A More Profitable Tesla Is Still a Pricey Ride
Surprise lift in automotive margins reverses damage from Robotaxi fallout, but valuation is now far above even AI stars
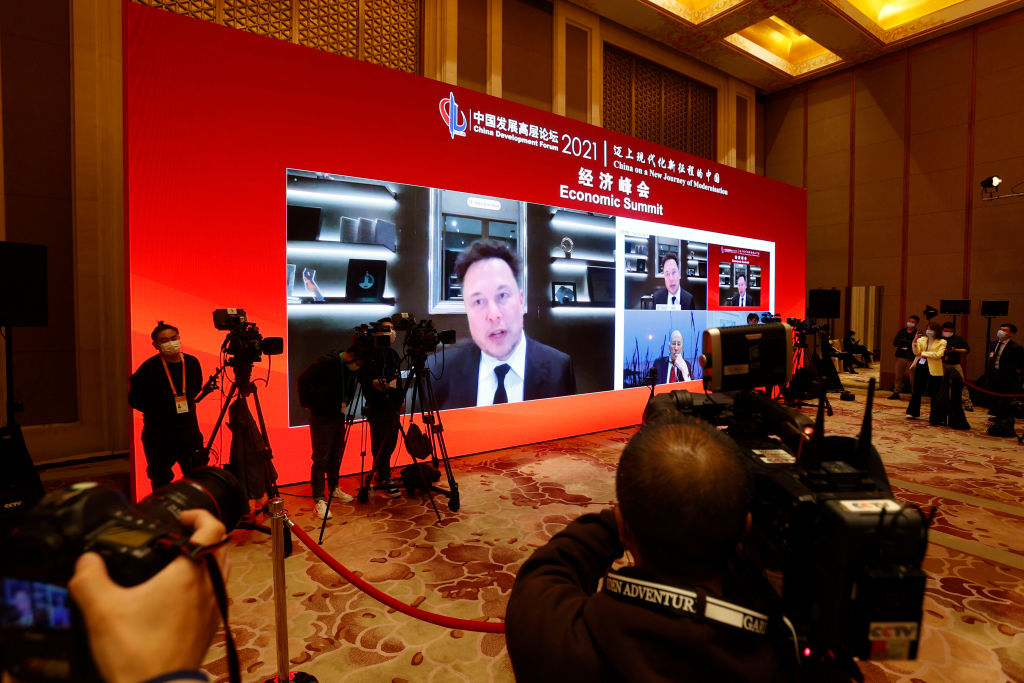
Elon Musk thinks of Tesla as an AI company. He’d be seriously bummed if it were valued like one.
Tesla’s third-quarter results gave the EV maker’s stock price a strong boost on Thursday, recovering the ground lost following the company’s disappointing Robotaxi event earlier this month. The reaction wasn’t entirely unwarranted: Tesla managed to surprise Wall Street by reversing the steady decline its automotive gross margins have suffered over the past two years. Strong growth in sales and gross profits in the company’s energy generation and storage segment also helped. Tesla’s total operating profit came in at $2.7 billion for the quarter—37% above Wall Street’s consensus forecast, according to FactSet.
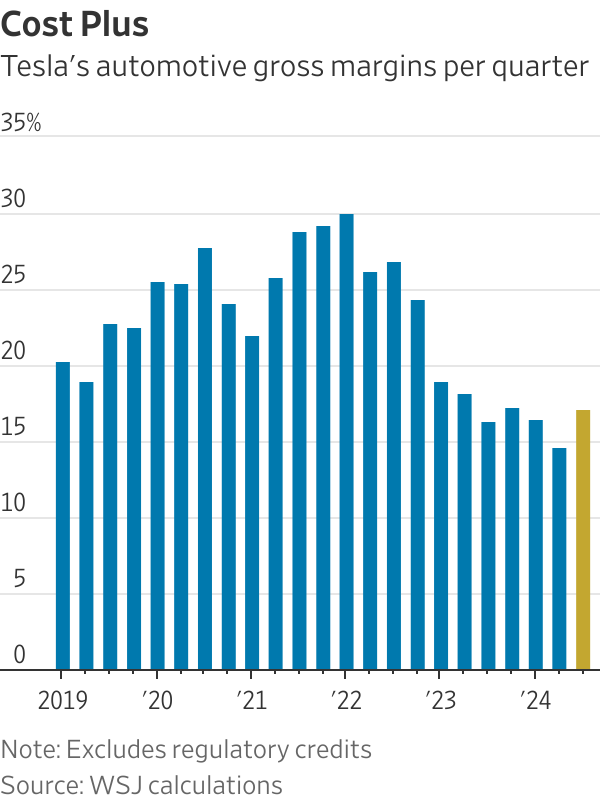
Still, Tesla’s overall growth is far below normal, or at least what has long been the company’s version of normal. Total automotive revenue rising 2% year over year in the third quarter comes after two consecutive quarters of declines. That is also a fraction of the 45% growth Tesla’s core business averaged on a quarterly basis from 2020 through 2023. The world’s largest EV maker can’t escape the gravity of a global auto-sales slowdown .
And even the profit boost might not be built to last. “Sustaining these margins in Q4, however, will be challenging, given the current economic environment,” said Tesla Chief Financial Officer Vaibhav Taneja on the company’s conference call on Wednesday.
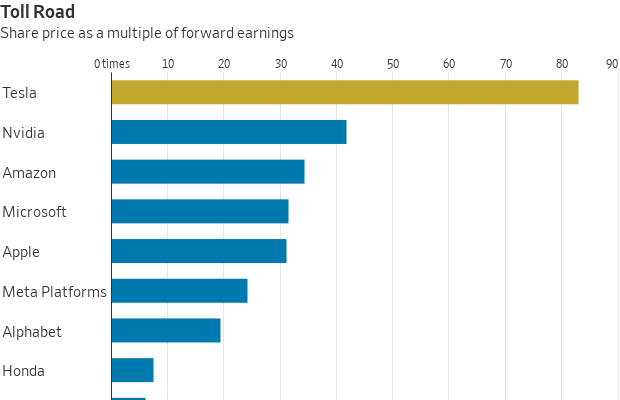
Analysts boosted their profit targets anyway. The consensus projection for Tesla’s per-share earnings over the next four quarters rose more than 5% following the company’s report. But even that doesn’t cover Tesla’s chunky valuation; Thursday’s jump of nearly 22% puts the stock price at around 83 times forward earnings. That is more than twice the multiple that megacap tech giants such as Apple , Microsoft and Amazon .com fetch. If Tesla were valued on par with Nvidia , whose chips Tesla is snapping up to power its ambitions in AI, autonomous driving and robotics, the stock price—and a good chunk of Musk’s net worth—would be be half its current level.
Hence, Tesla needs much, much more to go right than just a recovery in the global EV market. But its biggest ambitions are distant and by no means slam dunks. Musk reiterated his plan to have Robotaxis begin production in 2026 . The ultimate fate of that business, though, lies in the company’s ability to clear the necessary regulatory hurdles for self-driving cars in states like California—not to mention catching up to rivals such as Waymo that are already on the road.
“While compute capacity growth is a positive indicator that will support accelerated learning cycles, we remain cautious on Tesla’s system performance vs. peers given lack of driver-out regulatory approvals and limited detail on miles between engagement,” wrote Colin Rusch of Oppenheimer on Thursday.
The humanoid robot called Optimus is even more of a long shot—not that Musk qualifies it as such. “So I think it has a good chance of being the most valuable product ever made,” Musk said on Wednesday’s call.
Even some of Tesla’s near-term targets look ambitious. After scrapping its Model 2 project earlier this year, the company reiterated a plan to launch a “more affordable” car in the first half of next year, though details on that vehicle remain sparse. And Musk projected vehicle-sales growth of 20% to 30% next year—a sharp jump from the 13% pace analysts were projecting, according to FactSet.
“We struggle to handicap the unit growth, given the uncertain timing of volume production, a limited sense of how different the offerings will be relative to the current Model 3 and Y, and true delivered price,” wrote Toni Sacconaghi of Bernstein.
Tesla has to get an awful lot of rubber to meet the road.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
A long-standing cultural cruise and a new expedition-style offering will soon operate side by side in French Polynesia.
The pandemic-fuelled love affair with casual footwear is fading, with Bank of America warning the downturn shows no sign of easing.
The pandemic-fuelled love affair with casual footwear is fading, with Bank of America warning the downturn shows no sign of easing.
The boom in casual footware ushered in by the pandemic has ended, a potential problem for companies such as Adidas that benefited from the shift to less formal clothing, Bank of America says.
The casual footwear business has been on the ropes since mid-2023 as people began returning to office.
Analyst Thierry Cota wrote that while most downcycles have lasted one to two years over the past two decades or so, the current one is different.
It “shows no sign of abating” and there is “no turning point in sight,” he said.
Adidas and Nike alone account for almost 60% of revenue in the casual footwear industry, Cota estimated, so the sector’s slower growth could be especially painful for them as opposed to brands that have a stronger performance-shoe segment. Adidas may just have it worse than Nike.
Cota downgraded Adidas stock to Underperform from Buy on Tuesday and slashed his target for the stock price to €160 (about $187) from €213. He doesn’t have a rating for Nike stock.
Shares of Adidas listed on the German stock exchange fell 4.5% Tuesday to €162.25. Nike stock was down 1.2%.
Adidas didn’t immediately respond to a request for comment.
Cota sees trouble for Adidas both in the short and long term.
Adidas’ lifestyle segment, which includes the Gazelles and Sambas brands, has been one of the company’s fastest-growing business, but there are signs growth is waning.
Lifestyle sales increased at a 10% annual pace in Adidas’ third quarter, down from 13% in the second quarter.
The analyst now predicts Adidas’ organic sales will grow by a 5% annual rate starting in 2027, down from his prior forecast of 7.5%.
The slower revenue growth will likewise weigh on profitability, Cota said, predicting that margins on earnings before interest and taxes will decline back toward the company’s long-term average after several quarters of outperforming. That could result in a cut to earnings per share.
Adidas stock had a rough 2025. Shares shed 33% in the past 12 months, weighed down by investor concerns over how tariffs, slowing demand, and increased competition would affect revenue growth.
Nike stock fell 9% throughout the period, reflecting both the company’s struggles with demand and optimism over a turnaround plan CEO Elliott Hill rolled out in late 2024.
Investors’ confidence has faded following Nike’s December earnings report, which suggested that a sustained recovery is still several quarters away. Just how many remains anyone’s guess.
But if Adidas’ challenges continue, as Cota believes they will, it could open up some space for Nike to claw back any market share it lost to its rival.
Investors should keep in mind, however, that the field has grown increasingly crowded in the past five years. Upstarts such as On Holding and Hoka also present a formidable challenge to the sector’s legacy brands.
Shares of On and Deckers Outdoor , Hoka’s parent company, fell 11% and 48%, respectively, in 2025, but analysts are upbeat about both companies’ fundamentals as the new year begins.
The battle of the sneakers is just getting started.
From the shacks of yesterday to the sculptural sanctuaries of today, Australia’s coastal architecture has matured into a global benchmark for design.
ABC Bullion has launched a pioneering investment product that allows Australians to draw regular cashflow from their precious metal holdings.























