Why Is Everyone So Unhappy at Work Right Now?
U.S. employees are more dissatisfied than they were in the thick of the pandemic
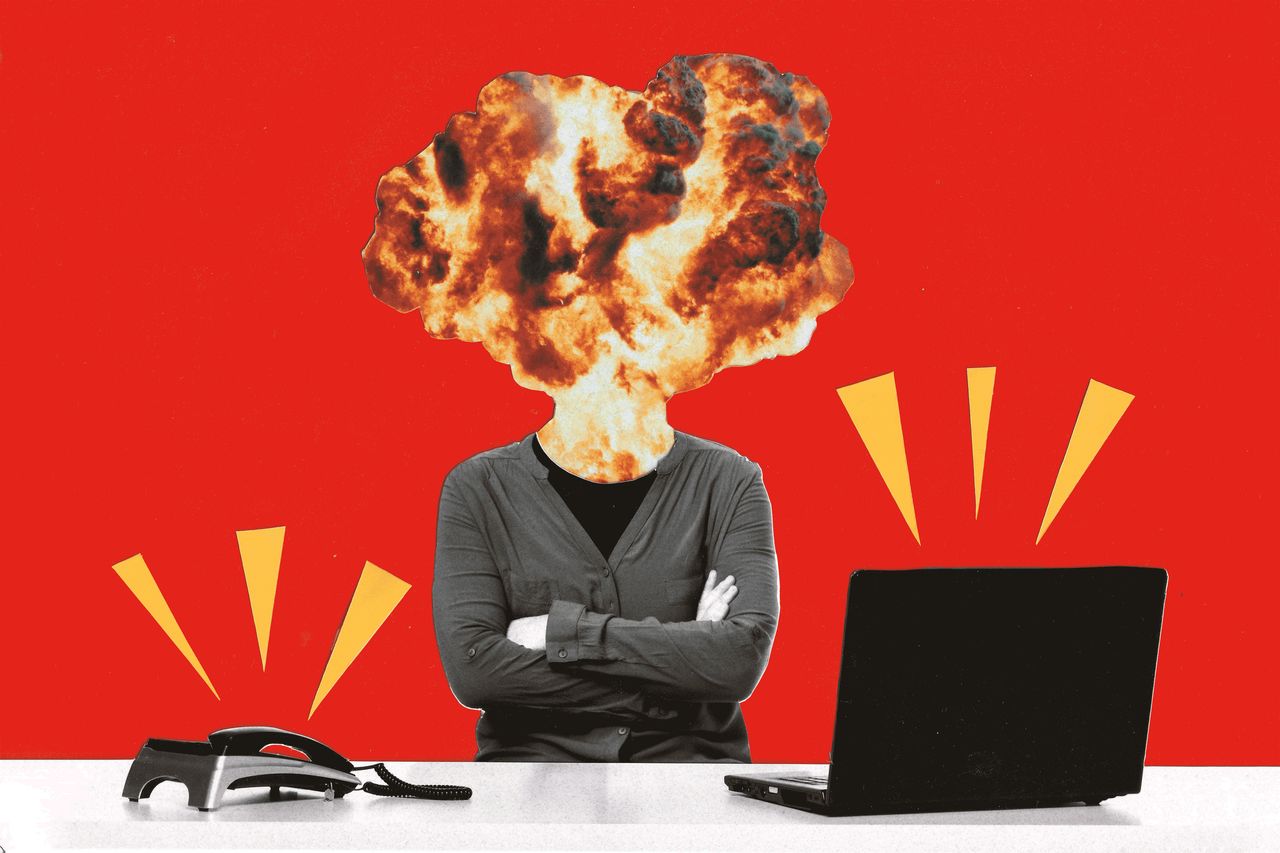
Americans, by many measures, are unhappier at work than they have been in years.
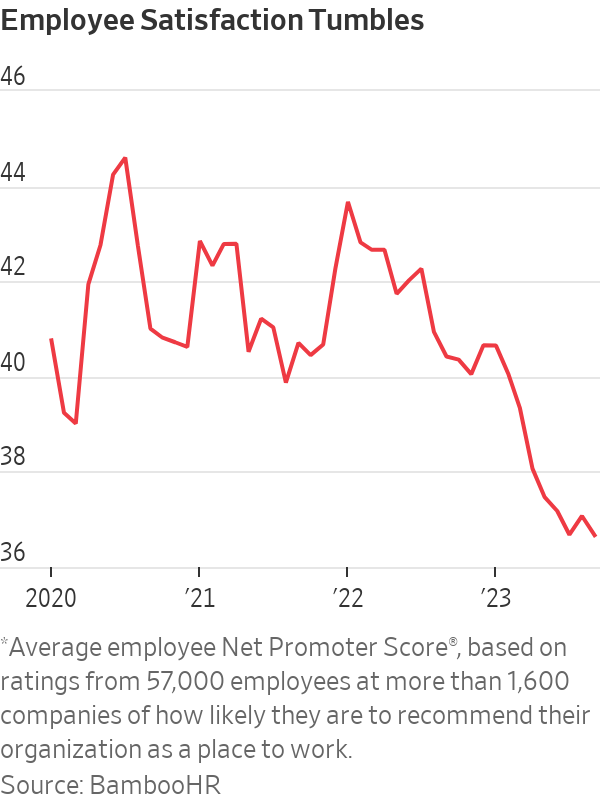
Despite wage increases, more paid time off and greater control over where they work, the number of U.S. workers who say they are angry, stressed and disengaged is climbing, according to Gallup’s 2023 workplace report. Meanwhile, a BambooHR analysis of data from more than 57,000 workers shows job-satisfaction scores have fallen to their lowest point since early 2020, after a 10% drop this year alone.
In interviews with workers around the country, it is clear the unhappiness is part of a rethinking of work life that began in 2020. The sources of workers’ discontent range from inflation, which is erasing much of recent pay gains, to the still-unsettled nature of the workday. People chafe against being micromanaged back to offices, yet they also find isolating aspects of hybrid and remote work. A cooling job market—especially in white-collar roles—is leaving many professionals feeling stuck.
Companies have largely moved on from pandemic operating mode, cutting costs and renewing a focus on productivity. The disconnect with workers has managers frustrated, and no quick fix seems to be at hand. Those in charge said they have given staff more money, flexibility and support, only to come up short.
The experiences of workers like Lindsey Leesmann suggest how expectations have shifted from just a few years ago. Leesmann, 38 years old, said she soured on a philanthropy job after having to return to the office two days a week earlier this year.
Prepandemic, she would have been happy working three days a week at home. “It would have been a dream come true.” Still, her team’s in-office requirements seemed like going backward, and made her feel that her professionalism and work quality were in doubt. Instead of collaborating more, she and others rarely left their desks, except for meetings or lunch, she said. Negative feelings followed her home on her hourlong commute, leaving her short-tempered with her kids.
“You try to keep work and home separate, but that sort of stuff is just impacting your mental health so much,” said Leesmann, who recently moved to a new job that requires five in-office days a month.
No more honeymoon
The discontent has business leaders struggling for answers, said Stephan Scholl, chief executive of Alight Solutions, a technology company focused on benefits and payroll administration. Many of the Fortune 100 companies on Alight’s client list boosted spending on employee benefits such as mental health, child care and well-being bonuses by 20% over the pandemic years.
“All that extra spend has not translated into happier employees,” Scholl said. In an Alight survey of 2,000 U.S. employees this year, 34% said they often dread starting their workday—an 11-percentage-point rise since 2020. Corporate clients have told him mental-health claims and costs from employee turnover are rising.
One factor is the share of workers who are relatively new to their roles after record levels of job-switching, said Benjamin Granger, chief workplace psychologist at software company Qualtrics. Many employers have focused more on hiring than situating new employees well, leaving many newbies feeling adrift. In other cases, workers discovered shiny-seeming new jobs weren’t a great fit.
The upshot is that the newest workers are among the least satisfied, Qualtrics data show—a reversal of the higher levels of enthusiasm that fresh hires typically voice. In its study of nearly 37,000 workers published last month, people less than six months into a job reported lower levels of engagement, feelings of inclusion and intent to stay than longer-tenured workers. They also scored lower on those metrics than new workers in 2022, suggesting the pay raises that lured many people to new jobs might not be as satisfying as they were a year or two ago.
“What happened to that honeymoon phase?” Granger said.
John Shurr, a 66-year-old former manufacturing engineer, took a job as an inventory manager at a heavy-equipment retailer in the spring in Missoula, Mont., after being laid off during the pandemic.
“It was a nice job title on a pretty rotten job,” said Shurr, who learned soon after starting that his duties would also include sales to walk-in customers.
When Shurr broached the subject, his boss asked him to give it a chance and said he was really needed on the showroom floor. Shurr, who describes himself as more of a computer guy, quit about a month later.
“I feel kind of trapped at the moment,” said Shurr, who has since taken a part-time job as a parts manager as he tries to find full-time work.
Bridging the distance
Long-distance relationships between bosses and staff might also be an issue. Nearly a third of workers at large firms don’t work in the same metro area as their managers, up from about 23% in February 2020, according to data from payroll provider ADP.
Distance has weakened ties among co-workers and heightened conflict, said Moshe Cohen, a mediator and negotiation coach who teaches conflict resolution at Boston University’s Questrom School of Business. He has noticed more employees calling co-workers or bosses toxic or impossible, signs that trust is thin.
Cohen’s corporate clients said their employees are increasingly transactional with one another. Some are coaching workers in the finer points of dialogue, such as saying hello first before jumping into the substance of a conversation.
“The idea of slowing down, taking the time, being genuine, trying to actually establish some sort of connection with the other person—that’s really missing,” Cohen said.
One Los Angeles-based consultant in his 20s, who asked to remain anonymous because he is seeking another job, said that when he started his job at a large company last year, his largely remote colleagues were focused on their own work, unwilling to show a new hire the ropes or invite him for coffee. Many leave cameras off for video calls and few people show up at the office, making it hard to build relationships.
“There’s zero humanity,” he said, noting that he is seeking another job with a strong office culture.
The share of U.S. companies mandating office attendance five days a week has fallen this year—to 38% in October from 49% at the start of the year—according to Scoop Technologies, a software firm that developed an index to monitor workplace policies of nearly 4,500 companies.
Some companies have reversed flexible remote-work policies—in large part, they said, to boost employee engagement and productivity—only to face worker backlash.
Not all the data point downward. A Conference Board survey in November 2022 of U.S. adults showed workers were more satisfied with their jobs than they had been in years. Key contingents among the happiest employees: people who voluntarily switched roles during the pandemic and those working a mix of in-person and remote days. But that poll was taken before a spate of layoffs at high-profile companies and big declines in the number of knowledge-worker and professional jobs advertised.
At Farmers Group, workers posted thousands of mostly negative comments on the insurer’s internal social-media platform after its new CEO nixed the company’s previous policy allowing most workers to be remote.
Employees like Kandy Mimande said they felt betrayed. “We couldn’t get the ‘why,’” said the 43-year-old, who had sold her car and spent thousands of dollars to redo her home office under the remote-work policy. She shelled out $10,000 for a used car for the commute. A company spokesperson said that not all employees will support every business decision and that Farmers hasn’t seen a significant impact on staff retention.
During a brief leave, Mimande realised she no longer felt a sense of purpose from her product-management job. She resigned last month after she and her wife decided they could live on one salary.
She now helps promote a band and pet-sits. “It’s so much easier for me to report to myself,” she said.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
Continued stagflation and cost of living pressures are causing couples to think twice about starting a family, new data has revealed, with long term impacts expected
Australia is in the midst of a ‘baby recession’ with preliminary estimates showing the number of births in 2023 fell by more than four percent to the lowest level since 2006, according to KPMG. The consultancy firm says this reflects the impact of cost-of-living pressures on the feasibility of younger Australians starting a family.
KPMG estimates that 289,100 babies were born in 2023. This compares to 300,684 babies in 2022 and 309,996 in 2021, according to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS). KPMG urban economist Terry Rawnsley said weak economic growth often leads to a reduced number of births. In 2023, ABS data shows gross domestic product (GDP) fell to 1.5 percent. Despite the population growing by 2.5 percent in 2023, GDP on a per capita basis went into negative territory, down one percent over the 12 months.
“Birth rates provide insight into long-term population growth as well as the current confidence of Australian families,” said Mr Rawnsley. “We haven’t seen such a sharp drop in births in Australia since the period of economic stagflation in the 1970s, which coincided with the initial widespread adoption of the contraceptive pill.”
Mr Rawnsley said many Australian couples delayed starting a family while the pandemic played out in 2020. The number of births fell from 305,832 in 2019 to 294,369 in 2020. Then in 2021, strong employment and vast amounts of stimulus money, along with high household savings due to lockdowns, gave couples better financial means to have a baby. This led to a rebound in births.
However, the re-opening of the global economy in 2022 led to soaring inflation. By the start of 2023, the Australian consumer price index (CPI) had risen to its highest level since 1990 at 7.8 percent per annum. By that stage, the Reserve Bank had already commenced an aggressive rate-hiking strategy to fight inflation and had raised the cash rate every month between May and December 2022.
Five more rate hikes during 2023 put further pressure on couples with mortgages and put the brakes on family formation. “This combination of the pandemic and rapid economic changes explains the spike and subsequent sharp decline in birth rates we have observed over the past four years,” Mr Rawnsley said.
The impact of high costs of living on couples’ decision to have a baby is highlighted in births data for the capital cities. KPMG estimates there were 60,860 births in Sydney in 2023, down 8.6 percent from 2019. There were 56,270 births in Melbourne, down 7.3 percent. In Perth, there were 25,020 births, down 6 percent, while in Brisbane there were 30,250 births, down 4.3 percent. Canberra was the only capital city where there was no fall in the number of births in 2023 compared to 2019.
“CPI growth in Canberra has been slightly subdued compared to that in other major cities, and the economic outlook has remained strong,” Mr Rawnsley said. “This means families have not been hurting as much as those in other capital cities, and in turn, we’ve seen a stabilisation of births in the ACT.”
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.






















