Why ESG Investing Might Never Recover
The appeal of the moniker is waning, probably because it is trying to serve too many interests at once
The ESG brand probably has its best days behind it.
Following a three-year craze for investment products focused on environmental, social and corporate-governance concerns, the percentage of newly created funds in the U.S. and Europe with ESG in their name has fallen from a peak of 8.3% to just 3.3%, according to an analysis of quarterly data by Morningstar Direct.
Likewise, online searches for “ESG investing” have plummeted back to mid-2019 levels, according to Google Trends. Mentions of the term in company analyst calls have dropped 59% from their quarterly peak in 2022, FactSet data suggest.
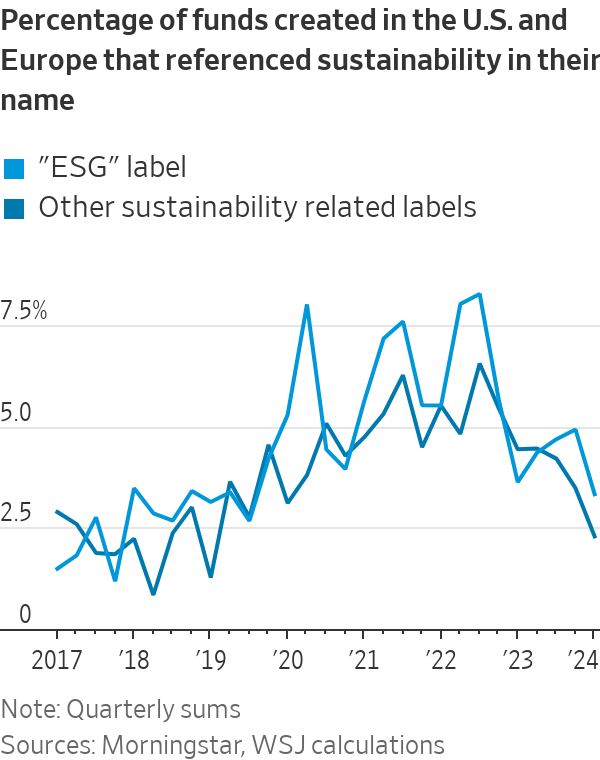
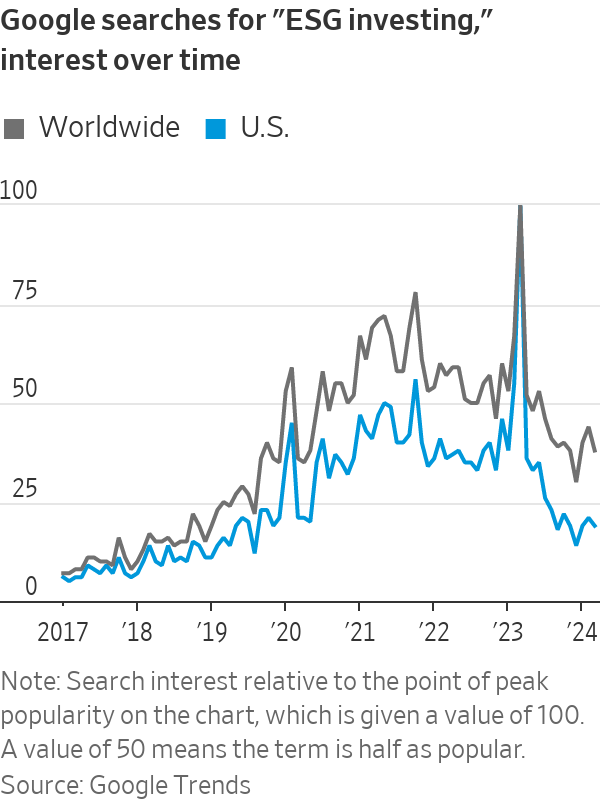
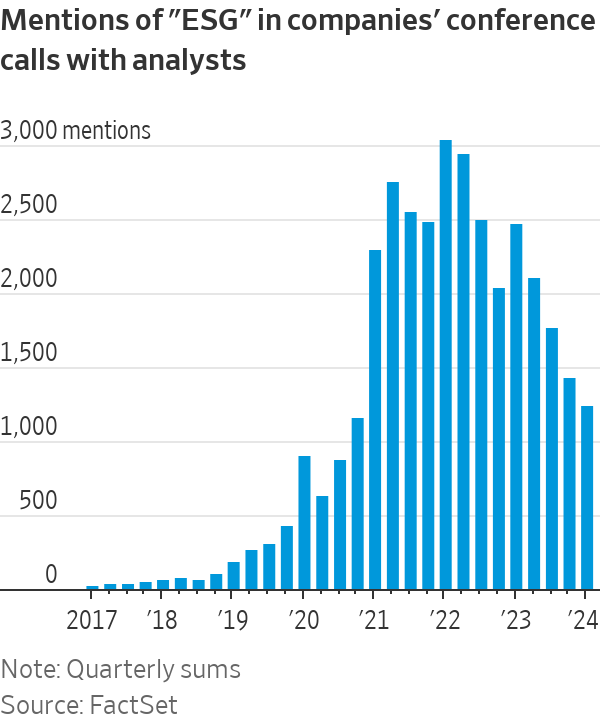
One explanation is the collapse of the clean-energy stocks most readily associated with the ESG movement. Flagging growth in electric-vehicle sales has hit sector behemoth Tesla . The S&P Global Clean Energy index, which lists solar-panel maker First Solar and Danish wind-turbine giant Vestas among its top constituents, has lost 31% since the start of 2023 as renewable-energy projects have been shelved. That compares with returns of 27% for global stocks.
The rise of ESG investing between 2019 and 2022 coincided with a surge in clean-tech valuations, and now the reverse is happening. Investors have pulled $2.2 billion from funds dedicated to decarbonisation since the start of the year, according to EPFR, and the outflows are getting larger every week.
There is a risk that ESG was an investment fad rather than a financial revolution extending across all industries.
The term was the product of an uneasy three-way alliance. On one side were ethically driven investors, who are particularly widespread in Scandinavia and include pension funds, universities and religious organisations united in wanting to shun contentious firms. On another were institutions such as the United Nations that aimed to channel money to industries that benefit society. Finally, there were investors who wanted to profit from the green revolution.
Asset managers jumped at the chance to cater to all three simultaneously. ESG allowed them to differentiate their products, revitalise the case for active management and, at a time of declining fees, charge more for stock screens that often lead to only small changes in allocations . Among U.S. equity funds, ESG strategies have an asset-weighted average fee of 0.52%, compared with 0.33% overall, Morningstar Direct data shows.
But the confusion of motivations made for contradictions and a lot of doublespeak. Neither ethical objectives nor bets on decarbonisation square logically with fund managers’ claims that ESG is a broad path to higher, safer returns.
Yes, an ESG focus can help active managers account for risks such as a regulatory backlash or governance blow up, which in some cases might be highlighted by new company disclosures. This month the European Union cleared the way toward requiring firms to better report and address sustainability impacts.
However, the assumption that integrating ESG criteria into their screening will lead to better stock picking seems flawed . The very popularity of ESG makes it unlikely that the market is under appreciating the risks. The rush of money into firms like Vestas, whose stock hit a price-to-earnings ratio of 534 in 2022, illustrates the risk that shares with high sustainability scores can get too expensive, leading to lower returns.
Ethical investors might be fine with this, but that just shifts the focus to what counts as ethical. Tellingly, interest in ESG has dropped more in the U.S., where the politicisation of EVs and culture wars surrounding Bud Light beer show how easily corporations can become ideological battlegrounds.
ESG ratings aren’t much help in navigating these issues. Different providers give wildly different scores to the same companies, even within the specific “E,” “S” and “G” factors, according to a February paper by the Leibniz Institute SAFE. Researchers also found that environmental concerns tend to explain most of the overall score.
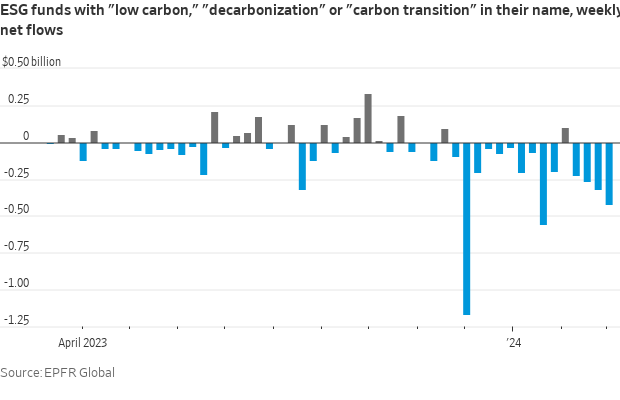
This is another hint that the ultimate driver of the pandemic-era ESG craze might have been a hunger for thematic investment. It has since found better sources of sustenance, as demonstrated by the breakneck growth of firms such as Global X, which is delivering increasingly granular offerings such as tracker funds for electric batteries, cloud computing and ageing populations.
Buyers of these products can be fickle and jump to the next theme—often too quickly for their own good, a Morningstar analysis showed last November. It is possible that the overly generic ESG brand will never recover its appeal, with the different parts of it eventually rebranded to suit their specific client bases. BlackRock , the world’s largest asset manager, has already dropped it and is now emphasising transition themes over ethical stewardship of companies.
Sustainable investing isn’t going anywhere. But a broad tent covering too many interests serves none of them well.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
Continued stagflation and cost of living pressures are causing couples to think twice about starting a family, new data has revealed, with long term impacts expected
Australia is in the midst of a ‘baby recession’ with preliminary estimates showing the number of births in 2023 fell by more than four percent to the lowest level since 2006, according to KPMG. The consultancy firm says this reflects the impact of cost-of-living pressures on the feasibility of younger Australians starting a family.
KPMG estimates that 289,100 babies were born in 2023. This compares to 300,684 babies in 2022 and 309,996 in 2021, according to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS). KPMG urban economist Terry Rawnsley said weak economic growth often leads to a reduced number of births. In 2023, ABS data shows gross domestic product (GDP) fell to 1.5 percent. Despite the population growing by 2.5 percent in 2023, GDP on a per capita basis went into negative territory, down one percent over the 12 months.
“Birth rates provide insight into long-term population growth as well as the current confidence of Australian families,” said Mr Rawnsley. “We haven’t seen such a sharp drop in births in Australia since the period of economic stagflation in the 1970s, which coincided with the initial widespread adoption of the contraceptive pill.”
Mr Rawnsley said many Australian couples delayed starting a family while the pandemic played out in 2020. The number of births fell from 305,832 in 2019 to 294,369 in 2020. Then in 2021, strong employment and vast amounts of stimulus money, along with high household savings due to lockdowns, gave couples better financial means to have a baby. This led to a rebound in births.
However, the re-opening of the global economy in 2022 led to soaring inflation. By the start of 2023, the Australian consumer price index (CPI) had risen to its highest level since 1990 at 7.8 percent per annum. By that stage, the Reserve Bank had already commenced an aggressive rate-hiking strategy to fight inflation and had raised the cash rate every month between May and December 2022.
Five more rate hikes during 2023 put further pressure on couples with mortgages and put the brakes on family formation. “This combination of the pandemic and rapid economic changes explains the spike and subsequent sharp decline in birth rates we have observed over the past four years,” Mr Rawnsley said.
The impact of high costs of living on couples’ decision to have a baby is highlighted in births data for the capital cities. KPMG estimates there were 60,860 births in Sydney in 2023, down 8.6 percent from 2019. There were 56,270 births in Melbourne, down 7.3 percent. In Perth, there were 25,020 births, down 6 percent, while in Brisbane there were 30,250 births, down 4.3 percent. Canberra was the only capital city where there was no fall in the number of births in 2023 compared to 2019.
“CPI growth in Canberra has been slightly subdued compared to that in other major cities, and the economic outlook has remained strong,” Mr Rawnsley said. “This means families have not been hurting as much as those in other capital cities, and in turn, we’ve seen a stabilisation of births in the ACT.”
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.






















