabriel Shahin, president of Falcon Wealth Planning, an investment adviser in Los Angeles. “There is a fire sale going on in emerging-market stocks, and this is one of the smartest plays in equity investing right now.”
Some see these investments as a hedge, considering this year’s U.S. stock rally—dominated by a small number of large-cap technology companies—could end at any time.
Emerging-markets ETFs come in many varieties, so investors can choose those that align with their macroeconomic outlook and financial goals.
While some of these funds invest in a broad basket of emerging-market countries that span the globe such as the $72.1 billion iShares Core MSCI Emerging Markets ETF (IEMG), others invest in geographic regions such as Asia or Latin America or are country-specific.
The $64.2 million Franklin FTSE Latin America ETF (FLLA), for example, invests in large-cap and midcap companies in Brazil, Chile, Colombia and Mexico. It has returned more than 19% year-to-date through Aug. 29 and 15.6% over the past year. The $175.8 million Franklin FTSE Taiwan ETF (FLTW) invests in midcap and large-cap Taiwanese companies. It has a year-to-date return of 14.7% and a one-year-return of 8.2% as of Aug. 29.
For investors concerned about the economic slowdown in China, there are emerging-markets ETFs that exclude Chinese equities such as the $5.16 billion iShares MSCI Emerging Markets ex-China (EMXC). Its top holdings are Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing, Samsung Electronics and Reliance Industries.
Some emerging-markets ETFs target small- or large-cap stocks. One is the $34.2 million VanEck Brazil Small-Cap ETF (BRF), which is up about 32% year-to-date and 11.4% over one year as of Aug. 29. Others focus on industry sectors such as technology and e-commerce.
While most emerging-markets equity ETFs track indexes, an increasing number of newer funds are actively managed. Of the 11 emerging-markets ETFs that have launched this year, eight are actively managed, including Global X Brazil Active ETF (BRAZ), a $2.61 million fund that invests in Brazilian companies such as Petrobras, a multinational petroleum company, and Vale, the world’s largest iron-ore producer.
There are even emerging-markets ETFs that pay dividends, such as the $243.5 million SPDR S&P Emerging Market Dividend ETF (EDIV), which is up 28.2% year-to-date through Aug. 29 and has a dividend yield of 3.78%.
According to Morningstar Direct, the top-performing emerging market ETFs this year through Aug. 29 are VanEck Brazil Small-Cap, SPDR S&P Emerging Market Dividend and iShares MSCI Brazil Small-Cap (EWZS), which is up 24.1% so far this year and 5.7% over one year.
The Cons
Some advisers, however, say investors looking at emerging-markets equity funds should proceed with caution.
“Emerging-markets equity ETFs are more volatile than international ETFs that focus on stocks in advanced economies,” says Lan Anh Tran, a research analyst at Morningstar Direct. Over the past 10 years ended July 31, 2023, the standard deviation of the MSCI Emerging Market Index was 16.2% higher than the MSCI World Index—a proxy for global developed-market stocks, she notes. Standard deviation measures volatility, with a higher number representing more volatility.
That’s because any sudden geopolitical event (such as the war in Ukraine) or any economic shock (like soaring inflation or a global supply-chain disruption) can have a jarring effect on emerging-market economies that are dependent on commodity exports, tourism and the health of advanced economies, investment strategists say.
There also is the risk of government influence and regulation on emerging-markets stocks, says Tran. A government, for example, can decide to nationalize an industry at any time, or exercise control over an industry sector.
Currency movements are another risk factor to consider, says CFRA’s Ullal. “If the dollar strengthens against local currencies, your fund returns will erode,” he says.
“It’s important that investors understand this is a high-risk, high-reward investment before they dive into them,” says Andrew J. Feldman, the founder of A.J. Feldman Financial in Chicago. “These funds can be highly volatile due to a host of systemic risks in emerging-market countries, including economic risk, geopolitical risk, currency risk and liquidity risk.”
These challenges make some investors skittish about investing in emerging-markets ETFs, says Kevin Shuller, founder and chief investment officer of Cedar Peak Wealth Advisors in Denver. “They believe that companies domiciled in the U.S. do a lot of business in emerging markets, so if you own the S&P 500 or MSCI EAFE index you have all the exposure you need.”
“It’s a good counterargument,” he says, “but [it] doesn’t take into account that the party in the U.S. stock market may not go on forever.”
Many investment advisers instead suggest individual investors take a step-by-step approach when choosing an emerging-markets ETF and allocate 5% to 10% of their equity portfolio in such vehicles.
“Country selection matters most so check the fund’s geographic exposure,” says Perth Tolle, founder of Life + Liberty Indexes and the $625.4 million Freedom 100 Emerging Markets ETF (FRDM), which invests in about 100 companies in 10 countries that aren’t autocracies but freer markets such as Chile, Poland, South Korea and Taiwan.
Also look at the methodologies and metrics the ETF uses when choosing stocks for its index or portfolio, as well as the fund fees. The average expense ratio for this ETF group is 0.51%, according to Morningstar Direct.
“A good way to assess a fund’s value is to look at its weighted average price to cash flow,” a measure of the price of a company’s stock relative to how much cash flow it generates, says Kevin Grogan, chief investment officer at Buckingham Wealth Partners in St. Louis. It gives a pulse reading on how cheap or expensive the emerging-markets stocks are in the fund.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
Continued stagflation and cost of living pressures are causing couples to think twice about starting a family, new data has revealed, with long term impacts expected
Australia is in the midst of a ‘baby recession’ with preliminary estimates showing the number of births in 2023 fell by more than four percent to the lowest level since 2006, according to KPMG. The consultancy firm says this reflects the impact of cost-of-living pressures on the feasibility of younger Australians starting a family.
KPMG estimates that 289,100 babies were born in 2023. This compares to 300,684 babies in 2022 and 309,996 in 2021, according to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS). KPMG urban economist Terry Rawnsley said weak economic growth often leads to a reduced number of births. In 2023, ABS data shows gross domestic product (GDP) fell to 1.5 percent. Despite the population growing by 2.5 percent in 2023, GDP on a per capita basis went into negative territory, down one percent over the 12 months.
“Birth rates provide insight into long-term population growth as well as the current confidence of Australian families,” said Mr Rawnsley. “We haven’t seen such a sharp drop in births in Australia since the period of economic stagflation in the 1970s, which coincided with the initial widespread adoption of the contraceptive pill.”
Mr Rawnsley said many Australian couples delayed starting a family while the pandemic played out in 2020. The number of births fell from 305,832 in 2019 to 294,369 in 2020. Then in 2021, strong employment and vast amounts of stimulus money, along with high household savings due to lockdowns, gave couples better financial means to have a baby. This led to a rebound in births.
However, the re-opening of the global economy in 2022 led to soaring inflation. By the start of 2023, the Australian consumer price index (CPI) had risen to its highest level since 1990 at 7.8 percent per annum. By that stage, the Reserve Bank had already commenced an aggressive rate-hiking strategy to fight inflation and had raised the cash rate every month between May and December 2022.
Five more rate hikes during 2023 put further pressure on couples with mortgages and put the brakes on family formation. “This combination of the pandemic and rapid economic changes explains the spike and subsequent sharp decline in birth rates we have observed over the past four years,” Mr Rawnsley said.
The impact of high costs of living on couples’ decision to have a baby is highlighted in births data for the capital cities. KPMG estimates there were 60,860 births in Sydney in 2023, down 8.6 percent from 2019. There were 56,270 births in Melbourne, down 7.3 percent. In Perth, there were 25,020 births, down 6 percent, while in Brisbane there were 30,250 births, down 4.3 percent. Canberra was the only capital city where there was no fall in the number of births in 2023 compared to 2019.
“CPI growth in Canberra has been slightly subdued compared to that in other major cities, and the economic outlook has remained strong,” Mr Rawnsley said. “This means families have not been hurting as much as those in other capital cities, and in turn, we’ve seen a stabilisation of births in the ACT.”
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.






















