Why No One Wants to Pay for the Green Transition
Investors and consumers balk at costs of replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy, highlighting painful economics of climate mitigation
In the past few years, Washington and Wall Street started fantasising that the transition to net-zero carbon emissions could be an economic bonanza. “When I think climate change, I think jobs,” President Biden said. When Wall Street heard green energy, it saw profits. As Ford Motor launched an electric Mustang and pickup truck, its market value topped $100 billion for the first time.
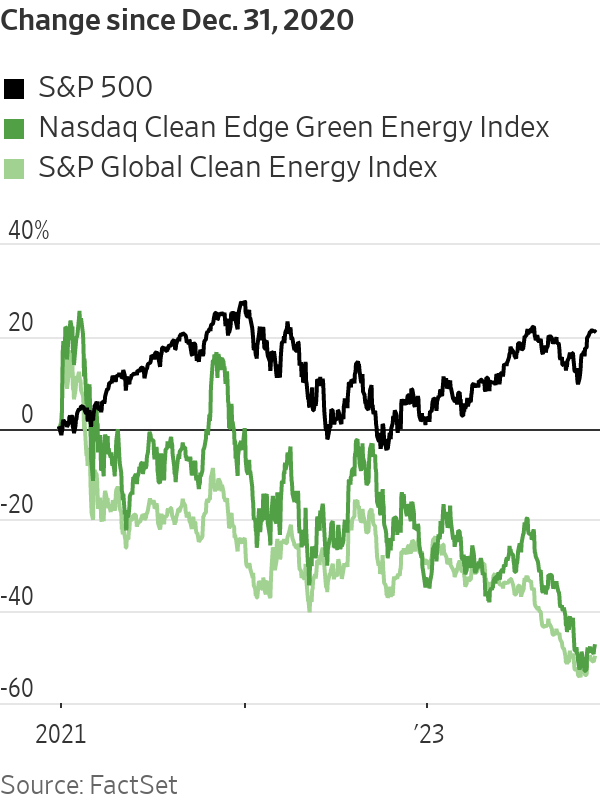
This year the fantasy ended. With electric vehicle demand falling short of expectations, manufacturers are dialling back production and buying back stock instead. Offshore wind developers have canceled projects. The S&P Global Clean Energy Index has fallen 30% this year. Ford’s market cap is down to $42 billion.
This doesn’t mean the transition to net zero is over. Officials meeting this week at the United Nations climate conference are just as worried about climate change. Renewable energy continues to expand. In the very long run, it is still the case that economic welfare will be higher with less global warming.
But the economics of getting to net zero remain, fundamentally, dismal: Someone has to pay for it, and shareholders and consumers decided this year it wouldn’t be them.
Politicians and the public tend to think all investment is good for growth, an error that leads to all sorts of muddled thinking about climate.
Technological transformations are positive supply shocks: a new, more efficient technology comes along, and investment naturally gravitates toward this new technology because it is profitable.
By contrast, the green transition is driven by public policy. It is “a negative supply shock, with an accompanying need to finance investments whose profitability cannot be taken for granted,” French economist Jean Pisani-Ferry wrote in a report commissioned by the French prime minister and released in English in November. “By putting a price—financial or implicit—on a free resource (the climate), the transition increases production costs, with no guarantee that the reduction in energy costs will eventually offset them, while the investments it calls for do not increase productive capacity but must nevertheless be financed.”
Pisani-Ferry, who is affiliated with the Bruegel think tank in Europe and the Peterson Institute for International Economics in Washington, is an uncommonly clear thinker on this issue.
He notes the transition involves hefty capital spending today to replace fossil-fuel consumption in the future. Pisani-Ferry estimates a middle-class French family would spend 44% of annual disposable income for a heat pump, and 120% for an electric car. These investments boost demand, but don’t leave families better off since they simply do the same thing as what they replace. And if taxes rise to pay for these investments, families will be worse off, financially.
“It would take an incredible act of blindness to fail to recognise that climate change is happening, that it is—and will increasingly become—severely damaging,” he writes. “It would also be incredibly flippant to claim that this urgent and imperative action will have no economic cost by 2030.”
The most efficient way to redirect consumption and investment from fossil fuels to zero-emissions energy is a carbon tax, or a cap-and-trade system. Europe has adopted such a system plus ever more stringent goals, especially after Russia cut off natural-gas supplies following its 2022 invasion of Ukraine. But as the cost has grown, so has public discontent, from France’s “yellow vest” protests in 2018 to last week’s first-place finish in Dutch elections by the far-right Freedom Party, which wants to ditch all climate regulations.
U.S. leaders have rejected any federal tax or fee on carbon. Biden’s solution is to not ask consumers to pay for the green transition; his Inflation Reduction Act pours, by some estimates, roughly $1 trillion into electric vehicles, renewable energy, hydrogen and other zero-emissions technology.
Subsidies can play a vital role by giving green energy time to scale up and innovate until it is competitive with fossil fuels. But the IRA has been undermined by extraneous conditions such as made-in-America requirements, and by green tech inflation—a byproduct of the IRA itself, which helped fuel demand.
Finally, Biden’s investment agenda was designed for the pre pandemic era when low interest rates flattered the financial profile of renewable energy investment and federal budget deficits were less likely to crowd out private investment. Those assumptions no longer apply.
For years, the cost of wind and solar plummeted, but since 2021 they have risen, according to investment bank Lazard. Interest rates are an important factor, which Lazard estimates affect offshore wind and solar more than natural gas.
Many developers can no longer economically supply power at the rates previously agreed to. Denmark’s Orsted, the world’s largest wind developer, took a $4 billion charge in early November for pulling out of two projects off New Jersey. The company today is worth 75% less than in early 2021.
ClearView Energy Partners estimates about 30% of state-contracted offshore wind capacity has been canceled, and another 25% may be rebid. ClearView analyst Timothy Fox noted lawmakers often mandate increased renewables, but utility regulators must approve the contracts, and one of their primary considerations is cost to ratepayers.
“I am an unapologetic economic regulator,” Diane Burman, a member of the New York state Public Service Commission, said in October as the commission refused to pay wind developers more. De carbonisation and grid improvement must proceed “with costs in mind.”
The financial appeal of EVs has similarly faded. Tesla proved making them can be profitable, but so far it looks like an outlier. Tesla captured the lion’s share of early adopters—drivers willing to put up with the cost and recharging hassle of an EV in return for performance and green credentials. For most drivers, the trade off still doesn’t work—even with subsidies.
True, the IRA has spurred a boom in EV and battery factories. But a successful green transition requires that those factories be profitable, and Detroit’s automakers are still losing money on every EV they sell.
EVs should eventually require less labor and thus be cheaper to build than gasoline-powered vehicles. But auto workers are no more willing to pay for the green transition than consumers or investors. In its recent strike, the United Auto Workers extracted commitments that make it even harder for Detroit to make money on EVs.
In a sobering report this week, Morgan Stanley auto analysts estimated the average non financial company in the S&P 500 spends its market cap in capital expenditure and research and development in about 50 years. GM and Ford spend theirs in 1.9 and 2.6 years, respectively. “This cannot continue, in our view.”
The green transition remains critical, but its path will be fraught until someone agrees to pay for it.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
Continued stagflation and cost of living pressures are causing couples to think twice about starting a family, new data has revealed, with long term impacts expected
Australia is in the midst of a ‘baby recession’ with preliminary estimates showing the number of births in 2023 fell by more than four percent to the lowest level since 2006, according to KPMG. The consultancy firm says this reflects the impact of cost-of-living pressures on the feasibility of younger Australians starting a family.
KPMG estimates that 289,100 babies were born in 2023. This compares to 300,684 babies in 2022 and 309,996 in 2021, according to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS). KPMG urban economist Terry Rawnsley said weak economic growth often leads to a reduced number of births. In 2023, ABS data shows gross domestic product (GDP) fell to 1.5 percent. Despite the population growing by 2.5 percent in 2023, GDP on a per capita basis went into negative territory, down one percent over the 12 months.
“Birth rates provide insight into long-term population growth as well as the current confidence of Australian families,” said Mr Rawnsley. “We haven’t seen such a sharp drop in births in Australia since the period of economic stagflation in the 1970s, which coincided with the initial widespread adoption of the contraceptive pill.”
Mr Rawnsley said many Australian couples delayed starting a family while the pandemic played out in 2020. The number of births fell from 305,832 in 2019 to 294,369 in 2020. Then in 2021, strong employment and vast amounts of stimulus money, along with high household savings due to lockdowns, gave couples better financial means to have a baby. This led to a rebound in births.
However, the re-opening of the global economy in 2022 led to soaring inflation. By the start of 2023, the Australian consumer price index (CPI) had risen to its highest level since 1990 at 7.8 percent per annum. By that stage, the Reserve Bank had already commenced an aggressive rate-hiking strategy to fight inflation and had raised the cash rate every month between May and December 2022.
Five more rate hikes during 2023 put further pressure on couples with mortgages and put the brakes on family formation. “This combination of the pandemic and rapid economic changes explains the spike and subsequent sharp decline in birth rates we have observed over the past four years,” Mr Rawnsley said.
The impact of high costs of living on couples’ decision to have a baby is highlighted in births data for the capital cities. KPMG estimates there were 60,860 births in Sydney in 2023, down 8.6 percent from 2019. There were 56,270 births in Melbourne, down 7.3 percent. In Perth, there were 25,020 births, down 6 percent, while in Brisbane there were 30,250 births, down 4.3 percent. Canberra was the only capital city where there was no fall in the number of births in 2023 compared to 2019.
“CPI growth in Canberra has been slightly subdued compared to that in other major cities, and the economic outlook has remained strong,” Mr Rawnsley said. “This means families have not been hurting as much as those in other capital cities, and in turn, we’ve seen a stabilisation of births in the ACT.”
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.






















