California Is Desperate for Affordable Housing But Can’t Stop Getting in Its Own Way
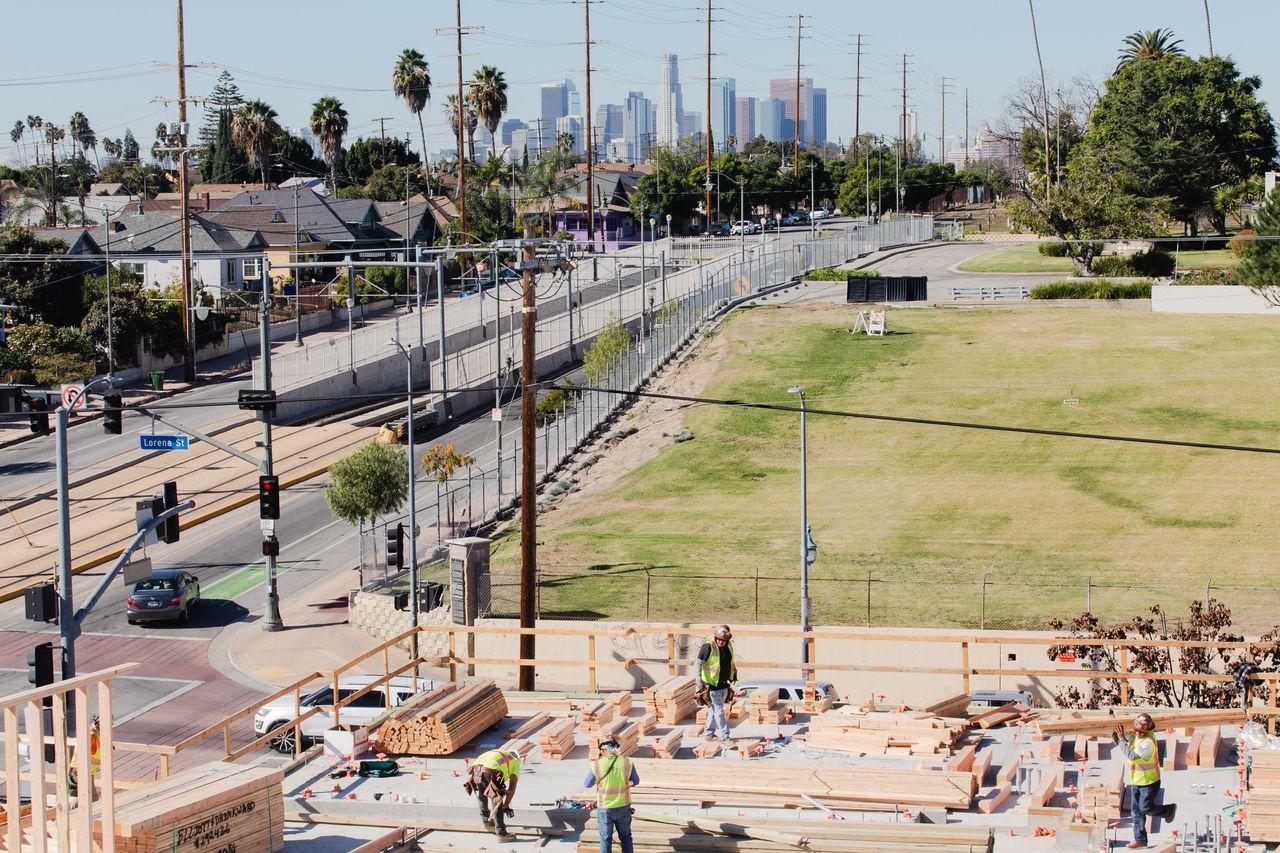
In Los Angeles, 49 units are taking 17 years to build, facing nearly every hurdle that state laws allow
A Los Angeles nonprofit was given government land in January 2007 to build a few dozen units of affordable housing. They’re finally hoping to open the building next year.
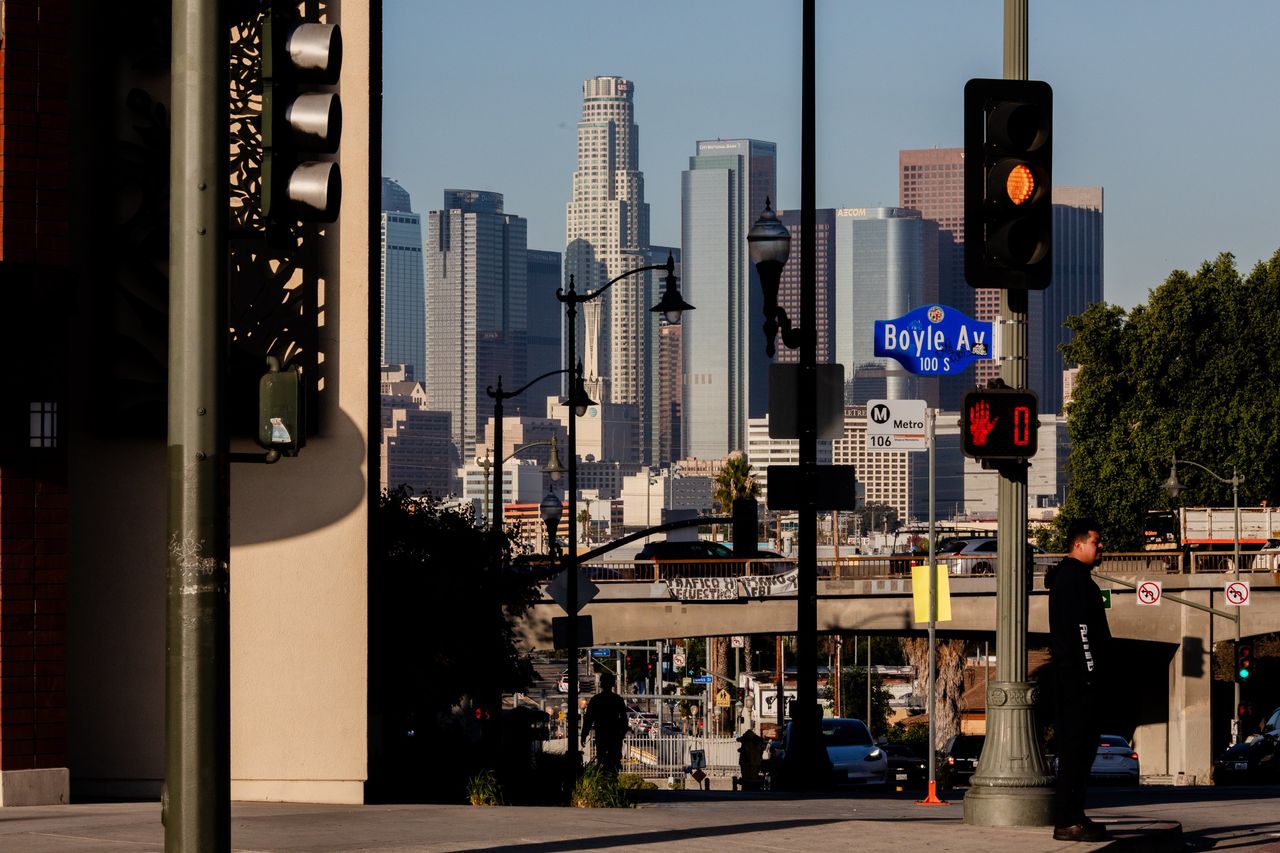
Lorena Plaza, a 49-unit development rising in the predominantly Latino neighbourhood of Boyle Heights in eastern Los Angeles, is taking longer to complete, a city official said, than practically any other residential building this size in the history of Los Angeles.
The 17 years of false starts and delays are an extreme instance of how difficult it has long been to build affordable housing in California—for both the homeless as well as lower and middle-income workers—and in other states with complex regulations and high costs.
The development has faced nearly every hurdle that California laws allow opponents to place in the way of affordable housing. Approvals by politicians and commissions took years, often held up by a single determined opponent on the city council. It took the developers more time to win over skeptical neighbours who were particularly opposed to nearby housing for the mentally ill and homeless. Financing hurdles and other costs piled up along the way. Construction finally began about a year ago.
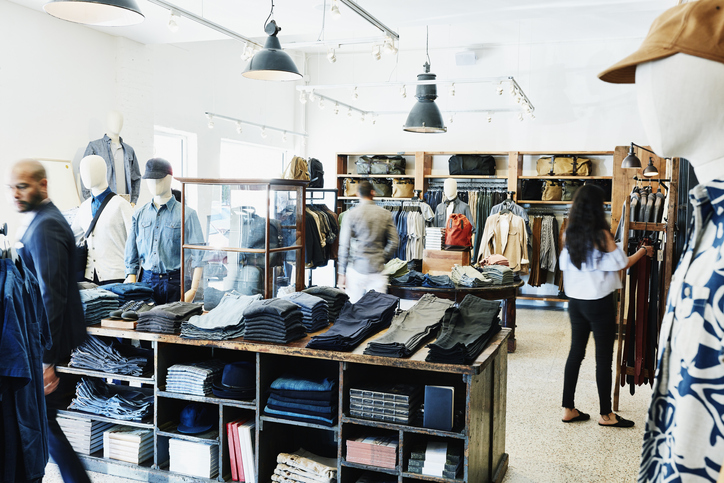
In California, affordable housing developers typically abide by a host of requirements when they take public subsidies, such as tougher energy-efficiency standards and higher wages for construction workers. They often need to build amenities such as offices for social workers and transit-boosting features such as bike storage.

Even home builders who are sympathetic to these priorities say those same objectives undermine the state’s ability to produce enough affordable housing. That means California will continue to suffer stubbornly high rates of homelessness that plague the Golden State and are evident on the tent-filled streets of cities like L.A.
“We’re really committed to things like climate change and we’re very committed to transit-oriented development,” said Linda Mandolini, president of Bay Area-based Eden Housing, a nonprofit low-income housing builder. “But those goals don’t come for free.”
Housing costs and homelessness have become the top political issue in the state, prompting officials to set ambitious goals to build more housing, faster. Los Angeles is aiming to construct more than 450,000 new homes by 2029, a feat that would require five times as much construction as occurred in the previous decade, according to a May report from researchers at the University of California Los Angeles’ Ziman Center for Real Estate and California State University Northridge.
Los Angeles Mayor Karen Bass has pointed to the delays with Lorena Plaza as an example of what the city is trying to fix. The mayor is expediting permits for projects in which all of the units are considered affordable and cutting other red tape that has sidelined projects.
“How on earth could we expect to house 40,000 [homeless] people if we continue to do business as usual?” the Democrat asked in a speech at the development’s construction site last year.
There are still serious impediments to building enough housing in Los Angeles and the state. Existing subsidies that fund affordable housing construction are oversubscribed. And cities keep looking for ways to block new housing, market-rate or affordable.
The Bay Area suburb of Woodside, for example, last year tried to declare that its entire city was a mountain lion refuge to prevent apartment development. The town, which later reversed the decision, didn’t return a request for comment.
Affordable housing faces hurdles outside of California, too. In New York City, a developer’s plan to build low-income apartments at the site of a community garden in lower Manhattan has been held up for a decade by city review processes and lawsuits filed by opponents. In Dallas, a mixed-income apartment complex planned for an empty field in the northern part of the city was delayed for more than three years by deed restrictions that allowed neighbouring property owners to dictate land use.
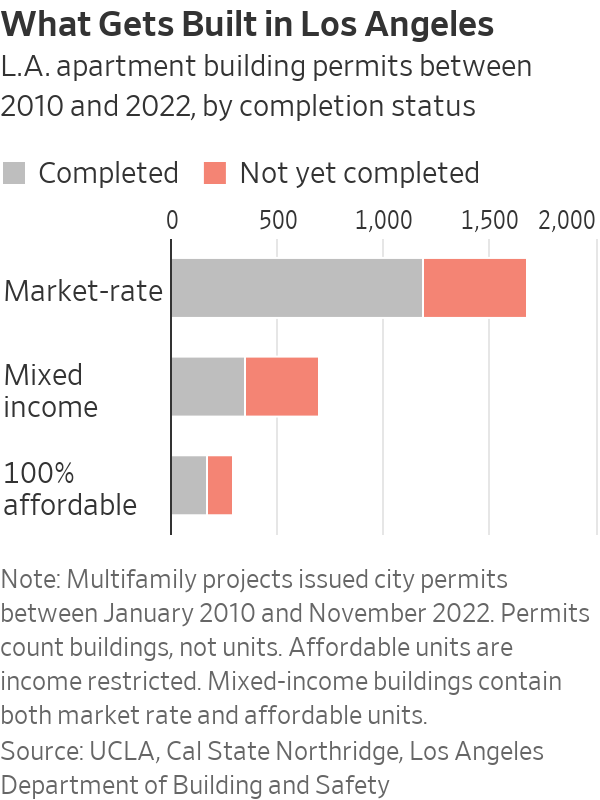
An apartment building takes an average of four years to build in L.A., according to a UCLA and CSU-Northridge analysis of building permits from 2010 to 2022. Two-and-a-half of those four years come after the approvals process.
About 36% of projects that received permits in California between 2010 and 2022 had not yet been completed, according to UCLA.
“Thinking about building in a city like Los Angeles and dealing with the politics, navigating the bureaucracy, it’s the last place I want to be,” said Caleb Roope, chief executive of the Pacific Companies, a West Coast affordable housing builder based in Idaho.
California Gov. Gavin Newsom is pushing changes at the state level, as are the mayors of other cities where housing construction has been painfully slow and homelessness has risen.
In San Jose, Calif., the average cost to build just one unit of low-income housing shot up by 24% in 2022 alone, hitting a new high of $938,700, or roughly what it costs to buy a three-bedroom bungalow there, according to an October report commissioned by the city.
San Francisco permitted 856 housing units this year through October. New Braunfels, Texas, which is one-eighth the size of San Francisco by population, permitted 1,940 units in the same period, according to data compiled by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development.
In Los Angeles, Lorena Plaza, if all goes as planned from here, will open in the late summer. Its 49 units will consist of studios up to three-bedroom apartments. They will measure between about 420 and 1,050 square feet and feature full-size kitchens. The rentals will be priced so that people making less than 50% of the area median income can afford them. The units cost $34.2 million to build.
The project’s wood beams are stacking up in Boyle Heights. It’s a neighbourhood that over the past century has made homeownership possible to a rotating cast: Irish and Jewish immigrants at the turn of the century gave way to Black residents barred from buying elsewhere, before becoming the predominantly Latino neighbourhood it is today. Vendors hawk elote, tamales and flowers on street corners.
The neighbourhood has also seen gentrification in recent years, which has turned this barrio into a hotbed of housing activism. On the surrounding blocks, taco trucks coexist with $45 men’s haircuts. A Starbucks drive-through sits on what was once a Unocal service station and the historic Boyle Hotel, which once boarded mariachi musicians, now houses a La Monarca, the local chain of upscale Mexican-American bakeries.
Some 74% of the neighbourhood’s residents are renters, and for more than two decades, rents have risen faster than in the rest of Los Angeles, according to one city government-commissioned study, amid an influx of higher-earning residents.
In 2007, A Community of Friends, a nonprofit developer known as ACOF, proposed to build permanent supportive housing, a type of project designed for low-income people with specific needs. In the case of Lorena Plaza, it meant some units would be set aside for those who had experienced homelessness or mental health issues, and who would rely on services such as social work and healthcare provided by on-site staff.
The Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority agreed to provide the land, but was slow to make it available, in large part because it was being used as a staging area during the construction of a train line. A global financial crisis further derailed plans. By the time the economy began rebounding in 2012, the deepest troubles for the 49 could-be apartments were setting in.
The city councilman representing the neighbourhood, Jose Huizar, had broad powers to delay projects on his turf. To get a city subsidy, the developers would need a signed letter from Huizar, who sat on the MTA board and remained opposed to the project for years.
Dora Leong Gallo, executive director of ACOF, recalled a nervous 2013 meeting with Huizar’s staff. Huizar’s staff wanted more commercial space, Gallo said. Once that was satisfied, they requested the approval of the Boyle Heights Neighborhood Council, a community advisory group.
“He moved the goal posts,” Gallo said.
Huizar is currently awaiting sentencing after pleading guilty to corruption charges unrelated to Lorena Plaza. His attorney said that “asking for additional commercial space and support from the neighbourhood council seem not only like routine asks, but responsible ones.”
In a series of heated community meetings, some area homeowners and renters including vendors at El Mercado, a bustling, three-story indoor market next door, chafed at the idea of sharing the neighbourhood with mentally ill and homeless residents.
“They’re trying to bring mentally ill people to put our children at risk,” Pedro Rosado, the owner of El Mercado, said during a 2013 hearing. Rosado died in 2015 and his children, Tony and Marlene, continued his appeals. They didn’t respond to requests for comment.
In 2015, the development got a boost after the neighbourhood council voted 15-1 to let ACOF proceed. It took about another year to receive city approval on all the necessary zoning and environmental reviews.
State law provided an opportunity to stall Lorena Plaza further. The Rosados appealed the project’s city-approved environmental review, claiming it was too dense for an already-overcrowded area, according to the filing.
A landmark state law called the California Environmental Quality Act, passed in 1970 and signed by Gov. Ronald Reagan, allows any opponent to use appeals to slow down development if they claim environmental reviews are flawed. In Los Angeles, appeals are heard by the city council’s Planning and Land Use Management Committee. That body was chaired by Huizar.
“He had double power,” said Jose Torres, the project manager for Lorena Plaza at the time. “One as a council member of his own district, and the other as the chair of PLUM.”
The committee didn’t schedule a hearing on the appeal for more than a year. When the project did get a hearing, Huizar sided with the Rosados, saying an abandoned oil well on the site posed a potential hazard.
By 2017, California’s housing crisis was worsening. Economists estimated there was a shortage of three million homes statewide. On the campaign trail, gubernatorial hopeful Newsom was vowing to spearhead an effort to alleviate homelessness and slow down home prices by building 3.5 million homes within eight years. While housing production has ticked up in recent years, it still sits well below half the pace needed to hit that figure.
Media attention zeroed in on the Lorena Plaza project and its years long saga, prompting the Chamber of Commerce and the United Way to rally behind it. In early 2018, Huizar called up the Los Angeles Times to say he had changed his mind after the developer made concessions and would push for the project’s approval.
The owners of El Mercado then turned to the courts, filing a lawsuit alleging ACOF didn’t properly address potential soil contamination. The case dragged on until ACOF and the business owners settled in 2020.
By 2021, when the Lorena Plaza developers secured all the necessary funding, the project’s costs had shot up by $9 million, or about one-third, in the five years after it first received approvals to build, Gallo said.
“It’s unfortunate what happened, but I think it’s very illustrative,” Gallo said. “I think a lot of things have changed as a result of this particular project.”
Much of what stifled construction of Lorena Plaza likely wouldn’t have happened now due to recent law changes. Developers no longer need a letter of support from their city council member to receive affordable housing funding.
Environmental appeals have to be heard within 75 days. Zoning approvals for affordable projects, which took more than a year at Lorena Plaza, are now happening as quickly as a few months-time under a Mayor Bass executive order.
David Aghaei, co-founder of Eleos Ventures, a developer with a pipeline of more than 20 all-affordable housing projects in Los Angeles, said the changes have significantly improved the timeline for four of his larger projects. One of them, which will bring 222 units of affordable housing to South Los Angeles, received planning approvals in five months. Historically, Aghaei said, that could have taken as long as two years.
The new rules mean Lorena Plaza may permanently hold the title for perhaps the city’s longest-running development. ACOF plans to start taking applications from prospective tenants in the spring.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
Ahead of the Games, a breakdown of the city’s most desirable places to live
PARIS —Paris has long been a byword for luxurious living. The traditional components of the upscale home, from parquet floors to elaborate moldings, have their origins here. Yet settling down in just the right address in this low-rise, high-density city may be the greatest luxury of all.
Tradition reigns supreme in Paris real estate, where certain conditions seem set in stone—the western half of the city, on either side of the Seine, has long been more expensive than the east. But in the fashion world’s capital, parts of the housing market are also subject to shifting fads. In the trendy, hilly northeast, a roving cool factor can send prices in this year’s hip neighborhood rising, while last year’s might seem like a sudden bargain.
This week, with the opening of the Olympic Games and the eyes of the world turned toward Paris, The Wall Street Journal looks at the most expensive and desirable areas in the City of Light.
The Most Expensive Arrondissement: the 6th
Known for historic architecture, elegant apartment houses and bohemian street cred, the 6th Arrondissement is Paris’s answer to Manhattan’s West Village. Like its New York counterpart, the 6th’s starving-artist days are long behind it. But the charm that first wooed notable residents like Gertrude Stein and Jean-Paul Sartre is still largely intact, attracting high-minded tourists and deep-pocketed homeowners who can afford its once-edgy, now serene atmosphere.
Le Breton George V Notaires, a Paris notary with an international clientele, says the 6th consistently holds the title of most expensive arrondissement among Paris’s 20 administrative districts, and 2023 was no exception. Last year, average home prices reached $1,428 a square foot—almost 30% higher than the Paris average of $1,100 a square foot.
According to Meilleurs Agents, the Paris real estate appraisal company, the 6th is also home to three of the city’s five most expensive streets. Rue de Furstemberg, a secluded loop between Boulevard Saint-Germain and the Seine, comes in on top, with average prices of $2,454 a square foot as of March 2024.
For more than two decades, Kyle Branum, a 51-year-old attorney, and Kimberly Branum, a 60-year-old retired CEO, have been regular visitors to Paris, opting for apartment rentals and ultimately an ownership interest in an apartment in the city’s 7th Arrondissement, a sedate Left Bank district known for its discreet atmosphere and plutocratic residents.
“The 7th was the only place we stayed,” says Kimberly, “but we spent most of our time in the 6th.”
In 2022, inspired by the strength of the dollar, the Branums decided to fulfil a longstanding dream of buying in Paris. Working with Paris Property Group, they opted for a 1,465-square-foot, three-bedroom in a building dating to the 17th century on a side street in the 6th Arrondissement. They paid $2.7 million for the unit and then spent just over $1 million on the renovation, working with Franco-American visual artist Monte Laster, who also does interiors.
The couple, who live in Santa Barbara, Calif., plan to spend about three months a year in Paris, hosting children and grandchildren, and cooking after forays to local food markets. Their new kitchen, which includes a French stove from luxury appliance brand Lacanche, is Kimberly’s favourite room, she says.
Another American, investor Ashley Maddox, 49, is also considering relocating.
In 2012, the longtime Paris resident bought a dingy, overstuffed 1,765-square-foot apartment in the 6th and started from scratch. She paid $2.5 million and undertook a gut renovation and building improvements for about $800,000. A centrepiece of the home now is the one-time salon, which was turned into an open-plan kitchen and dining area where Maddox and her three children tend to hang out, American-style. Just outside her door are some of the city’s best-known bakeries and cheesemongers, and she is a short walk from the Jardin du Luxembourg, the Left Bank’s premier green space.
“A lot of the majesty of the city is accessible from here,” she says. “It’s so central, it’s bananas.” Now that two of her children are going away to school, she has listed the four-bedroom apartment with Varenne for $5 million.
The Most Expensive Neighbourhoods: Notre-Dame and Invalides
Garrow Kedigian is moving up in the world of Parisian real estate by heading south of the Seine.
During the pandemic, the Canada-born, New York-based interior designer reassessed his life, he says, and decided “I’m not going to wait any longer to have a pied-à-terre in Paris.”
He originally selected a 1,130-square-foot one-bedroom in the trendy 9th Arrondissement, an up-and-coming Right Bank district just below Montmartre. But he soon realised it was too small for his extended stays, not to mention hosting guests from out of town.
After paying about $1.6 million in 2022 and then investing about $55,000 in new decor, he put the unit up for sale in early 2024 and went house-shopping a second time. He ended up in the Invalides quarter of the 7th Arrondissement in the shadow of one Paris’s signature monuments, the golden-domed Hôtel des Invalides, which dates to the 17th century and is fronted by a grand esplanade.
His new neighbourhood vies for Paris’s most expensive with the Notre-Dame quarter in the 4th Arrondissement, centred on a few islands in the Seine behind its namesake cathedral. According to Le Breton, home prices in the Notre-Dame neighbourhood were $1,818 a square foot in 2023, followed by $1,568 a square foot in Invalides.
After breaking even on his Right Bank one-bedroom, Kedigian paid $2.4 million for his new 1,450-square-foot two-bedroom in a late 19th-century building. It has southern exposures, rounded living-room windows and “gorgeous floors,” he says. Kedigian, who bought the new flat through Junot Fine Properties/Knight Frank, plans to spend up to $435,000 on a renovation that will involve restoring the original 12-foot ceiling height in many of the rooms, as well as rescuing the ceilings’ elaborate stucco detailing. He expects to finish in 2025.
Over in the Notre-Dame neighbourhood, Belles demeures de France/Christie’s recently sold a 2,370-square-foot, four-bedroom home for close to the asking price of about $8.6 million, or about $3,630 a square foot. Listing agent Marie-Hélène Lundgreen says this places the unit near the very top of Paris luxury real estate, where prime homes typically sell between $2,530 and $4,040 a square foot.
The Most Expensive Suburb: Neuilly-sur-Seine
The Boulevard Périphérique, the 22-mile ring road that surrounds Paris and its 20 arrondissements, was once a line in the sand for Parisians, who regarded the French capital’s numerous suburbs as something to drive through on their way to and from vacation. The past few decades have seen waves of gentrification beyond the city’s borders, upgrading humble or industrial districts to the north and east into prime residential areas. And it has turned Neuilly-sur-Seine, just northwest of the city, into a luxury compound of first resort.
In 2023, Neuilly’s average home price of $1,092 a square foot made the leafy, stately community Paris’s most expensive suburb.
Longtime residents, Alain and Michèle Bigio, decided this year is the right time to list their 7,730-square-foot, four-bedroom townhouse on a gated Neuilly street.
The couple, now in their mid 70s, completed the home in 1990, two years after they purchased a small parcel of garden from the owners next door for an undisclosed amount. Having relocated from a white-marble château outside Paris, the couple echoed their previous home by using white- and cream-coloured stone in the new four-story build. The Bigios, who will relocate just back over the border in the 16th Arrondissement, have listed the property with Emile Garcin Propriétés for $14.7 million.
The couple raised two adult children here and undertook upgrades in their empty-nester years—most recently, an indoor pool in the basement and a new elevator.
The cool, pale interiors give way to dark and sardonic images in the former staff’s quarters in the basement where Alain works on his hobby—surreal and satirical paintings, whose risqué content means that his wife prefers they stay downstairs. “I’m not a painter,” he says. “But I paint.”
The Trendiest Arrondissement: the 9th
French interior designer Julie Hamon is theatre royalty. Her grandfather was playwright Jean Anouilh, a giant of 20th-century French literature, and her sister is actress Gwendoline Hamon. The 52-year-old, who divides her time between Paris and the U.K., still remembers when the city’s 9th Arrondissement, where she and her husband bought their 1,885-square-foot duplex in 2017, was a place to have fun rather than put down roots. Now, the 9th is the place to do both.
The 9th, a largely 19th-century district, is Paris at its most urban. But what it lacks in parks and other green spaces, it makes up with nightlife and a bustling street life. Among Paris’s gentrifying districts, which have been transformed since 2000 from near-slums to the brink of luxury, the 9th has emerged as the clear winner. According to Le Breton, average 2023 home prices here were $1,062 a square foot, while its nearest competitors for the cool crown, the 10th and the 11th, have yet to break $1,011 a square foot.
A co-principal in the Bobo Design Studio, Hamon—whose gut renovation includes a dramatic skylight, a home cinema and air conditioning—still seems surprised at how far her arrondissement has come. “The 9th used to be well known for all the theatres, nightclubs and strip clubs,” she says. “But it was never a place where you wanted to live—now it’s the place to be.”
With their youngest child about to go to college, she and her husband, 52-year-old entrepreneur Guillaume Clignet, decided to list their Paris home for $3.45 million and live in London full-time. Propriétés Parisiennes/Sotheby’s is handling the listing, which has just gone into contract after about six months on the market.
The 9th’s music venues were a draw for 44-year-old American musician and piano dealer, Ronen Segev, who divides his time between Miami and a 1,725-square-foot, two-bedroom in the lower reaches of the arrondissement. Aided by Paris Property Group, Segev purchased the apartment at auction during the pandemic, sight unseen, for $1.69 million. He spent $270,000 on a renovation, knocking down a wall to make a larger salon suitable for home concerts.
During the Olympics, Segev is renting out the space for about $22,850 a week to attendees of the Games. Otherwise, he prefers longer-term sublets to visiting musicians for $32,700 a month.
Most Exclusive Address: Avenue Junot
Hidden in the hilly expanses of the 18th Arrondissement lies a legendary street that, for those in the know, is the city’s most exclusive address. Avenue Junot, a bucolic tree-lined lane, is a fairy-tale version of the city, separate from the gritty bustle that surrounds it.
Homes here rarely come up for sale, and, when they do, they tend to be off-market, or sold before they can be listed. Martine Kuperfis—whose Paris-based Junot Group real-estate company is named for the street—says the most expensive units here are penthouses with views over the whole of the city.
In 2021, her agency sold a 3,230-square-foot triplex apartment, with a 1,400-square-foot terrace, for $8.5 million. At about $2,630 a square foot, that is three times the current average price in the whole of the 18th.
Among its current Junot listings is a 1930s 1,220-square-foot townhouse on the avenue’s cobblestone extension, with an asking price of $2.8 million.
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.






















