Is Germany’s Economic Model Truly Kaputt?
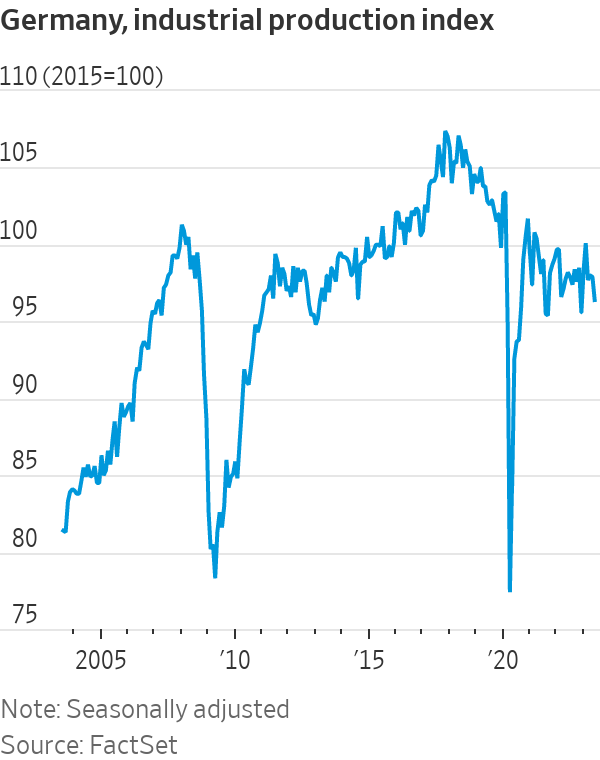
More than two decades after Germany was famously called “the sick man of the euro” by The Economist magazine, investors must wonder if the country’s industrial heart is once again critically weak. This week brought more dismal German economic data: Industrial production fell 1.5% in June from the previous month, worse than analysts expected. Though figures released on Friday showed a rise in exports, the volume of goods Germany sends abroad is still close to lows plumbed in the 2009 global financial crisis.
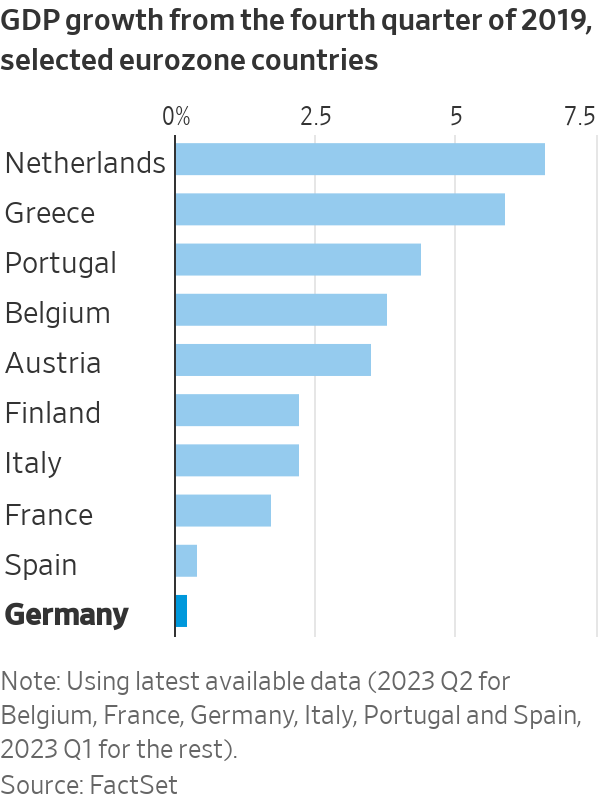
German gross domestic product has clocked three quarters of negative or zero growth , making the country the worst performer among major eurozone nations since 2019. Previously it was the top performer. How long this “slowcession” lasts is a crucial question for picking stocks in Europe. Despite the recent economic reversal, the DAX has been by far the best equity index in the eurozone over 20 years, returning almost 360%.
By comparison, investing in long-stagnant Italy yielded a paltry 140% return. German industrial output has been in decline since 2018, when global vehicle sales fell for the first time in almost a decade. A postpandemic rebalancing of spending toward services has made the situation worse. Growth in China, the fourth-largest market for German exporters, has slowed.
On Thursday, shares in Siemens —the largest industrial firm in Europe—fell 5% after it cited these two factors as the cause of a fall in orders during the second quarter. Some of the grit that has gotten into the German economic machine might be hard to dislodge . Chinese carmakers have turned from partners into fierce competitors as Volkswagen , BMW and Mercedes-Benz play catch-up in electric-vehicle technology.
It isn’t just China that is seeking to substitute imports for domestic products; the Biden administration is copying Beijing’s playbook. There is also energy. At the same time as German industry has lost Russia as its main source of cheap gas, Berlin has closed the country’s last three nuclear power plants. Angst has gripped German officials and executives in an echo of worries voiced at the start of the millennium, when unemployment surged and globalisation ravaged factories.
Back then, the response was a policy package that prioritised international competitiveness, incentivising the creation of low-pay “minijobs.” The government embraced fiscal austerity and nudged unions to push for wage restraint. The result was a 20-year decline in unemployment and a current-account surplus that reached an eye-watering 8% of GDP even as the U.S. ran huge deficits. Many economists praised German labor flexibility and fiscal austerity.
Conversely, critics pointed out that surpluses made most households worse off, and that Germany’s factory-job losses were just as large as America’s. Politics aside, it was largely a fortuitous jump in foreign demand that drove growth, allowing the nation to solidify gains in industries where it already had an advantage.
“Over the last 20 years, Germany always had an external sugar daddy: China, the eurozone and then the U.S.,” said Carsten Brzeski , chief economist at ING.
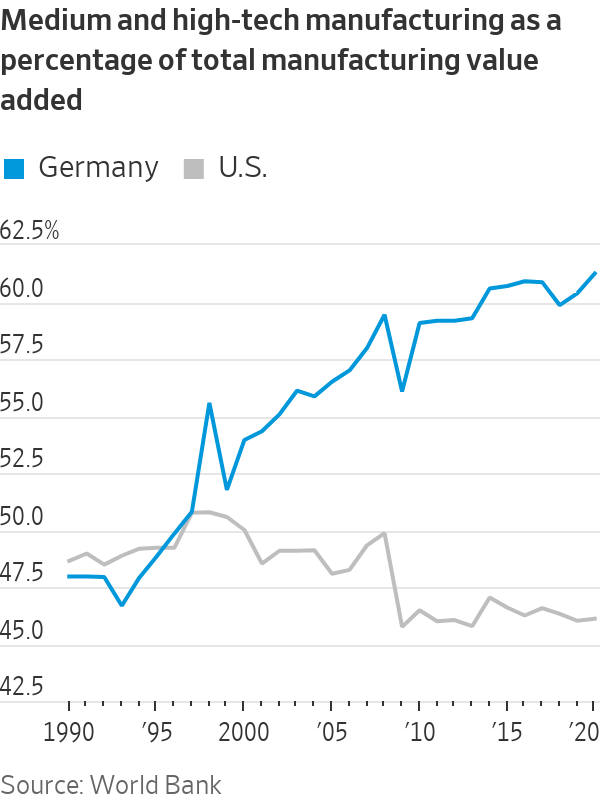
The flaw in this model was that it outsourced economic policy, leading to problematic dependencies on geopolitical rivals. It also fostered an excessive focus on old winners at the expense of new digital technologies and renewable energy. Bearish investors are right that it will take years to rectify these problems, particularly given the complexity of consensus-based German politics. Yet the German export-led model also got a lot right. As in China or South Korea, it channeled demand toward higher-productivity, higher-wage firms.

Unlike in the U.S., German manufacturing became more complex. That allowed the country’s industrial base to survive better than in other Western countries. In a world where nations are scrambling to reshore industries, Germany already has them. The readiest answer to its growth challenge isn’t to turn away from manufacturing but to double down by taking a page from Chinese and now U.S. industrial policy.
The German government is already doing this with semiconductors as part of the European Chips Act. Back in June, it signed off on 10 billion euros (around $11 billion) in subsidies for American chip maker Intel to build two plants, and earlier this week it committed €5 billion to help Taiwan’s TSMC set up a factory with local partners like Infineon.
A similar approach is needed to upgrade the country’s power generation and transmission and accelerate the transformation of carmakers and other industrial incumbents. Long-term energy guarantees could stem cost swings in the meantime. Given its political influence over the European Union, it seems hard to imagine that the bloc’s green-economy push could somehow leave Germany in a less dominant position . Historically, this is one patient that always leaves the hospital.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
The sports-car maker delivered 279,449 cars last year, down from 310,718 in 2024.
Chinese carmaker GAC will expand its Australian electric vehicle line-up with the city-focused AION UT hatchback.
The sports-car maker delivered 279,449 cars last year, down from 310,718 in 2024.
Porsche car deliveries fell 10% in 2025 as demand was hit by a slowdown in luxury spending in China and as it ceased production of its 718 Boxster and 718 Cayman models through the year.
The German luxury sports-car maker said Friday that it delivered 279,449 cars in the year, down from 310,718 in 2024.
The company had a tumultuous year as it contended with a stuttering transition to electric vehicles and a tough Chinese market, while the Trump administration’s automotive tariffs presented a further headwind.
Deliveries in its largest sales region of North America were virtually flat at 86,229, but continued challenges in China meant deliveries in the country dropped 26% to 41,938 vehicles.
Automakers have faced intense competition in China, sparking a prolonged price war as rivals cut prices to win customers, while a lengthy property market slump and economic-growth concerns in the country has also led to buyers pulling back on luxury spending.
“Key reasons for the decline remain the challenging market conditions, particularly in the luxury segment, and the very intense competition in the Chinese market, especially for all-electric models,” the company said.
Other German brands including Audi, BMW and Mercedes-Benz have all recently reported that the challenging Chinese market hit demand last year.
In Europe, Porsche deliveries fell 13% to 66,340 cars excluding its home market of Germany, while German deliveries dropped 16%.
The company cut guidance several times last year as it warned of hits from U.S. import tariffs, investments in new combustion engines and hybrid models amid the slow uptake of EVs, and the competitive situation in China.
Porsche also last year announced plans to scale back its EV ambitions and instead expand its lineup with more gas-powered and plug-in hybrid models than it had originally planned.
However, in its statement Friday, the company said it increased its share of electrified-vehicle deliveries in the year. Around 34% of vehicles delivered worldwide were electrified, an increase of 7.4 percentage points on year, with about 22% all-electric vehicles and 12% plug-in hybrids.
That leaves its global share of fully-electric vehicles at the upper end of its target range of 20% to 22% for 2025.
In Europe, for the first time in 2025, more electrified vehicles than purely combustion engine vehicles were delivered.
The Macan topped the delivery charts in the year, while the 911 reached a record high with 51,583 deliveries worldwide, it said.
Porsche said it is investing in its three-pronged powertrain strategy and will continue to respond to increasing demand for personalization requests from customers.
“We have a clear focus for 2026,” Sales and Marketing Chief Matthias Becker said. “We want to manage supply and demand in accordance with our ‘value over volume’ strategy.
“At the same time, we are realistically planning our volume for 2026 following the end of production of the 718 and Macan with combustion engines.”
The era of the gorgeous golden retriever is over. Today’s most coveted pooches have frightful faces bred to tug at our hearts.
Australia’s housing market defies forecasts as prices surge past pandemic-era benchmarks.























