Energy, Climate and AI Bets Are Powering Europe’s Venture Sector
Russia’s invasion of Ukraine has spurred funding of tech that could boost Europe’s quest for energy security
Venture capitalists’ appetite for energy and artificial-intelligence investments is putting Europe’s venture sector on a hot streak.
European governments’ focus on energy security amid heightened geopolitical tensions has helped spur a capital rush, investors and analysts say. That coupled with the emergence of Europe-based AI startups, which can be less expensive than their U.S. counterparts, is also drawing investors.
European startups raised $15.5 billion in the second quarter, up 14% from the first quarter and up 12% from the same quarter of last year, according to Europe-based analytics firm Dealroom.co. Meanwhile, the amount invested into North American startups rose 9.6% in the second quarter from the prior quarter while Asia deal value rose 6.4% over the same period.
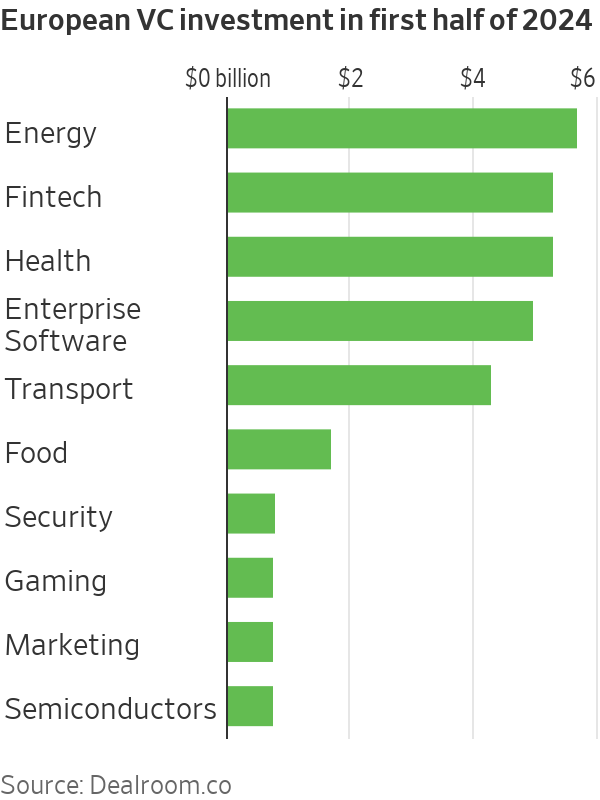
Energy was the most funded sector in Europe in the first half of the year, netting $5.7 billion, while funding raised by AI startups accounted for a record 18% of venture funding in Europe, up from about 11% in 2021, Dealroom.co said. Before last year, energy startups typically raised less capital than fintech, health and enterprise software startups.
Russia’s invasion of Ukraine spurred European governments—which were historically dependent on Russian fossil fuels—to develop greater energy security. Support has reached startups in the form of grants and other government-backed investment opportunities.
“It has been a major shift,” said Orla Browne , head of insights at Dealroom.co. “The exposure of energy-security issues with the invasion of Ukraine has filtered down to startups.”
Large AI deals have also drawn capital to Europe. In May, Wayve, a U.K.-based developer of autonomous driving software, raised $1 billion from investors including SoftBank Group , chip maker Nvidia and Microsoft . In June, French startup Mistral AI raised $646 million from investors including the venture arm of software giant Salesforce , General Catalyst and Lightspeed Venture Partners.
In Europe, investors say they can scoop up shares of startups for less money compared with the prices that their counterparts in the U.S. command. Meanwhile, Europe’s technical universities are supplying promising entrepreneurs, particularly in the AI field.
“We have hired a world-class team at salaries that cost 30% or less than you would get for a similar team in [Silicon Valley] with the caliber being as good,” said Dominic Vergine , chief executive of Monumo in Cambridge, England, which uses AI to make electric motors more efficient.
Europe’s climate regulations have also helped attract funding for energy startups, for example the European Commission’s Innovation Fund.
Danijel Višević, co-founder of Berlin-based World Fund, said funding from countries like Germany and France as well as from the European Union helped push more capital into climate startups. “Europe has started to reap the rewards of the fruits it sowed with climate tech R&D,” said Višević.
He added that given the long-term effects of climate change, funding in the sector is likely to be stable, both from venture-capital firms and governments, for years to come.
Even so, Europe’s venture sector faces some headwinds. In the second quarter, the continent saw $2.2 billion in exits, a third fewer than in the same quarter a year ago and 93% under the second quarter of 2021, a banner year for exits worldwide, according to a report by professional-services firm KPMG. Exits include initial public offerings and mergers and acquisitions and are the primary way venture investors cash out of their startup investments.
High interest rates, which typically encourage investors to divert capital away from venture to fixed-income strategies, have also hurt the industry. European startups’ second-quarter haul is far below the record $34.6 billion they netted during the same quarter of 2021.
Investors are eager for a turnaround. Last year, Planet First Partners, which has offices in London and Luxembourg, raised a €450 million fund, equivalent to $485 million, in part on the thesis that Europe’s favourable climate regulations are a financial tailwind for energy startups.
In March, the firm invested in Sunfire, a German startup developing hydrogen energy technology aimed at reducing reliance on fossil-based energy from oil, gas and coal. The investment came as part of a €215 million Series E equity funding round and included an additional term loan of up to €100 million from the European Investment Bank.
Sergio Carvalho , a partner and head of sustainability at Planet First Partners, said the firm has invested in Sunfire in part for its potential to help Europe become more energy independent. PFP’s first investment in Sunfire was before the invasion of Ukraine. “Europe has been pushing decarbonisation systematically,” Carvalho said.
Last year, Sunfire received €169 million from a European Union initiative that funds projects that address EU-wide challenges.
In July, Index Ventures, which was founded in Europe and has offices in London, San Francisco and New York, raised $2.3 billion in new funds—an $800 million venture fund and a $1.5 billion growth fund. Hannah Seal , an Index partner in London who focuses on enterprise AI deals, among other sectors, said she expects roughly half of the venture fund to be used to invest in startups that are based in Europe.
“The first half of this year was one of the busiest we’ve ever had,” Seal said about AI dealmaking in Europe. “We’re seeing a general stabilisation in the global economy which is obviously impacting sentiment.”
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
A divide has opened in the tech job market between those with artificial-intelligence skills and everyone else.
A 30-metre masterpiece unveiled in Monaco brings Lamborghini’s supercar drama to the high seas, powered by 7,600 horsepower and unmistakable Italian design.
A divide has opened in the tech job market between those with artificial-intelligence skills and everyone else.
There has rarely, if ever, been so much tech talent available in the job market. Yet many tech companies say good help is hard to find.
What gives?
U.S. colleges more than doubled the number of computer-science degrees awarded from 2013 to 2022, according to federal data. Then came round after round of layoffs at Google, Meta, Amazon, and others.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts businesses will employ 6% fewer computer programmers in 2034 than they did last year.
All of this should, in theory, mean there is an ample supply of eager, capable engineers ready for hire.
But in their feverish pursuit of artificial-intelligence supremacy, employers say there aren’t enough people with the most in-demand skills. The few perceived as AI savants can command multimillion-dollar pay packages. On a second tier of AI savvy, workers can rake in close to $1 million a year .
Landing a job is tough for most everyone else.
Frustrated job seekers contend businesses could expand the AI talent pipeline with a little imagination. The argument is companies should accept that relatively few people have AI-specific experience because the technology is so new. They ought to focus on identifying candidates with transferable skills and let those people learn on the job.
Often, though, companies seem to hold out for dream candidates with deep backgrounds in machine learning. Many AI-related roles go unfilled for weeks or months—or get taken off job boards only to be reposted soon after.
Playing a different game
It is difficult to define what makes an AI all-star, but I’m sorry to report that it’s probably not whatever you’re doing.
Maybe you’re learning how to work more efficiently with the aid of ChatGPT and its robotic brethren. Perhaps you’re taking one of those innumerable AI certificate courses.
You might as well be playing pickup basketball at your local YMCA in hopes of being signed by the Los Angeles Lakers. The AI minds that companies truly covet are almost as rare as professional athletes.
“We’re talking about hundreds of people in the world, at the most,” says Cristóbal Valenzuela, chief executive of Runway, which makes AI image and video tools.
He describes it like this: Picture an AI model as a machine with 1,000 dials. The goal is to train the machine to detect patterns and predict outcomes. To do this, you have to feed it reams of data and know which dials to adjust—and by how much.
The universe of people with the right touch is confined to those with uncanny intuition, genius-level smarts or the foresight (possibly luck) to go into AI many years ago, before it was all the rage.
As a venture-backed startup with about 120 employees, Runway doesn’t necessarily vie with Silicon Valley giants for the AI job market’s version of LeBron James. But when I spoke with Valenzuela recently, his company was advertising base salaries of up to $440,000 for an engineering manager and $490,000 for a director of machine learning.
A job listing like one of these might attract 2,000 applicants in a week, Valenzuela says, and there is a decent chance he won’t pick any of them. A lot of people who claim to be AI literate merely produce “workslop”—generic, low-quality material. He spends a lot of time reading academic journals and browsing GitHub portfolios, and recruiting people whose work impresses him.
In addition to an uncommon skill set, companies trying to win in the hypercompetitive AI arena are scouting for commitment bordering on fanaticism .
Daniel Park is seeking three new members for his nine-person startup. He says he will wait a year or longer if that’s what it takes to fill roles with advertised base salaries of up to $500,000.
He’s looking for “prodigies” willing to work seven days a week. Much of the team lives together in a six-bedroom house in San Francisco.
If this sounds like a lonely existence, Park’s team members may be able to solve their own problem. His company, Pickle, aims to develop personalised AI companions akin to Tony Stark’s Jarvis in “Iron Man.”
Overlooked
James Strawn wasn’t an AI early adopter, and the father of two teenagers doesn’t want to sacrifice his personal life for a job. He is beginning to wonder whether there is still a place for people like him in the tech sector.
He was laid off over the summer after 25 years at Adobe , where he was a senior software quality-assurance engineer. Strawn, 55, started as a contractor and recalls his hiring as a leap of faith by the company.
He had been an artist and graphic designer. The managers who interviewed him figured he could use that background to help make Illustrator and other Adobe software more user-friendly.
Looking for work now, he doesn’t see the same willingness by companies to take a chance on someone whose résumé isn’t a perfect match to the job description. He’s had one interview since his layoff.
“I always thought my years of experience at a high-profile company would at least be enough to get me interviews where I could explain how I could contribute,” says Strawn, who is taking foundational AI courses. “It’s just not like that.”
The trouble for people starting out in AI—whether recent grads or job switchers like Strawn—is that companies see them as a dime a dozen.
“There’s this AI arms race, and the fact of the matter is entry-level people aren’t going to help you win it,” says Matt Massucci, CEO of the tech recruiting firm Hirewell. “There’s this concept of the 10x engineer—the one engineer who can do the work of 10. That’s what companies are really leaning into and paying for.”
He adds that companies can automate some low-level engineering tasks, which frees up more money to throw at high-end talent.
It’s a dynamic that creates a few handsomely paid haves and a lot more have-nots.
A cluster of century-old warehouses beneath the Harbour Bridge has been transformed into a modern workplace hub, now home to more than 100 businesses.
BMW has unveiled the Neue Klasse in Munich, marking its biggest investment to date and a new era of electrification, digitalisation and sustainable design.























