Is China’s Economic Predicament as Bad as Japan’s? It Could Be Worse
From demographics to decoupling, China faces challenges Japan didn’t after its 1980s bubble
HONG KONG—Starting in the 1990s Japan became synonymous with economic stagnation, as a boom gave way to lethargic growth, declining population and deflation.
Many economists say China today looks similar. The reality: In many ways its problems are more intractable than Japan’s. China’s public debt levels are higher by some measures than Japan’s were and its demographics are worse. The geopolitical tensions that China is dealing with go beyond the trade frictions Japan once faced with the U.S.
Another headwind: China’s government, which has been cracking down on the private sector in recent years, seems ideologically less inclined than Tokyo was then to support growth.
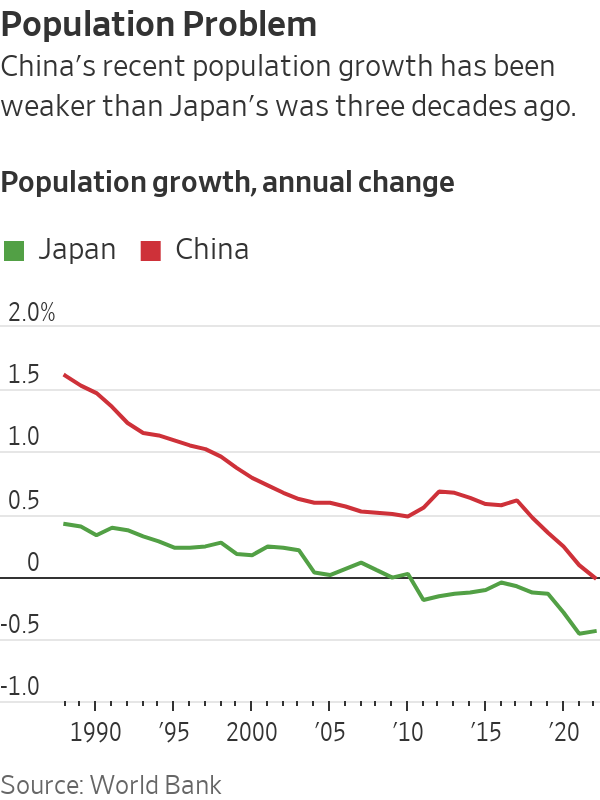
None of this means China is sure to repeat the years of economic stagnation that Japan is only now showing signs of exiting. It has some advantages that Japan didn’t. Its economic growth in coming years is likely to be well above Japan’s in the 1990s.
Even so, economists say the parallels are a warning for Communist Party leaders in Beijing: If they don’t act more forcefully, the country could get stuck in a protracted period of economic sluggishness similar to Japan’s. Despite piecemeal steps in recent weeks, including modest interest-rate cuts, Beijing has held back on major stimulus to revive growth.
“China’s policy responses so far could put it on track for ‘Japanification,’” said Johanna Chua, chief Asia economist at Citigroup. She believes China’s overall growth prospects could be slowing more sharply than Japan’s.
China today and Japan 30 years ago share many similarities, including high debt levels, an aging population and signs of deflation.
During a long postwar economic expansion, Japan became an export powerhouse that American politicians and corporate executives worried would be unstoppable. Then in the early 1990s, real estate and stock market bubbles burst and the economy hit the skids.
Policy makers cut interest rates to virtually zero, but growth failed to rebound as consumers and companies focused on repaying debt to repair their balance sheets instead of borrowing to finance new spending and investment.
Richard Koo, an economist at the research arm of Japanese investment bank Nomura Securities, famously coined the term “balance sheet recession” to describe the phenomenon.
China, too, has seen a property bubble pop after years of extraordinary economic growth. Chinese consumers are now paying off mortgages early, despite government efforts to get them to borrow and spend more.
Private firms are also reluctant to invest despite lower interest rates, stirring anxiety among economists that monetary easing might be losing its potency in China.
By some measures, China’s asset bubbles aren’t as big. Morgan Stanley estimates that China’s ratio of property value to gross domestic product peaked at 260% in 2020, up from 170% of GDP in 2014; home prices have only fallen slightly since the peak, according to official data. China’s equity markets hit a recent peak of 80% of GDP in 2021 and now sit at 67% of GDP.
In Japan, land values as a percentage of GDP reached 560% of GDP in 1990 before falling back to 394% by 1994, Morgan Stanley estimates. The Tokyo Stock Exchange’s market capitalisation rose to 142% of GDP in 1989 from 34% in 1982.
Also in China’s favour, its urbanisation rate is lower, standing at 65% in 2022, versus Japan’s, which was at 77% in 1988. That could give China more potential to raise productivity and growth as people move to cities and take on nonagricultural jobs.
China’s tighter control over its capital markets means the risk of a sharp appreciation of its currency, which would harm exports, is low. Japan had to deal with a sharp increase in its currency several times in recent decades, which at times added to its economic struggles.
“We believe worries on China being trapped in a balance sheet recession are overdone,” economists from Bank of America recently wrote.
Yet in other ways, China’s problems will be harder to tackle than Japan’s.
Its population is ageing faster; it began to decline in 2022. In Japan, that didn’t happen until 2008, nearly two decades after its bubble burst.
Worse, China appears to be entering a period of weaker long-term growth rates before reaching rich-world status, i.e. it is getting old before it gets rich: China’s per capita income was $12,850 in 2022, much lower than Japan in 1991 at $29,080, World Bank data shows.
Then there is the problem of debt. Once off-balance-sheet borrowing by local governments is factored in, total public debt in China reached 95% of GDP in 2022, compared with 62% of GDP in Japan in 1991, according to J.P. Morgan. That limits authorities’ ability to pursue fiscal stimulus.
External pressures also appear to be tougher for China. Japan faced a lot of heat from its trading partners, but as a military ally of the U.S., it never risked a “new Cold War”—as some analysts now describe the U.S.-China relationship. Efforts by the U.S. and its allies to block China’s access to advanced technologies and reduce reliance on Chinese supply chains have sparked a plunge in foreign direct investment into China this year, which could significantly slow growth in the long run.
Many analysts worry Beijing is underestimating the risk of long-term stagnation—and doing too little to avoid it. Moderate cuts to key interest rates, lowering down payment ratios for apartments and recent vocal support for the private sector have done little to revive sentiment so far. Economists including Xiaoqin Pi from Bank of America argue that more coordinated easing in fiscal, monetary and property policies will be needed to put China’s growth back on track.
But President Xi Jinping is ideologically opposed to increasing government support for households and consumers, which he derides as “welfarism.”
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
No trip to Singapore is complete without a meal (or 12) at its hawker centres, where stalls sell multicultural dishes from generations-old recipes. But rising costs and demographic change are threatening the beloved tradition.
In Singapore, it’s not unusual for total strangers to ask, “Have you eaten yet?” A greeting akin to “Good morning,” it invariably leads to follow-up questions. What did you eat? Where did you eat it? Was it good? Greeters reserve the right to judge your responses and offer advice, solicited or otherwise, on where you should eat next.
Locals will often joke that gastronomic opinions can make (and break) relationships and that eating is a national pastime. And why wouldn’t it be? In a nexus of colliding cultures—a place where Malays, Indians, Chinese and Europeans have brushed shoulders and shared meals for centuries—the mix of flavours coming out of kitchens in this country is enough to make you believe in world peace.
While Michelin stars spangle Singapore’s restaurant scene , to truly understand the city’s relationship with food, you have to venture to the hawker centres. A core aspect of daily life, hawker centres sprang up in numbers during the 1970s, built by authorities looking to sanitise and formalise the city’s street-food scene. Today, 121 government-run hawker centres feature food stalls that specialise in dishes from the country’s various ethnic groups. In one of the world’s most expensive cities, hawker dishes are shockingly cheap: A full meal can cost as little as $3.
Over the course of many visits to Singapore, I’ve fallen in love with these places—and with the scavenger hunts to find meals I’ll never forget: delicate bowls of laksa noodle soup, where brisk lashes of heat interrupt addictive swirls of umami; impossibly flaky roti prata dipped in curry; the beautiful simplicity of an immaculately roasted duck leg. In a futuristic and at times sterile city, hawker centres throw back to the past and offer a rare glimpse of something human in scale. To an outsider like me, sitting at a table amid the din of the lunch-hour rush can feel like glimpsing the city’s soul through all the concrete and glitz.
So I’ve been alarmed in recent years to hear about the supposed demise of hawker centres. Would-be hawkers have to bid for stalls from the government, and rents are climbing . An upwardly mobile generation doesn’t want to take over from their parents. On a recent trip to Singapore, I enlisted my brother, who lives there, and as we ate our way across the city, we searched for signs of life—and hopefully a peek into what the future holds.
At Amoy Street Food Centre, near the central business district, 32-year-old Kai Jin Thng has done the math. To turn a profit at his stall, Jin’s Noodle , he says, he has to churn out at least 150 $4 bowls of kolo mee , a Malaysian dish featuring savoury pork over a bed of springy noodles, in 120 minutes of lunch service. With his sister as sous-chef, he slings the bowls with frenetic focus.
Thng dropped out of school as a teenager to work in his father’s stall selling wonton mee , a staple noodle dish, and is quick to say no when I ask if he wants his daughter to take over the stall one day.
“The tradition is fading and I believe that in the next 10 or 15 years, it’s only going to get worse,” Thng said. “The new generation prefers to put on their tie and their white collar—nobody really wants to get their hands dirty.”
In 2020, the National Environment Agency , which oversees hawker centres, put the median age of hawkers at 60. When I did encounter younger people like Thng in the trade, I found they persevered out of stubbornness, a desire to innovate on a deep-seated tradition—or some combination of both.
Later that afternoon, looking for a momentary reprieve from Singapore’s crushing humidity, we ducked into Market Street Hawker Centre and bought juice made from fresh calamansi, a small citrus fruit.
Jamilah Beevi, 29, was working the shop with her father, who, at 64, has been a hawker since he was 12. “I originally stepped in out of filial duty,” she said. “But I find it to be really fulfilling work…I see it as a generational shop, so I don’t want to let that die.” When I asked her father when he’d retire, he confidently said he’d hang up his apron next year. “He’s been saying that for many years,” Beevi said, laughing.
More than one Singaporean told me that to truly appreciate what’s at stake in the hawker tradition’s threatened collapse, I’d need to leave the neighbourhoods where most tourists spend their time, and venture to the Heartland, the residential communities outside the central business district. There, hawker centres, often combined with markets, are strategically located near dense housing developments, where they cater to the 77% of Singaporeans who live in government-subsidised apartments.
We ate laksa from a stall at Ghim Moh Market and Food Centre, where families enjoyed their Sunday. At Redhill Food Centre, a similar chorus of chattering voices and clattering cutlery filled the space, as diners lined up for prawn noodles and chicken rice. Near our table, a couple hungrily unwrapped a package of durian, a coveted fruit banned from public transportation and some hotels for its strong aroma. It all seemed like business as usual.
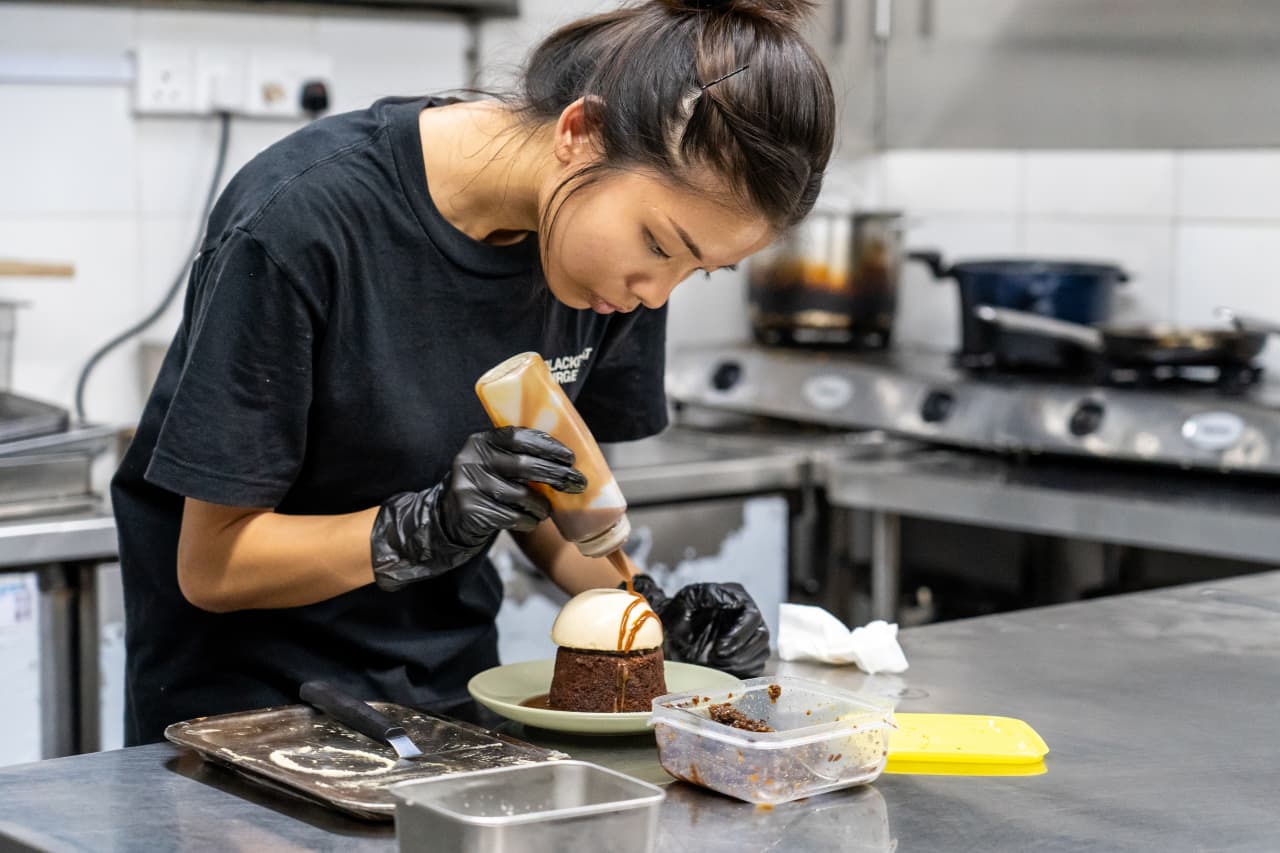
Then we went to Blackgoat . Tucked in a corner of the Jalan Batu housing development, Blackgoat doesn’t look like an average hawker operation. An unusually large staff of six swirled around a stall where Fikri Amin Bin Rohaimi, 24, presided over a fiery grill and a seriously ambitious menu. A veteran of the three-Michelin-star Zén , Rohaimi started selling burgers from his apartment kitchen in 2019, before opening a hawker stall last year. We ordered everything on the menu and enjoyed a feast that would astound had it come out of a fully equipped restaurant kitchen; that it was all made in a 130-square-foot space seemed miraculous.
Mussels swam in a mushroom broth, spiked with Thai basil and chives. Huge, tender tiger prawns were grilled to perfection and smothered in toasted garlic and olive oil. Lamb was coated in a whisper of Sichuan peppercorns; Wagyu beef, in a homemade makrut-lime sauce. Then Ethel Yam, Blackgoat’s pastry chef prepared a date pudding with a mushroom semifreddo and a panna cotta drizzled in chamomile syrup. A group of elderly residents from the nearby towers watched, while sipping tiny glasses of Tiger beer.
Since opening his stall, Rohaimi told me, he’s seen his food referred to as “restaurant-level hawker food,” a categorisation he rejects, feeling it discounts what’s possible at a hawker centre. “If you eat hawker food, you know that it can often be much better than anything at a restaurant.”
He wants to open a restaurant eventually—or, leveraging his in-progress biomedical engineering degree, a food lab. But he sees the modern hawker centre not just as a steppingstone, but a place to experiment. “Because you only have to manage so many things, unlike at a restaurant, a hawker stall right now gives us a kind of limitlessness to try new things,” he said.
Using high-grade Australian beef and employing a whole staff, Rohaimi must charge more than typical hawker stalls, though his food, around $12 per 100 grams of steak, still costs far less than high-end restaurant fare. He’s found that people will pay for quality, he says, even if he first has to convince them to try the food.
At Yishun Park Hawker Centre (now temporarily closed for renovations), Nurl Asyraffie, 33, has encountered a similar dynamic since he started Kerabu by Arang , a stall specialising in “modern Malay food.” The day we came, he was selling ayam percik , a grilled chicken leg smothered in a bewitching turmeric-based marinade. As we ate, a hawker from another stall came over to inquire how much we’d paid. When we said around $10 a plate, she looked skeptical: “At least it’s a lot of food.”
Asyraffie, who opened the stall after a spell in private dining and at big-name restaurants in the region, says he’s used to dubious reactions. “I think the way you get people’s trust is you need to deliver,” he said. “Singapore is a melting pot; we’re used to trying new things, and we will pay for food we think is worth it.” He says a lot of the same older “uncles” who gawked at his prices, are now regulars. “New hawkers like me can fill a gap in the market, slightly higher than your chicken rice, but lower than a restaurant.”
But economics is only half the battle for a new generation of hawkers, says Seng Wun Song, a 64-year-old, semiretired economist who delves into the inner workings of Singapore’s food-and-beverage industry as a hobby. He thinks locals and tourists who come to hawker centers to look for “authentic” Singaporean food need to rethink what that amorphous catchall word really means. What people consider “heritage food,” he explains, is a mix of Malay, Chinese, Indian and European dishes that emerged from the country’s founding. “But Singapore is a trading hub where people come and go, and heritage moves and changes. Hawker food isn’t dying; it’s evolving so that it doesn’t die.”
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.






















