Plant-Based Plastics Gain Favour as Companies Pursue Sustainability Goals
Bioplastic production is growing at a record clip amid strong demand from fashion and food-packaging companies, in particular
The future is more plastic. Plant-based plastic, that is.
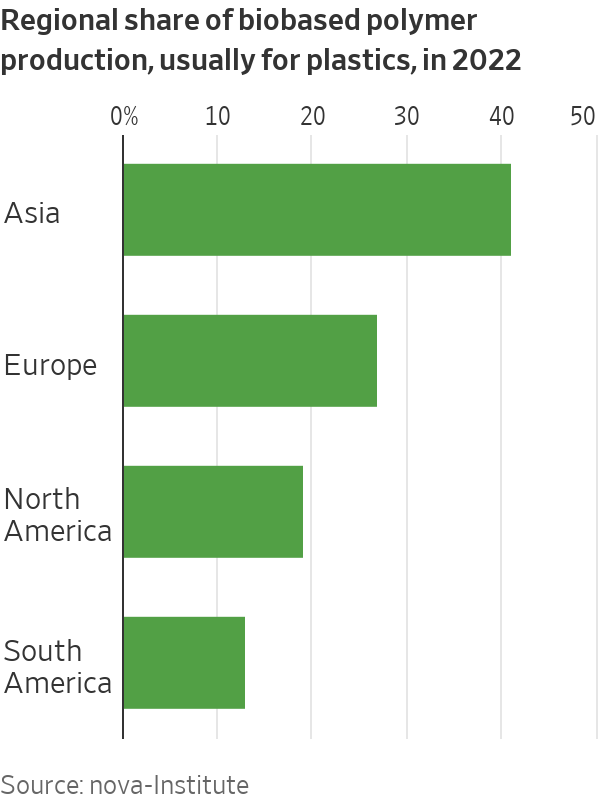
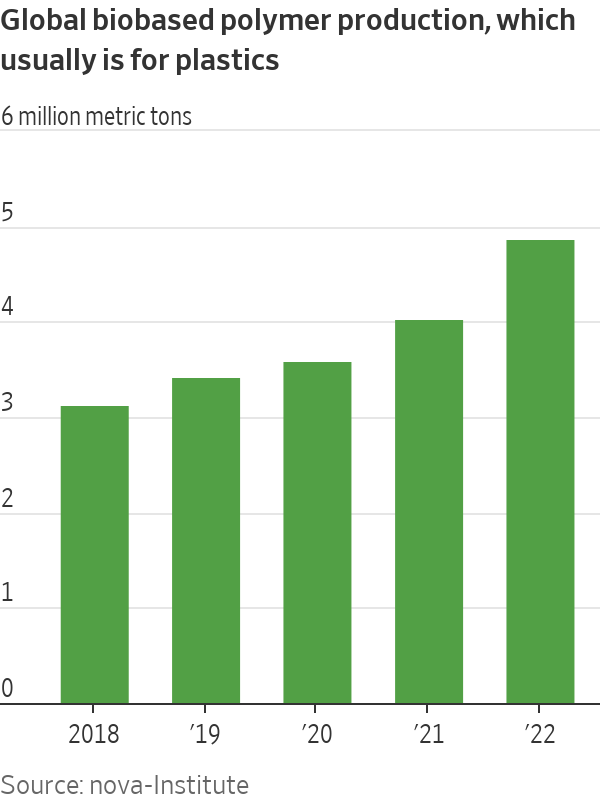
Plant-based plastics, or bioplastics, have accounted for just 1% of the world’s plastic production for well over a decade, according to a review of more than 100 companies by research organisation nova-Institute. Bioplastics haven’t taken off largely because they are typically 50% to 80% more expensive than traditional fossil-fuel-based plastics, but their production is now growing 14% a year, putting them on track to reach up to 3% of the plastics market in the next five years.
Bioplastics are expanding faster than recycled plastic in some cases, such as in Asian countries like China and Japan that are mandating more ecologically friendly materials, nova-Institute founder Michael Carus said. Even if global plastic recycling rates someday reach 70% compared with around 9% today, bioplastics alongside materials made from captured carbon dioxide will have a big role to play asthe world transitions away from fossil-fuel-based materials, he said.
“Not one of them can do it alone,” Carus said, referring to the sustainable materials that will drive the green transition.
Bioplastics’ benefits
Bioplastics are usually derived from plants rich in starch, sugar or pulp, such as corn, wheat, sugar cane, wood and cotton, which makes them costlier than plastics made from fossil fuels because crops need fertiliser and other resources such as water. However, the environmental benefits of plant-based plastics are increasingly appealing to companies promising to use more sustainable materials by the end of the decade.
Plants absorb the atmosphere’s carbon dioxide, which cuts the greenhouse-gas emissions from making bioplastics to at least half that of fossil-fuel-based plastics. Bioplastics can also sometimes cause less pollution when they degrade in the environment.
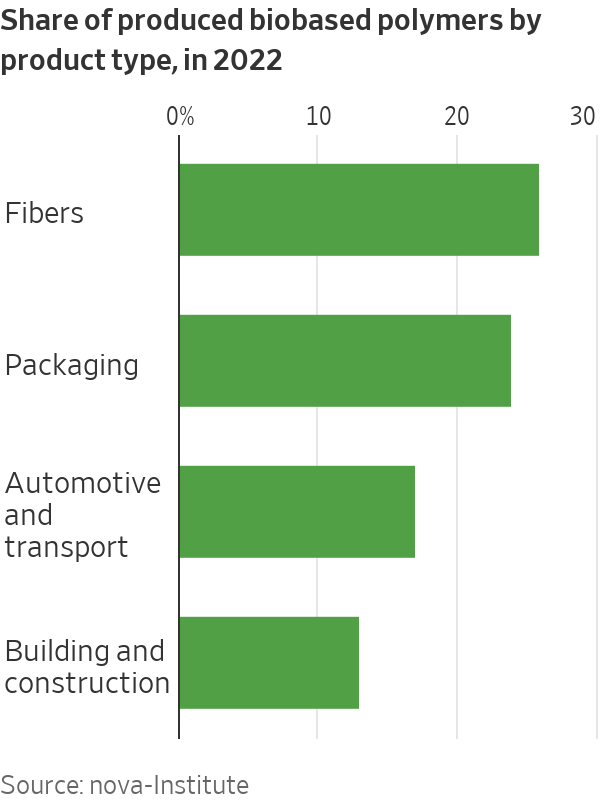
Broadly, there are two types of bioplastics: Materials that have similar performance to plastic, such as pulp-derived cellulose acetate found in eyeglasses and textiles, and bioplastics that are chemically identical to conventional plastics, such as a polyethylene, polyester and nylon. Around half of today’s bioplastics are biodegradable, according to nova-Institute, meaning they break down more naturally and are less harmful to habitats. Still, many of these bioplastics require industrial composting facilities to degrade and aren’t designed to be thrown away in a home garden.
Some of the earliest adopters of bioplastics are fashion companies, including Lululemon, which has a goal to replace the majority of oil-based nylon with plant-based nylon by 2030. A big selling point for the sportswear company is using plants to make chemically identical nylon that can be easily switched in, but still cuts emissions by nearly half.
The strongest demand for bioplastics is currently from fashion and food-packaging companies, but interest is also rising from companies in cosmetics, electronics and more durable goods such as tools, Eastman Chemical’s Chief Technology Officer Chris Killian said.
Eastman, formerly a division of Kodak, earns more than $1 billion of its $10 billion or so in yearly sales from bioplastics made from cellulose acetate, a material it has produced for more than 70 years. Cellulose acetate, which Eastman makes from cotton linters and wood pulp, was first used in Kodak film in the company’s early days, but it is now expanding into packaging, textiles and other applications. In 2022, Eastman signed an agreement with Warby Parker for the material to be used in eyewear.
“It has a great deal of legs,” he said of the cellulose acetate-derived plastics.
Challenges ahead
Plant-based plastics remain a tough sell because fossil-fuel-based plastics are much cheaper, but prices could fall if companies continue to buy more bioplastics and governments encourage their use. This year, the Biden administration called on the federal government to assess the potential for biomaterials, including for plastics, fuels and medicines. And last year, the U.S. Defense Department said it would invest $1.2 billion in bio manufacturing. The European Union is also considering mandating bioplastics under packaging rules that are being discussed.
In the U.S., there is government support at the state and federal level to convert biological raw materials into fuels such as ethanol, but that level of support doesn’t yet exist for plant-based plastics, said Manav Lahoti, chemical giant Dow’s global sustainability director, olefins, aromatics and alternatives.
“The market is ready to take off on the demand side,” he said. “But to make the economics work, there is some regulatory support that is required.”
Another hurdle to scaling up bioplastics is what happens at their end of life. Only plant-based plastics that are chemically identical to fossil-fuel–based versions can enter the existing and growing recycling infrastructure. The world’s limited amount of feedstock, which often goes to feeding cattle and other livestock, also presents challenges to using more bioplastics.
One answer: turning agricultural waste into recyclable plastics.
This year, Dow struck an agreement with biomass refinery startup New Energy Blue to buy bioethylene made from the stalks and leaves of corn grown in Iowa. Dow will then make conventional and recyclable plastics from the material and sell to companies in transportation, footwear, and packaging.
Dow is already providing bioplastics for Crocs shoes and LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton’s perfume packaging, and sees demand outstripping supply, said Haley Lowry, Dow’s global sustainability director for packaging and specialty plastics.
“We are trying to find more sources,” she said. “The demand from our customers is there; it’s really finding the sources of biofeed that makes sense.”
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
No trip to Singapore is complete without a meal (or 12) at its hawker centres, where stalls sell multicultural dishes from generations-old recipes. But rising costs and demographic change are threatening the beloved tradition.
In Singapore, it’s not unusual for total strangers to ask, “Have you eaten yet?” A greeting akin to “Good morning,” it invariably leads to follow-up questions. What did you eat? Where did you eat it? Was it good? Greeters reserve the right to judge your responses and offer advice, solicited or otherwise, on where you should eat next.
Locals will often joke that gastronomic opinions can make (and break) relationships and that eating is a national pastime. And why wouldn’t it be? In a nexus of colliding cultures—a place where Malays, Indians, Chinese and Europeans have brushed shoulders and shared meals for centuries—the mix of flavours coming out of kitchens in this country is enough to make you believe in world peace.
While Michelin stars spangle Singapore’s restaurant scene , to truly understand the city’s relationship with food, you have to venture to the hawker centres. A core aspect of daily life, hawker centres sprang up in numbers during the 1970s, built by authorities looking to sanitise and formalise the city’s street-food scene. Today, 121 government-run hawker centres feature food stalls that specialise in dishes from the country’s various ethnic groups. In one of the world’s most expensive cities, hawker dishes are shockingly cheap: A full meal can cost as little as $3.
Over the course of many visits to Singapore, I’ve fallen in love with these places—and with the scavenger hunts to find meals I’ll never forget: delicate bowls of laksa noodle soup, where brisk lashes of heat interrupt addictive swirls of umami; impossibly flaky roti prata dipped in curry; the beautiful simplicity of an immaculately roasted duck leg. In a futuristic and at times sterile city, hawker centres throw back to the past and offer a rare glimpse of something human in scale. To an outsider like me, sitting at a table amid the din of the lunch-hour rush can feel like glimpsing the city’s soul through all the concrete and glitz.
So I’ve been alarmed in recent years to hear about the supposed demise of hawker centres. Would-be hawkers have to bid for stalls from the government, and rents are climbing . An upwardly mobile generation doesn’t want to take over from their parents. On a recent trip to Singapore, I enlisted my brother, who lives there, and as we ate our way across the city, we searched for signs of life—and hopefully a peek into what the future holds.
At Amoy Street Food Centre, near the central business district, 32-year-old Kai Jin Thng has done the math. To turn a profit at his stall, Jin’s Noodle , he says, he has to churn out at least 150 $4 bowls of kolo mee , a Malaysian dish featuring savoury pork over a bed of springy noodles, in 120 minutes of lunch service. With his sister as sous-chef, he slings the bowls with frenetic focus.
Thng dropped out of school as a teenager to work in his father’s stall selling wonton mee , a staple noodle dish, and is quick to say no when I ask if he wants his daughter to take over the stall one day.
“The tradition is fading and I believe that in the next 10 or 15 years, it’s only going to get worse,” Thng said. “The new generation prefers to put on their tie and their white collar—nobody really wants to get their hands dirty.”
In 2020, the National Environment Agency , which oversees hawker centres, put the median age of hawkers at 60. When I did encounter younger people like Thng in the trade, I found they persevered out of stubbornness, a desire to innovate on a deep-seated tradition—or some combination of both.
Later that afternoon, looking for a momentary reprieve from Singapore’s crushing humidity, we ducked into Market Street Hawker Centre and bought juice made from fresh calamansi, a small citrus fruit.
Jamilah Beevi, 29, was working the shop with her father, who, at 64, has been a hawker since he was 12. “I originally stepped in out of filial duty,” she said. “But I find it to be really fulfilling work…I see it as a generational shop, so I don’t want to let that die.” When I asked her father when he’d retire, he confidently said he’d hang up his apron next year. “He’s been saying that for many years,” Beevi said, laughing.
More than one Singaporean told me that to truly appreciate what’s at stake in the hawker tradition’s threatened collapse, I’d need to leave the neighbourhoods where most tourists spend their time, and venture to the Heartland, the residential communities outside the central business district. There, hawker centres, often combined with markets, are strategically located near dense housing developments, where they cater to the 77% of Singaporeans who live in government-subsidised apartments.
We ate laksa from a stall at Ghim Moh Market and Food Centre, where families enjoyed their Sunday. At Redhill Food Centre, a similar chorus of chattering voices and clattering cutlery filled the space, as diners lined up for prawn noodles and chicken rice. Near our table, a couple hungrily unwrapped a package of durian, a coveted fruit banned from public transportation and some hotels for its strong aroma. It all seemed like business as usual.
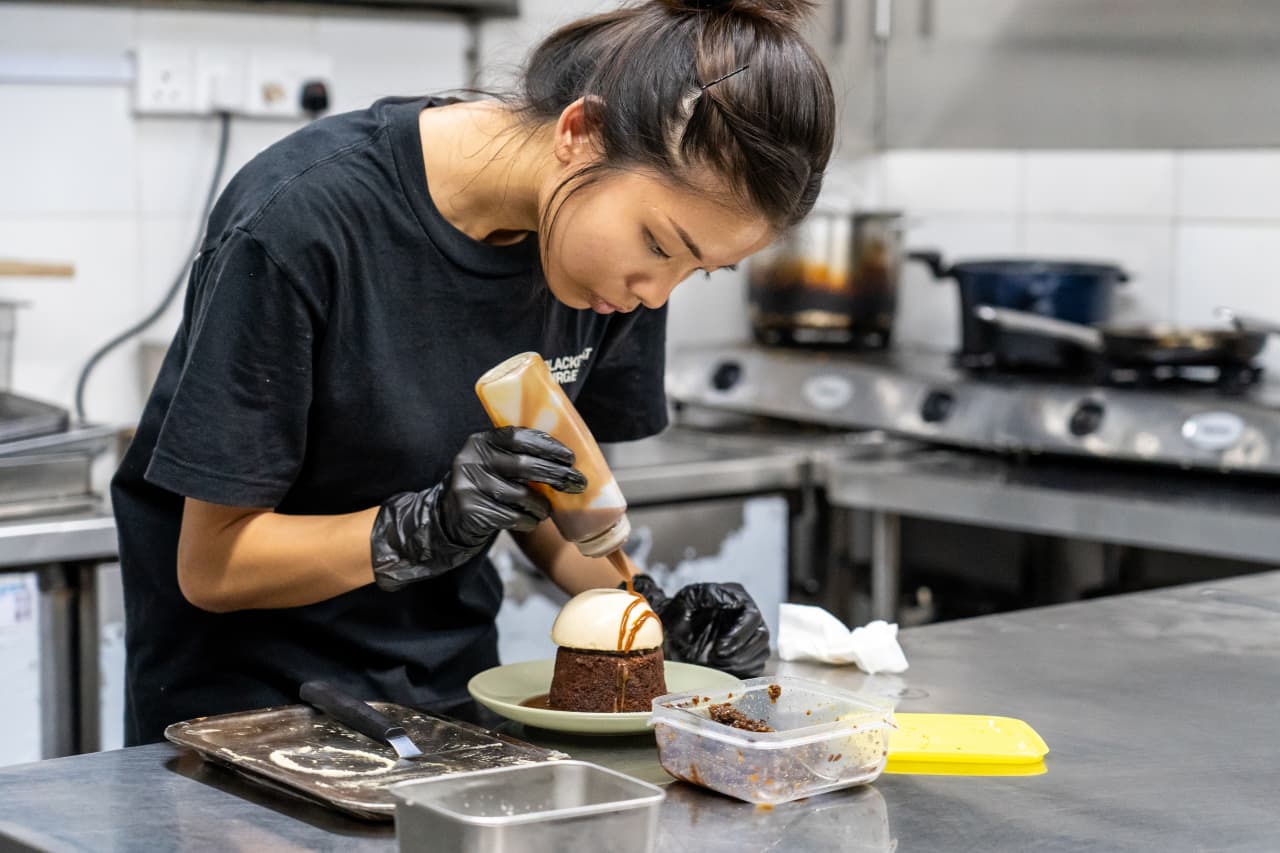
Then we went to Blackgoat . Tucked in a corner of the Jalan Batu housing development, Blackgoat doesn’t look like an average hawker operation. An unusually large staff of six swirled around a stall where Fikri Amin Bin Rohaimi, 24, presided over a fiery grill and a seriously ambitious menu. A veteran of the three-Michelin-star Zén , Rohaimi started selling burgers from his apartment kitchen in 2019, before opening a hawker stall last year. We ordered everything on the menu and enjoyed a feast that would astound had it come out of a fully equipped restaurant kitchen; that it was all made in a 130-square-foot space seemed miraculous.
Mussels swam in a mushroom broth, spiked with Thai basil and chives. Huge, tender tiger prawns were grilled to perfection and smothered in toasted garlic and olive oil. Lamb was coated in a whisper of Sichuan peppercorns; Wagyu beef, in a homemade makrut-lime sauce. Then Ethel Yam, Blackgoat’s pastry chef prepared a date pudding with a mushroom semifreddo and a panna cotta drizzled in chamomile syrup. A group of elderly residents from the nearby towers watched, while sipping tiny glasses of Tiger beer.
Since opening his stall, Rohaimi told me, he’s seen his food referred to as “restaurant-level hawker food,” a categorisation he rejects, feeling it discounts what’s possible at a hawker centre. “If you eat hawker food, you know that it can often be much better than anything at a restaurant.”
He wants to open a restaurant eventually—or, leveraging his in-progress biomedical engineering degree, a food lab. But he sees the modern hawker centre not just as a steppingstone, but a place to experiment. “Because you only have to manage so many things, unlike at a restaurant, a hawker stall right now gives us a kind of limitlessness to try new things,” he said.
Using high-grade Australian beef and employing a whole staff, Rohaimi must charge more than typical hawker stalls, though his food, around $12 per 100 grams of steak, still costs far less than high-end restaurant fare. He’s found that people will pay for quality, he says, even if he first has to convince them to try the food.
At Yishun Park Hawker Centre (now temporarily closed for renovations), Nurl Asyraffie, 33, has encountered a similar dynamic since he started Kerabu by Arang , a stall specialising in “modern Malay food.” The day we came, he was selling ayam percik , a grilled chicken leg smothered in a bewitching turmeric-based marinade. As we ate, a hawker from another stall came over to inquire how much we’d paid. When we said around $10 a plate, she looked skeptical: “At least it’s a lot of food.”
Asyraffie, who opened the stall after a spell in private dining and at big-name restaurants in the region, says he’s used to dubious reactions. “I think the way you get people’s trust is you need to deliver,” he said. “Singapore is a melting pot; we’re used to trying new things, and we will pay for food we think is worth it.” He says a lot of the same older “uncles” who gawked at his prices, are now regulars. “New hawkers like me can fill a gap in the market, slightly higher than your chicken rice, but lower than a restaurant.”
But economics is only half the battle for a new generation of hawkers, says Seng Wun Song, a 64-year-old, semiretired economist who delves into the inner workings of Singapore’s food-and-beverage industry as a hobby. He thinks locals and tourists who come to hawker centers to look for “authentic” Singaporean food need to rethink what that amorphous catchall word really means. What people consider “heritage food,” he explains, is a mix of Malay, Chinese, Indian and European dishes that emerged from the country’s founding. “But Singapore is a trading hub where people come and go, and heritage moves and changes. Hawker food isn’t dying; it’s evolving so that it doesn’t die.”
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.






















