The Sandwich Generation Is Stressed Out, Low on Money and Short on Time
As millennials start to hit middle age—and boomers near their 80s—the number of Americans caring for both older and younger generations is poised to surge
At 34, Kait Giordano is juggling her job, a newborn and two parents with dementia.
Just over a month into motherhood, she tends to her infant son and her live-in parents in the morning and afternoon, some days with the help of a rotating cast of paid companions at their Tucker, Ga., home. In the evenings, her husband, Tamrin, takes over while she colours hair.
They had already delayed starting a family when Kait’s father moved in a few years ago. Her mother moved in this year. “We chose to take this on,” she says. “We didn’t want to wait any longer.”
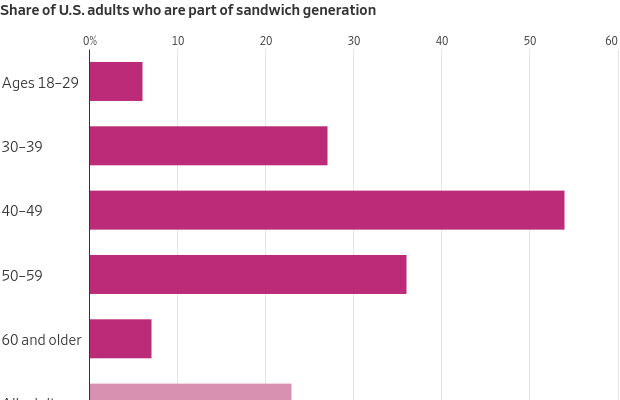
More Americans shoulder a double load of caring for their children and at least one adult , often a parent. The “sandwich generation” has grown to at least 11 million in the U.S., according to one estimate, and shifts in demographics, costs and work are making it a longer and tougher slog.
People are having children later, and they are living longer , often with care-intensive conditions such as dementia. That means many are taking care of elderly parents when their own kids are still young and require more intensive parenting—and for longer stretches of their lives than previous generations of sandwiched caregivers.
As the oldest millennials start to hit middle age —and baby boomers near their 80s—the number of Americans caring for older and younger family makes up a significant part of the electorate. Vice President Kamala Harris invoked the sandwich generation when she recently proposed expanding Medicare benefits to cover home healthcare.
“There are so many people in our country who are right in the middle,” the Democratic presidential candidate said on ABC’s “The View” this month. “It’s just almost impossible to do it all, especially if they work.”
Responding to the Harris proposal, former President Donald Trump ’s campaign said he would give priority to home-care benefits by shifting resources to at-home senior care and provide tax credits to support unpaid family caregivers.
The growing burden on this sandwich generation weakens careers and quality of life, and has ramifications for society at large. It is a drag on monthly budgets and long-term financial health.
A 40-something contributing $1,500 a month over five years to support an aging parent stands to lose more than $1 million in retirement savings, according to an analysis by Steph Wagner , national director of women and wealth at Northern Trust Wealth Management.
“It’s become incredibly expensive to manage the longevity that we’ve created,” says Bradley Schurman , an author and demographic strategist, who says that the demands of caring for older generations could push more people in midlife to retreat from the workforce, particularly women. “That’s a massive risk for the U.S. economy.”
Career goals on hold
Not too long ago, the typical sandwich caregiver was a woman in her late 40s with teenage kids and maybe a part-time job. Now, according to a 2023 AARP report, the average age of these caregivers is 44, and a growing share are men. Nearly a third are millennials and Gen Z. They are in the critical early-to-middle stages of their careers and three-quarters of them work full or part time.
Diana Fuller, 49, says being the go-to person for her 83-year-old mother’s care for more than four years has been stressful, even with her mother now living in a nearby, $10,000-a month memory-care centre in Charlotte., N.C. (Long-term-care insurance covers 75%; the rest is paid out of her mother’s savings.)
She has put on the back burner career goals such as ramping up the leg warmer business she started with her sister. She has missed moments such as her 9-year-old son’s school holiday concert last year because of her mother’s frequent hospital stays.
Her husband picks up a lot of the child care duties when her mom is in the hospital. Still, she says, “it often feels like everything is about to implode.”
The financial pressures are also growing for the sandwich generation. According to a Care.com survey of 2,000 parents, 60% of U.S. families spent 20% or more of their annual household income on child care last year, up from 51% of families in 2021. Meanwhile, the median cost of a home health aide climbed 10% last year to $75,500, data from long-term-care insurer Genworth Financial show.
Caregivers often risk paying for such costs in their own old age, financial advisers say. More than half reported in a 2023 New York Life survey that they had made a sacrifice to their own financial security to provide care for their parents on top of their children.
Long-distance care
Many in the sandwich generation say they feel torn between the needs of their kids and parents. Liam Davitt , a public-relations professional, and his wife, Lisa Fels Davitt , recently moved from their Washington, D.C., condo to suburban New Jersey so that their 7-year-old son could be closer to cousins and go to a good public school. (They had previously paid for private school.)
That meant moving away from his 84-year-old mother in an independent living community. The long distance has made helping her even with little things more complicated, such as troubleshooting glitches with her iPhone. He recently enlisted a nearby fraternity brother to help her assemble a new walker.
An avid runner, he says he finds himself taking care of himself—avoiding potentially ankle-twisting mud runs and keeping up with his doctors’ appointments, for example—out of fear he won’t be able to care for his younger and older family.
“If all of a sudden I’m less mobile, then I’m more of a burden on my own family” says Davitt. He is planning to move his mother closer by.
The Giordanos, in Georgia, have made adjustments, too. With their newborn keeping them busy, they installed cameras and door chimes to help monitor Kait’s parents.
Her parents enjoy pushing their grandson in the stroller around the house while supervised, she says. When Tamrin comes home from work, he gives his in-laws dinner and medications while holding the baby.
The couple isn’t sure when they’ll have another child, which would require paying for more help.
“We may have to wait,” Kait said. “We’re very much living in the moment.”
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
From citrus oils to warming spices, the classic G&T is being reimagined at home as a more thoughtful, seasonal ritual for modern entertaining.
From the Caribbean to Australia’s east coast, Oyster’s latest world rally promises a bluewater voyage designed for owners seeking ultimate sailing experiences.
Building a property portfolio can fast-track wealth creation, but only with the right strategy. Here is how to balance income, growth and risk from the start.
Property prices are rising, and buyer confidence is improving, making it an appealing time to start building a property portfolio.
But while the idea of owning multiple properties is attractive, many investors chase passive income without a clear strategy.
This can lead to over-leveraging and financial stress when interest rates rise or market conditions shift.
A smarter approach is to build a balanced portfolio that considers income, capital growth and risk.
Here are six key factors to weigh up before you begin.
Start with your current position
The foundation of any successful portfolio is understanding where you stand.
Before buying your first or next property, be clear on how much capital you have, your borrowing capacity and the level of risk you can comfortably manage.
Too many investors rush into high-yield assets without considering whether they suit their circumstances.
The result can be properties that look good on paper but prove difficult to hold.
Knowing your financial position helps determine whether to focus on cash-flow-positive properties, growth assets or a balanced mix of both.
Target assets that deliver real value
Not all properties are equal. When building a portfolio designed to generate income, quality matters more than headline yield.
In the commercial sector, smaller retail assets can offer a practical entry point.
They are often more affordable than large industrial properties while still delivering solid rental returns and value-add potential.
A tenancy leased below market rates, for example, can become a strategic purchase. When the lease is reviewed, bringing rent in line with market levels can lift both income and capital value.
Simple improvements such as updated fit-outs, better amenities or modest refurbishments can also increase tenant demand and justify higher rents.
Focusing on assets where you can influence performance helps create sustainable income and build equity for future investments.

Residential properties still play an important role
Residential property remains a core component of a balanced portfolio, offering stability to complement commercial holdings.
Long-term capital growth is largely driven by land value, so buying in areas with limited supply and strong demand can support future appreciation.
Dual-income strategies can also strengthen returns.
Adding a granny flat or secondary dwelling to a house can increase rental income without the need to purchase another property.
This approach can boost cash flow while keeping debt exposure manageable.
Use leverage carefully
Leverage can accelerate portfolio growth, but it also increases risk.
Before taking on additional debt, stress-test each purchase.
Consider whether you could comfortably hold the property if interest rates rose by several percentage points, and ensure you have buffers for vacancies or unexpected costs.
For business owners and SMSF investors, borrowing can provide access to assets that might otherwise be out of reach.
However, decisions should be based on what you can sustainably manage, not simply on how much a lender is willing to approve.
Diversify across and within asset classes
A resilient portfolio is built on diversification across locations, asset types and ownership structures.
Investing across different states can help manage land tax thresholds and take advantage of varying property cycles.
Within commercial property, combining retail, medical and selected office assets can reduce reliance on a single sector.
In residential markets, balancing growth-focused properties with income-producing assets can improve performance across changing conditions.
Ownership structures also matter. Whether property is held personally, in a trust or through an SMSF should align with long-term tax planning and wealth objectives.
Professional advice can help ensure the portfolio is positioned for sustainable growth.

Focus on creating income, not just finding it
One of property’s advantages is the ability to actively improve returns.
Renovations, secondary dwellings and reviewing under-market leases can increase both rental income and capital value.
These strategies allow investors to generate equity and strengthen cash flow without relying solely on market growth.
The goal is not to own the most properties, but to own the right ones.
A small number of well-selected, well-managed assets often outperform a scattered portfolio built without a clear strategy.
Financial independence is more likely when a portfolio supports itself and delivers a steady, reliable income stream.
Abdullah Nouh is the founder of Mecca Property Group, a boutique buyer’s agency in Melbourne helping Australians build wealth through strategic property investment.
Here’s how they are looking at artificial intelligence, interest rates and economic pressures.
As the season turns, Handpicked Wines’ latest Pinot Noir and Chardonnay releases reveal how subtle shifts in place shape what ends up in the glass.
























