Japan Is Back. Is Inflation the Reason?
Deflation might be vanquished, but the payoff could be elusive
The Nikkei stock index recorded last week its first new high in 34 years, a fitting tribute to Japan’s re-emergence as a genuinely exciting economy.
It also comes amid mounting evidence that Japan has finally broken the hold of deflation. Inflation in January was 2.2%, the 22nd month above 2%. Wage growth has picked up too.
This appears to vindicate the economic consensus that deflation was a primary driver of Japan’s decades long malaise. But that conclusion might be premature. Proof of deflation’s harm has been elusive, and the benefits of low, positive inflation might be similarly subtle.
Consumers are often surprised to hear that deflation is supposed to be bad. In the U.S., where prices have risen steeply since 2021 , normal people, and even economists, wouldn’t object if they fell a bit.
The trouble arises when prices fall persistently, year in and year out, because wages, incomes and the prices of assets such as property tend to follow. Debtors struggle to repay loans and might slash spending or default, endangering the financial system. That is what happened in the U.S. when prices fell 27% from 1929 to 1933.
Even mild deflation can, in theory, inhibit growth. Central banks stimulate spending by lowering nominal interest rates below inflation to make the real—i.e., inflation-adjusted—cost of borrowing negative. That is almost impossible when inflation is itself negative.
The roots of deflation
Japan’s deflation began after its property and stock-market bubbles burst in the early 1990s. Ensuing losses at banks eroded their ability to lend. Inflation turned negative in 1999.
Western economists such as future Federal Reserve Chair Ben Bernanke argued that curing deflation was essential to restoring Japan’s economic health. The Bank of Japan agreed, at first half heartedly and then wholeheartedly.
It used zero, then negative, short-term interest rates. Next came purchases of short-term, then long-term, government securities. Finally, the BOJ even bought shares in companies with newly created money to stimulate spending and raise inflation.
The BOJ only succeeded in bringing inflation up to around zero. It took the global supply chain shocks of the pandemic to finally push underlying inflation to 2%, the bank’s target .
Japan’s 25 years of zero to negative inflation was accompanied by one of the rich world’s lowest growth rates. Japanese deflation became a cautionary tale for other countries, most recently China, where prices are currently falling .
Yet proving that deflation was behind Japan’s problems is maddeningly hard. Arguably, it was more symptom than cause.
In the early 1990s, working-age population growth turned negative. This happened just as Japan’s post-World War II phase of catching up to other developed nations ended. Meanwhile, industry began moving production to lower-wage countries.
All this, plus the banking crisis, put structural downward pressure on prices, wages and growth.
Underlying performance
Adjusted for its shrinking population, however, Japan’s performance has been respectable. From 1991 to 2019, its output per hour worked rose 1.3% a year. This was slower than in the U.S. but comparable with Canada, France, Germany and Britain, and faster than Italy or Spain, according to the economists Jesús Fernández-Villaverde, Gustavo Ventura and Wen Yao.
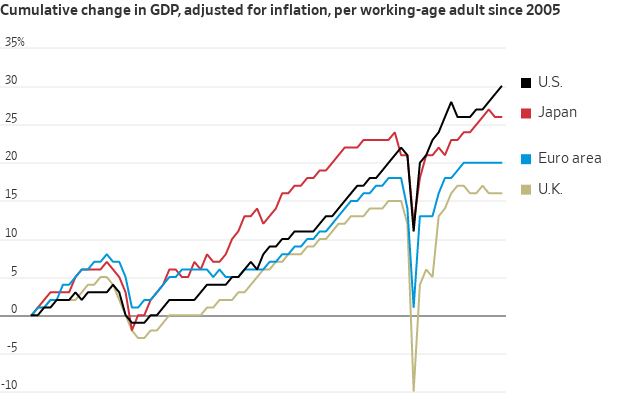
Since 2019, output per working-age person rose 7% in the U.S., 5% in Japan, 2% in the eurozone and zero in Britain, by my calculations. (This might overstate Japan’s performance because many of its elderly still work.) As any visitor can attest, Japan remains a prosperous, harmonious and well-ordered place.
“Had you appointed me governor of the Bank of Japan for 25 years with all the power in the world, I don’t think I would have been able to do better,” said Fernández-Villaverde.
This doesn’t prove deflation was benign. Growth (and deflation) might have been worse without the BOJ’s herculean monetary efforts. And if inflation had been positive, growth might have been stronger.
Still, it raises an awkward question: If zero to negative inflation is so damaging, where is the evidence?
The price mechanism
The harm might lie in subtle behavioural changes by investors, companies and the public. For example, in a market economy, changing relative prices and wages are critical signals for reallocating capital and labor from stagnant to growing sectors.
Relative prices changes are unusually rare in Japan, according to the University of Tokyo economist Tsutomu Watanabe. He has found that from 1995 through 2021, prices of more than half of products didn’t change at all from year to year. This wasn’t just because average inflation was lower; price changes deviated from the average much less than in other countries.
In a December speech, Bank of Japan Governor Kazuo Ueda said years of low to negative inflation led to a “status quo in wage- and price-setting behaviour,” so many prices and wages didn’t change. “The know-how for raising prices was thus lost,” he said.

The absence of this price-discovery function, Ueda contended, sapped productivity and dynamism.
Watanabe’s research shows that since January 2022, prices have been less sticky and more dispersed. Coincidentally, the Nikkei’s latest rally began a year later.
This in great part reflects the enthusiasm of foreign investors such as Warren Buffett , shareholder-friendly changes in corporate governance, and Japan’s importance as an alternative to China for high-end manufacturing and technology.
Inflation, though, might also be a factor, said Paul Sheard , a former vice chairman at S&P Global who has studied the Japanese economy for decades. He added that investors care about nominal, not real, stock prices, earnings, dividends and cash flow.
Higher inflation flatters all those metrics. That benefit might be neutralised by higher interest rates, but Japanese bond yields have risen less than expected inflation, so real yields are down to minus 0.6%.
So perhaps inflation is reviving businesses’ and investors’ animal spirits. Even so, growth last year was about the same as before the pandemic and turned slightly negative in the third and fourth quarters, producing a technical recession . What’s more, wages have lagged behind inflation, and Prime Minister Fumio Kishida ’s approval ratings have plummeted.
Japan might have prevailed in its war against deflation. But ordinary Japanese have yet to see a peace dividend.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
The budget is being framed ahead of a federal election expected to be held in early 2025
SYDNEY—Australian Treasurer Jim Chalmers will deliver the government’s 2024-2025 federal budget next Tuesday amid concerns that strong revenue growth will tempt him toward a jump in spending, stoking the case for higher interest rates.
Economists expect Chalmers to announce a budget surplus for 2023-2024, supported in part by high commodity prices and strength in the job market, with unemployment continuing to hover near its lowest level in half a century.
The question on the lips of the governor of the Reserve Bank of Australia, Michele Bullock , will be how much of that revenue will flow back into the economy by things like added measures aimed at easing a cost-of-living surge for consumers.
Bullock told reporters Tuesday that the RBA’s board had considered a further rise in interest rates, sending a shot across the bow of the center-left Labor government ahead of the budget.
The budget is being framed ahead of a federal election expected to be held in early 2025.
The public acknowledgment of the RBA board’s discussion of what would be a 14th interest-rate rise in two years signaled that the central bank has grown more concerned about the inflation outlook after first-quarter data came in above its own expectations.
Economists have warned that the RBA isn’t even close to a decision to cut interest rates, and the more likely outcome at the moment is that the central bank will need to tighten the policy screws further before the end of this year.
“The challenge fiscal policymakers face is that although they are flush with revenue, a cautious approach ought to be taken to additional spending because the economy is still operating at full employment, and inflation is still too high,” said Paul Bloxham, chief economist at HSBC Australia.
“Loosening fiscal policy settings at this point could mean that monetary policy would need to be tightened further yet—or that rates need to be higher for longer,” he added.
The RBA is conscious of the fact that significant income tax cuts will be delivered midyear and that they target low- and middle-income earners, who are more likely to spend added income than save it.
The government has already signalled its plans to spend in the area of subsidies for local manufacturing, including for the production of solar panels.
In addition, the budget will focus on business tax incentives, increased defence spending, funding for domestic violence support, changes to student debt policy and infrastructure.
Chalmers has played down the risk over the budget stoking the flames of inflation.
“It will be a responsible budget, a restrained budget, and it will maintain our focus on that inflation fight,” he said Thursday in a radio interview.
“There will be help for people with the cost of living, but we’ll make sure that that cost-of-living help is part of the solution and not part of the problem when it comes to inflation,” he added.
A risk that the RBA will also be alert to is the probability that the government will hold back some of its revenue gains to support added spending closer to the election.
Josh Williamson , chief economist at Citi Australia, said Chalmers will likely push new spending into the future to avoid overheating the economy now.
“The government does not want to be seen promoting policies that add to the risk of further policy tightening,” he said.
This suggests that new spending will be pushed into the government’s forward budgetary projections, while measures that directly reduce inflation could be announced virtually immediately, Williamson added.
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.