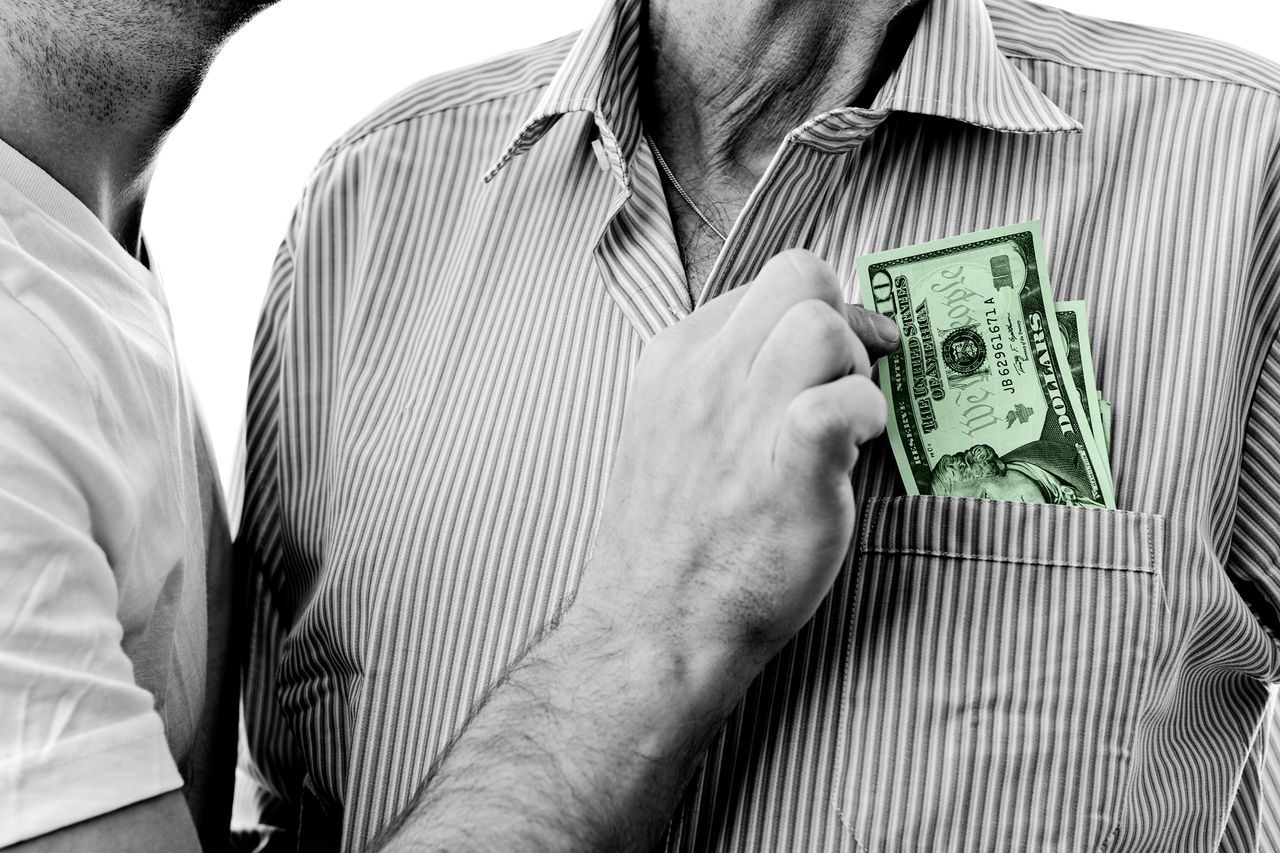
Well Into Adulthood and Still Getting Money From Their Parents
Nearly 60% of parents provide financial help to their adult kids, a new study finds
Parents have always supported their children into adulthood, from funding weddings to buying a home. Now the financial umbilical cord extends much later into adulthood.
About 59% of parents said they helped their young adult children financially in the past year, according to a report released Thursday by the Pew Research Center that focused on adults under age 35. (This question hadn’t been asked in prior surveys.) More young adults are also living with their parents. Among adults under age 25, 57% live with their parents, up from 53% in 1993.
Parental support is continuing later in life because younger people now take longer to reach many adult milestones—and getting there is more expensive than it has been for past generations, economists and researchers said. There is also a larger wealth gap between older Americans and younger ones, giving some parents more means and reason to help. In short, adulthood no longer means moving off the parental payroll.
“That transition has gotten later and later, for a lot of different reasons. Now it’s age 25, 30, 35, 40,” said Sarah Behr, founder of Simplify Financial Planning in San Francisco.
Kami Loukipoudis, a 39-year-old director of design, and husband Adam Stojanik, a 39-year-old high-school teacher, knew they would need parental assistance to buy in New York’s expensive home market.
“We could pay a mortgage, but that down payment was the absolute crusher,” Stojanik said. “The idea of trying to save up on our own—as long as we were paying rents in NY, would’ve taken 300 years.”
Loukipoudis’s mother gave them the money for a 10% down payment on a two-bedroom apartment in the New York borough of Queens.
The young-adult allowance
Adult children aren’t necessarily getting larger checks from their parents, but they are staying on the parental payroll for longer than previous generations, according to Marla Ripoll, professor of economics at the University of Pittsburgh who studied the trend by analysing payments from parents to adult children over a 20-year span.
Ripoll found that 14% of adult children receive a transfer of money from their parents at least once in any given year, and roughly half get financial help at some point within that period. Those rates have been stable for years. What has changed is that the transfers now continue for much longer, she found. This longer-term help might be a drag on social mobility, as it becomes even harder for young people from lower-income families to catch up, researchers said.
Of the young adult children who said they received financial help from a parent in the past year, most said they put it toward day-to-day household expenses, such as phone bills and subscriptions to streaming services like Netflix, according to the Pew survey.
The amount of money and the frequency of help varies by age; those on the older end of the 18-to-34 cohort are far likelier to say they are completely financially independent from their parents compared with younger adult children, as many in the latter group are completing their education. Nearly a third of young adult children between the ages of 30 and 34 say they still get parental help.
Heather McAfee, a 33-year-old physical therapist in Austin, Texas, said she lived at home between 2019 and 2021; otherwise she wouldn’t have been able to make progress paying down her student loans while rent prices in her area remained so high. The plan worked—she has since reduced her student-debt balance from $83,000 to $15,000.
“It helped tremendously,” she said. “I didn’t have to take out more loans to pay for apartment living or anything like that. That stress was gone.”
Setting limits on financial help
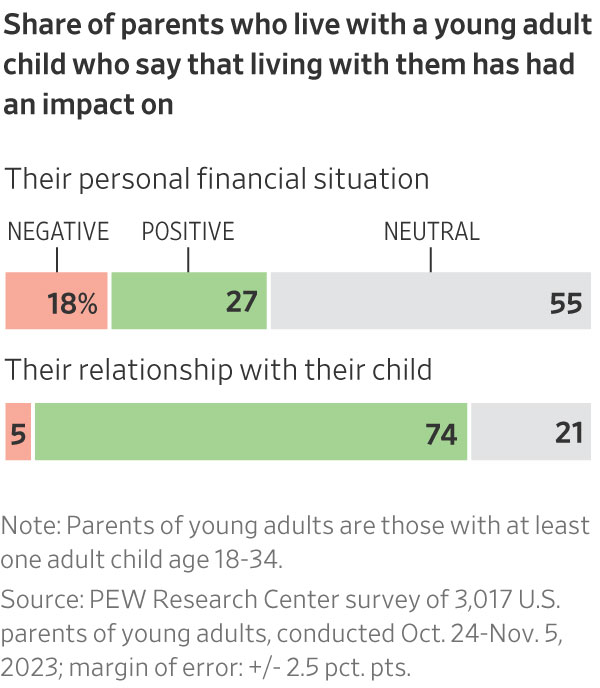
A little more than half of parents surveyed said that having their adult children home brought them closer together or improved their relationship, but nearly 20% said it dented their personal finances.
Financial advisers often find themselves in the tricky position of speaking to both ends of the equation: adult children who need assistance and the parents determined to help children well into middle age, within limits.
Whereas previous generations would step into a greater sense of financial independence in their early 20s, young adult children today are often unable to reach similar markers of such independence—living on their own or buying their first home, for example—without greater financial resources.
Families typically don’t set concrete rules around when financial help will happen and what the money is used for, which can result in surprises down the road, Behr said.
In one case, Behr’s clients received the down payment they needed to purchase a condo from a generous mother-in-law. Years later, that same mother-in-law told them she expected a payout once the couple sold the home.
The hand-me-down payment
Down-payment help from parents—a given for many first-time home buyers—is growing thanks to higher home prices and elevated mortgage rates.
About a fifth of first-time home buyers said they got help from a relative or friend when pulling together the money needed for a down payment, according to a 2023 survey of home buyers and sellers from the National Association of Realtors. And 38% of home buyers under age 30 received help with the down payment from their parents, according to a survey this spring by Redfin.
Wealthy families often go further than helping with the down payment. They become a true bank of mom and dad and write a mortgage. The Internal Revenue Service sets minimum levels of interest for such loans, which remain significantly cheaper than current mortgage rates.
Timothy Burke, chief executive at National Family Mortgage, which facilitates such loans, said parents are often frustrated on behalf of their house-hunting children. High interest rates and the cutthroat housing market are holding their children back from reaching a milestone the parents themselves were more easily able to access.
Mei Chao, a 41-year-old stay-at-home mom, and her husband, William Chao, a 44-year-old information-technology specialist, bought their first house as a couple in 2017. They relied on financial help from her husband’s two sisters and his mother to help them bridge a gap in their house-buying timeline. While they waited to sell William’s Manhattan condo, they used the money from the family to purchase the new house in Queens.
The structure of the agreements got tricky. After selling the condo in Manhattan, Mei and her husband were able to repay his sisters in full. But they didn’t have enough money left over from the sale to do the same for Mei’s mother-in-law. So they kept the mother-in-law’s name on the deed to the house—a concession Mei said they were both more than happy to make.
“Ultimately, it all worked out. I’m glad his mother pushed us,” Mei said. “Without her help, I could not say we would have this home.”
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
Continued stagflation and cost of living pressures are causing couples to think twice about starting a family, new data has revealed, with long term impacts expected
Australia is in the midst of a ‘baby recession’ with preliminary estimates showing the number of births in 2023 fell by more than four percent to the lowest level since 2006, according to KPMG. The consultancy firm says this reflects the impact of cost-of-living pressures on the feasibility of younger Australians starting a family.
KPMG estimates that 289,100 babies were born in 2023. This compares to 300,684 babies in 2022 and 309,996 in 2021, according to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS). KPMG urban economist Terry Rawnsley said weak economic growth often leads to a reduced number of births. In 2023, ABS data shows gross domestic product (GDP) fell to 1.5 percent. Despite the population growing by 2.5 percent in 2023, GDP on a per capita basis went into negative territory, down one percent over the 12 months.
“Birth rates provide insight into long-term population growth as well as the current confidence of Australian families,” said Mr Rawnsley. “We haven’t seen such a sharp drop in births in Australia since the period of economic stagflation in the 1970s, which coincided with the initial widespread adoption of the contraceptive pill.”
Mr Rawnsley said many Australian couples delayed starting a family while the pandemic played out in 2020. The number of births fell from 305,832 in 2019 to 294,369 in 2020. Then in 2021, strong employment and vast amounts of stimulus money, along with high household savings due to lockdowns, gave couples better financial means to have a baby. This led to a rebound in births.
However, the re-opening of the global economy in 2022 led to soaring inflation. By the start of 2023, the Australian consumer price index (CPI) had risen to its highest level since 1990 at 7.8 percent per annum. By that stage, the Reserve Bank had already commenced an aggressive rate-hiking strategy to fight inflation and had raised the cash rate every month between May and December 2022.
Five more rate hikes during 2023 put further pressure on couples with mortgages and put the brakes on family formation. “This combination of the pandemic and rapid economic changes explains the spike and subsequent sharp decline in birth rates we have observed over the past four years,” Mr Rawnsley said.
The impact of high costs of living on couples’ decision to have a baby is highlighted in births data for the capital cities. KPMG estimates there were 60,860 births in Sydney in 2023, down 8.6 percent from 2019. There were 56,270 births in Melbourne, down 7.3 percent. In Perth, there were 25,020 births, down 6 percent, while in Brisbane there were 30,250 births, down 4.3 percent. Canberra was the only capital city where there was no fall in the number of births in 2023 compared to 2019.
“CPI growth in Canberra has been slightly subdued compared to that in other major cities, and the economic outlook has remained strong,” Mr Rawnsley said. “This means families have not been hurting as much as those in other capital cities, and in turn, we’ve seen a stabilisation of births in the ACT.”
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.






















