Global Economy Slows, but Seems to Be Faring Better Than Feared
A weak start to 2023 is expected in many rich countries, but U.S. and European slumps could be relatively short
The global economy continued to deteriorate as 2022 draws to a close, but not as severely as economists previously feared, raising the possibility the world could avoid a deep slump next year.
Business surveys released Wednesday pointed to declines in output across the U.S. and Europe’s largest economies in November. But the figures and other economic readings pointed to a mixed outlook, with some parts of both economies continuing to show resilience despite high inflation and rising interest rates.
In China, the world’s second-largest economy, the outlook is highly uncertain as the country faces a surge in Covid-19 cases. Economists expect a rebound in growth next year as Beijing attempts to ease tough pandemic policies.
A tight U.S. labour market and still strong household balance sheets are supporting consumer spending, the economy’s main engine. A healthy consumer helped power retail sales in October and could keep the world’s largest economy growing at the end of this year. The U.S. outlook depends in part on how it weathers the Federal Reserve’s interest-rate increases aimed at cooling inflation that is running near a 40-year high.
Europe is experiencing less economic disruption from Russia’s decision to limit energy supplies than analysts earlier feared. Many households and businesses in the region are adapting by, for instance, cutting back on energy consumption, said Adam Posen, president of the Peterson Institute for International Economics. European governments also distributed larger-than-anticipated sums of fiscal support to households to help address rising energy and food costs, he added.
“We’re going to end up with more than 75% of the world’s economy actually doing pretty well,” Mr. Posen said. The U.S. and European Union “are likely to have relatively short, not terrible recessions and return to growth possibly by as early as the fourth quarter of 2023.”
Still, many developing countries are falling behind. David Malpass, the head of the World Bank, earlier warned developing countries face an additional economic risk: Policies adopted by advanced economies to address inflation and economic slowdown could leave insufficient capital for poorer nations.
S&P Global said its composite output index for the U.S., which includes services and manufacturing activity, fell to 46.3 in November from 48.2 a month earlier, among the quickest contractions since 2009. An index below 50 signals contracting economic activity, while above 50 signals growth.
“Companies are reporting increasing headwinds from the rising cost of living, tightening financial conditions—notably higher borrowing costs—and weakened demand across both home and export markets,” said Chris Williamson, chief business economist at S&P Global Market Intelligence.
U.S. businesses reported that inflationary pressures eased in November, however, with prices for materials and freight costs cooling.
The economic cost of higher energy prices was evident in surveys of purchasing managers at European businesses, which recorded another month of declining activity in November. S&P Global said its composite output index for the eurozone rose to 47.8 in November from 47.3 in October, but remained below the 50 mark that distinguishes a contraction from an expansion.
The global economic outlook remains highly uncertain. One big question in the U.S. is how quickly inflation comes down. The pace at which it does will help determine how high the Fed raises interest rates and how long it keeps them there. The central bank has raised rates at the fastest pace since the 1980s this year. Many economists expect higher borrowing costs to hurt spending with greater force in the coming months, threatening U.S. growth.
Fed staff early this month saw a U.S. recession next year “as almost as likely” as their baseline projection of weak growth, according to minutes of the policy makers’ Nov. 1-2 policy meeting released Wednesday. That represented a downgrade of the economic outlook due to the tightening in financial conditions that had occurred this fall.
Europe’s economies face the strongest economic headwinds in the months ahead. Russian natural-gas giant Gazprom PJSC on Tuesday threatened to further throttle exports to Europe via Ukraine from next week, putting in question one of the last remaining routes for Russian gas to reach Europe.
A reduction in Covid-19 restrictions in China is key to an expected rebound in growth there next year, but the recent surge in infections has raised questions about how quickly that can proceed.
“This fine-tuning of its Covid-19 policy is now being tested as cases continue to climb, especially in its manufacturing hub of Guangzhou,” said Magdalene Teo, head of fixed income research in Asia for Julius Baer. “China is realising that reopening this winter will not be easy.”
Many forecasters see global output rising by around 2% next year. That would be a sharp deceleration from this year and well below its 3.3% average in the decade leading up to the start of the Covid-19 pandemic, but still producing a small rise in output per person.
Even with a weak start to 2023 expected in many of the world’s richest countries, economists are wary of forecasting a global recession.
“Even though we do not formally forecast a global recession from a narrow technical viewpoint, it will feel like one for large parts of the global economy,” said Marcelo Carvalho, global head of economics at BNP Paribas.
In practical terms, this means the hardship many nations, businesses and consumers around the world have experienced this year—with strong regional variations—isn’t over.
The U.S. is expected to eke out meagre gains next year. The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development projects U.S. economic output will grow at an annual rate of 0.5% in 2023, down from an estimated 1.8% in 2022. Economists surveyed by the Wall Street Journal think U.S. gross domestic product will grow at an annual rate of 0.4% in 2023, and they see a rising chance for a recession in the next year.
Europe seems likely to avoid the worst outcomes from energy disruptions. A mild October and high levels of gas storage make it less likely that Europe’s factories will face energy rationing. As a result, economists at Barclays expect a 1.3% drop in gross domestic product there, less than their worst-case scenario of a 5% decline.
While conditions could start improving next year, economists warned the global economy remains in a precarious position.
“The risks that things could go wrong are increasing compared to where they were in the past few months,” said Alvaro Pereira, acting chief economist at the OECD.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
A sharp rebound in tourism in Europe’s sunbelt powers its economic rebound as core manufacturing centres struggle to recover
Europe’s economy has a north-south divide—and now it’s the poorer south that is powering the region’s return to growth.
Southern Europe, which for decades has had lower growth, productivity and wealth than the north, powered an upside-down recovery on the continent at the start of the year. Buoyant tourism revenue around the Mediterranean helped to offset sluggishness in Europe’s manufacturing heartlands.
The south’s transformation from laggard into growth engine reflects both a rapid rebound in visitor numbers from the collapse during the Covid-19 pandemic and a series of blows the continent’s large manufacturing sector has suffered, from surging energy prices to trade conflicts.
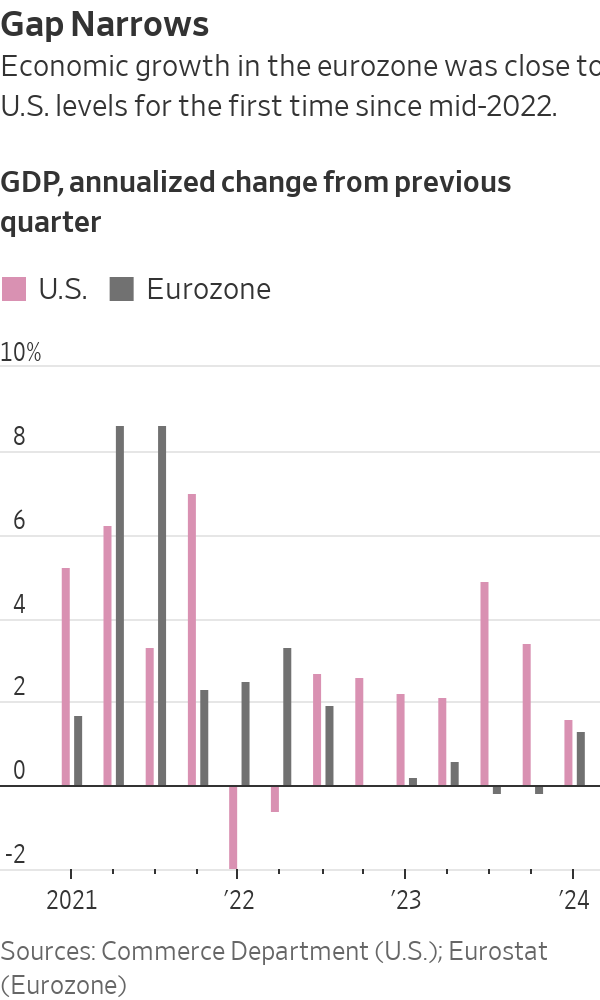
Now growth in the south is more than offsetting the north’s manufacturing malaise: As a whole, the eurozone economy grew at an annualised rate of 1.3% in the first quarter, ending nearly 18 months of economic stagnation in a sign that the currency area is recovering from the damage done by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
It was the eurozone’s strongest performance since the third quarter of 2022, and approached the U.S. economy’s 1.6% first-quarter growth rate, which was a slowdown from a racy pace of 3.4% at the end of last year.
In the 2010s, Germany helped to drag the continent out of its debt crisis thanks to strong exports of cars and capital goods. Between 2021 and 2023, Italy, Spain, Greece and Portugal contributed between a quarter and half of the European Union’s annual growth, according to a report last year by French credit insurer Coface —a trend now confirmed and amplified in the latest data.
In the first quarter, Spain was the fastest-growing of the big eurozone economies. It and Portugal recorded growth of 0.7% in the three months through the end of March from the previous quarter, while Italy’s economy grew by 0.3%. France and Germany both grew by 0.2%, the latter rebounding from a 0.5% quarter-on-quarter contraction at the end of last year.
This means Germany’s economy has grown by 0.3% in total since the end of 2019, compared with 8.7% for the U.S., 4.6% for Italy and 2.2% for France, according to UniCredit data.
In Spain, strong growth “seems to have been entirely due to strong tourism numbers,” said Jack Allen-Reynolds, an economist with Capital Economics. Tourism accounts for around 10% of the economies of Spain, Italy, Greece and Portugal.
The euro rose by about a quarter-cent against the dollar, to $1.0725, after the latest growth and inflation data were published.
The recovery comes as the European Central Bank signals it is preparing to reduce interest rates in June after a historic run of increases since mid-2022 that took it the key rate to 4%. Inflation in the eurozone remained at 2.4% in April, while underlying inflation cooled slightly, from 2.9% to 2.7%, according to separate data published Tuesday.
“The ECB hawks will point to the strong GDP number as [an] argument that ECB can take its rates lower gradually,” said Kamil Kovar, senior economist at Moody’s Analytics.
The eurozone economy has flatlined since late 2022 as Russia’s attack on its neighbor sent food and energy prices soaring in Europe and sapped business and household confidence. Gross domestic product fell in both the third and fourth quarters of last year, meeting a definition of recession widely used in Europe, but not in the U.S.
Southern Europe is one of only a handful of regions where international tourist arrivals returned to pre pandemic levels last year, according to United Nations data. Tourism revenue across the EU was one-quarter higher in the three months through the end of last June than in the same period in 2019, according to Coface data.
The recovery in international tourism was “notably driven by the arrival of many Americans who…were able to take advantage of favorable exchange rates,” Coface analysts wrote. “On the other hand, the end of the zero-Covid policy in China has initiated a gradual return of Chinese tourists, although remaining below 2019 levels.”
In Portugal, the number of foreign tourists hit a record of more than 18 million last year, up 11% compared with the prepandemic year of 2019, official data showed in January. American tourists in particular have returned to Europe in force.
Tourist numbers in Asia Pacific and the Americas continued to lag 2019 levels by 35% and 10% last year, respectively, the data show.
It is unclear how much further the tourism boom can run, but economists expect the region’s economic recovery to strengthen later this year as cooling inflation boosts household spending power and lower energy costs aid factory output.
Recent surveys point to an improved outlook for growth. Consumer confidence has risen to its highest level in two years, and a leading business-sentiment index has shown steady improvement from the start of 2024.
“We think that the combination of a robust labor market, comparatively strong wage hikes and lower inflation compared with last year will finally lead to a moderate recovery in consumer spending in the next few quarters,” said Andreas Rees , an economist with UniCredit in Frankfurt.
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Consumers are going to gravitate toward applications powered by the buzzy new technology, analyst Michael Wolf predicts























