Desperate Chinese Property Developers Resort to Bizarre Marketing Tactics
The country’s real-estate slump is getting worse—and looks set to drag on for years
China’s real-estate crisis has dragged down the economy, caused massive layoffs and pushed multibillion-dollar companies to the point of collapse.
Economists think it is about to get worse.
Sales of newly built homes in China fell 6% last year, returning to a level not seen since 2016, according to China’s statistics bureau. Secondhand home prices in its four wealthiest cities—Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou and Shenzhen—declined by between 11% and 14% in December from the year before, according to the broker Centaline Property.
Developers are starting fewer projects. Homeowners are paying back their mortgages early and borrowing less. Once-thriving property companies are stuck in protracted negotiations with foreign investors, following defaults on about $125 billion of overseas bonds between 2020 and late 2023, according to figures from S&P Global Ratings.
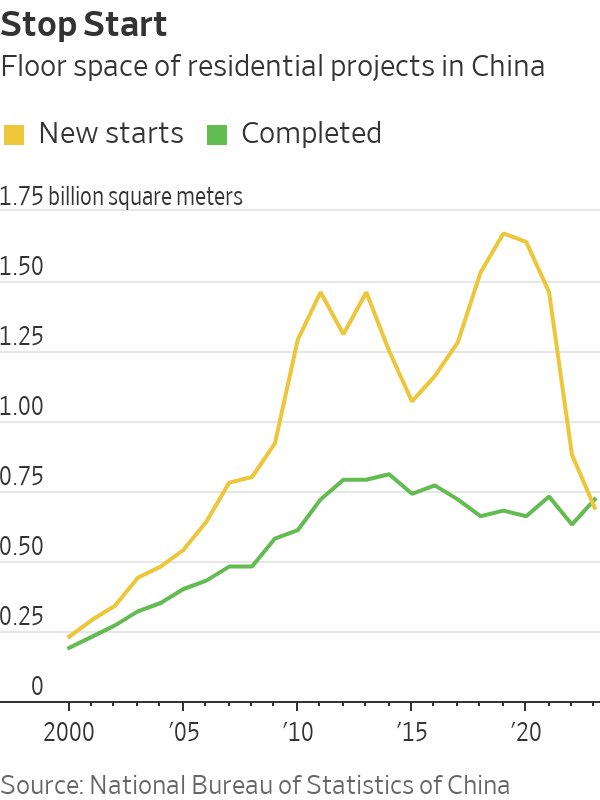
Chinese developers and local governments are so desperate to attract home buyers that some have resorted to bizarre marketing strategies.
A property company in Tianjin ran a video advertisement featuring the slogan “buy a house, get a wife for free.” It was a play on words, using the same Chinese characters as the phrase “buy a house, and give it to your wife”—but presented in a sentence structure typically used to offer freebies for home buyers. In September, the company was fined $4,184 for the ad.
A residential compound in eastern China’s Zhejiang province promised last year to give home buyers a 10-gram gold bar.
Earlier this month, Sheng Songcheng, former head of the statistics department at the People’s Bank of China, told a local conference that the housing downturn would last another two years. He thinks new-home sales will fall more than 5% in both 2024 and 2025.
Wall Street economists are also ringing alarm bells about how long the real-estate slump will last.
“Not too many people are buying, can buy or want to buy,” said Raymond Yeung, chief China economist at ANZ. He said there had been a fundamental shift in the way Chinese people view the property sector, with housing no longer seen as a safe investment.
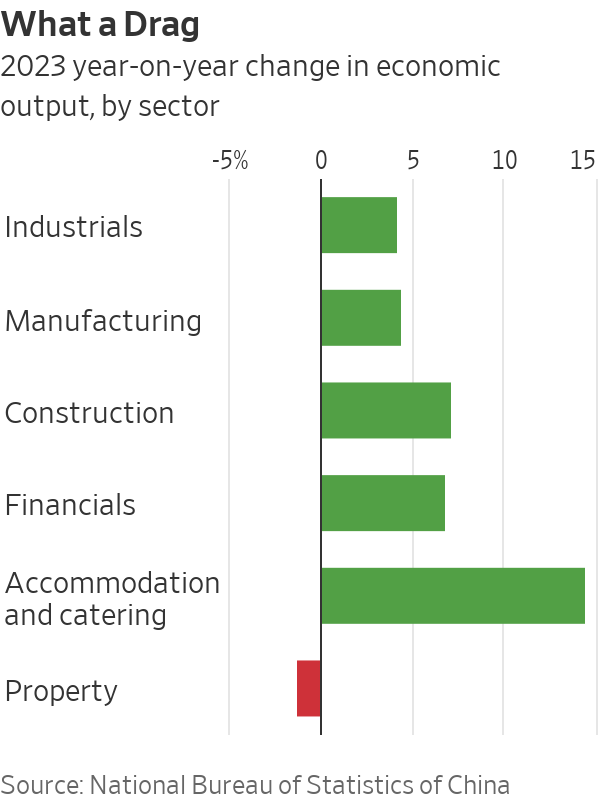
China’s real-estate sector and related industries once accounted for around a quarter of gross domestic product and the sector’s slump has been a significant drag on the world’s second-largest economy. That has increased calls for Beijing to do more to prop up the sector, but so far Chinese officials have stuck to piecemeal policies rather than introducing a landmark stimulus package.
A number of economists are making comparisons to Japan, which spent decades trying to rebound from a crash in real-estate and stock prices. China’s stock market is in a years-long slump.
China’s central bank can help make the situation less painful, but it will need to be aggressive, said Li-gang Liu, head of Asia Pacific economic analysis at Citi Global Wealth Investments. The central bank still has policy room and could take one big step to make a significant impact, he said.
Liu Yuan, head of property research at Centaline, said that without the government’s help, new-home prices will need to drop by another 50% from current levels before they reach a bottom. This is based on the assumption that the tipping point will only come when it is cheaper to buy than to rent houses, Liu said.
China’s real-estate downturn has claimed dozens of victims. More than 50 developers—mostly privately owned—have defaulted on their debt. Developers still have millions of unfinished homes that were sold but not delivered. Chinese authorities have set aside billions of dollars to help builders complete apartments but the logjam is growing.
The crisis has drained the coffers of some Chinese local governments, which previously relied on land sales as a main source of income. Economists estimate they have hidden debt worth anything from $400 billion to more than $800 billion. To quiet talk of potential defaults, the central government has set up debt-swap programs to help some of them refinance.
Some economists are optimistic. In the first half of this year, buyers of secondhand homes will gradually return to the new-home market and prop up the sector, said Helen Qiao, chief China economist at Bank of America. “Things will slowly get better from here,” Qiao said.
But most are still expecting more pain, and investors are bearish. A benchmark of Hong Kong-listed property stocks had fallen for four years in a row before the start of this year. Since Jan. 1, it is down another 15%.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
A Sydney site with a questionable past is reborn as a luxe residential environment ideal for indulging in dining out
Long-term Sydney residents always had handful of not-so-glamourous nicknames for the building on the corner of Cleveland and Baptist Streets straddling Redfern and Surry Hills, but after a modern rebirth that’s all changed.
Once known as “Murder Mall” or “Methadone Mall”, the 1960s-built Surry Hills Shopping Centre was a magnet for colourful characters and questionable behaviour. Today, however, a $500 million facelift of the site — alongside a slow and steady gentrification of the two neighbouring suburbs — the prime corner property has been transformed into a luxury apartment complex Surry Hills Village by developer Toga Group.
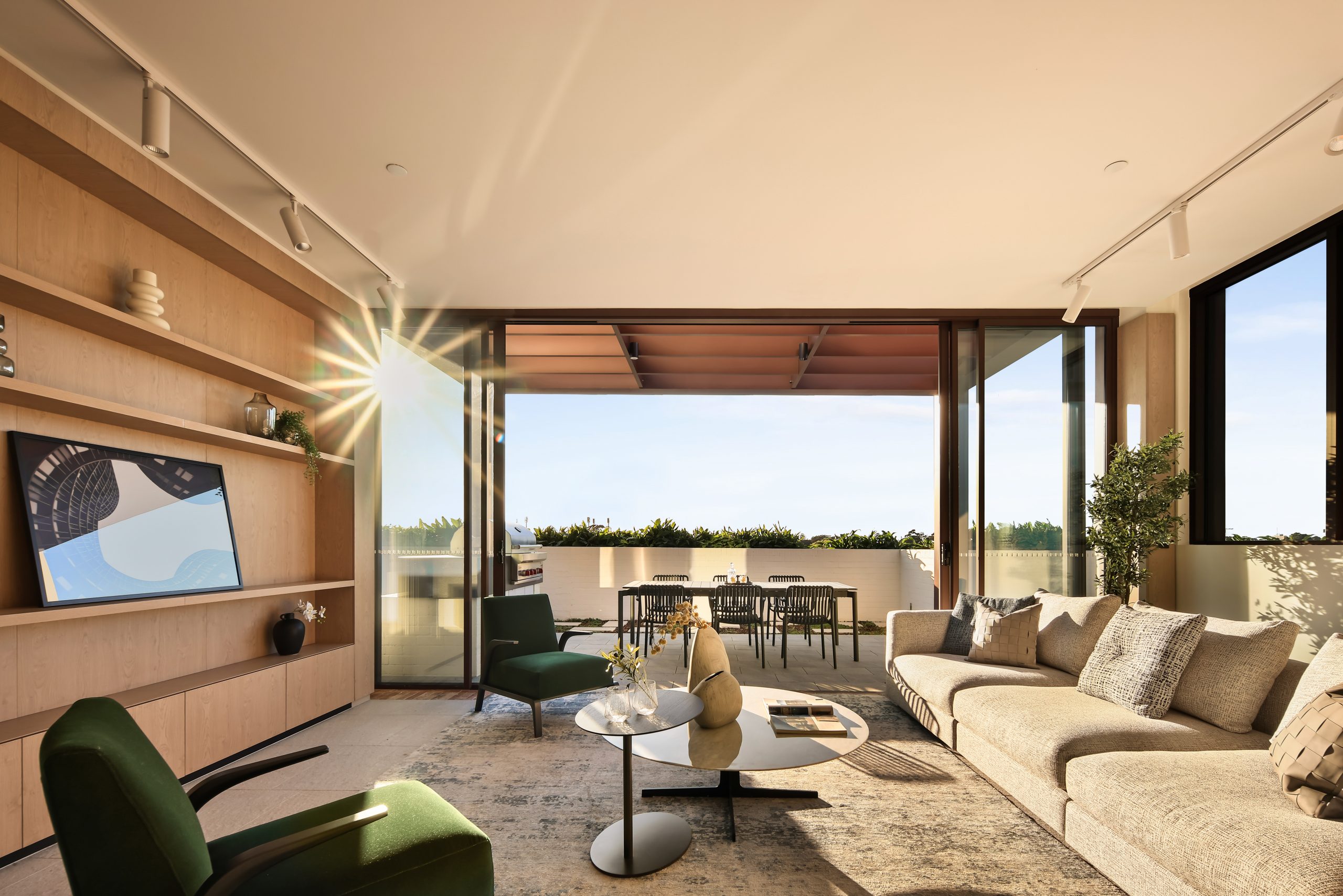
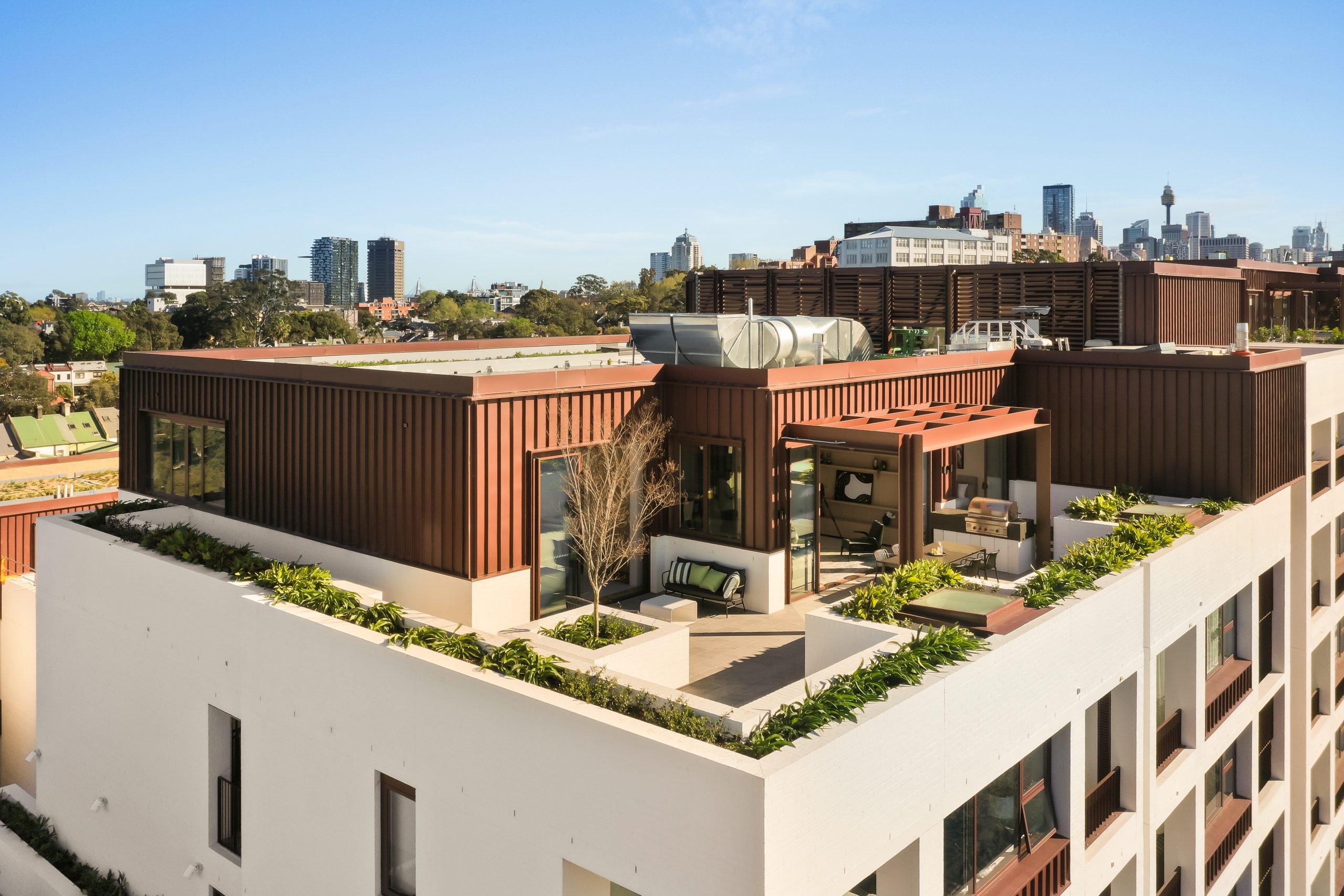
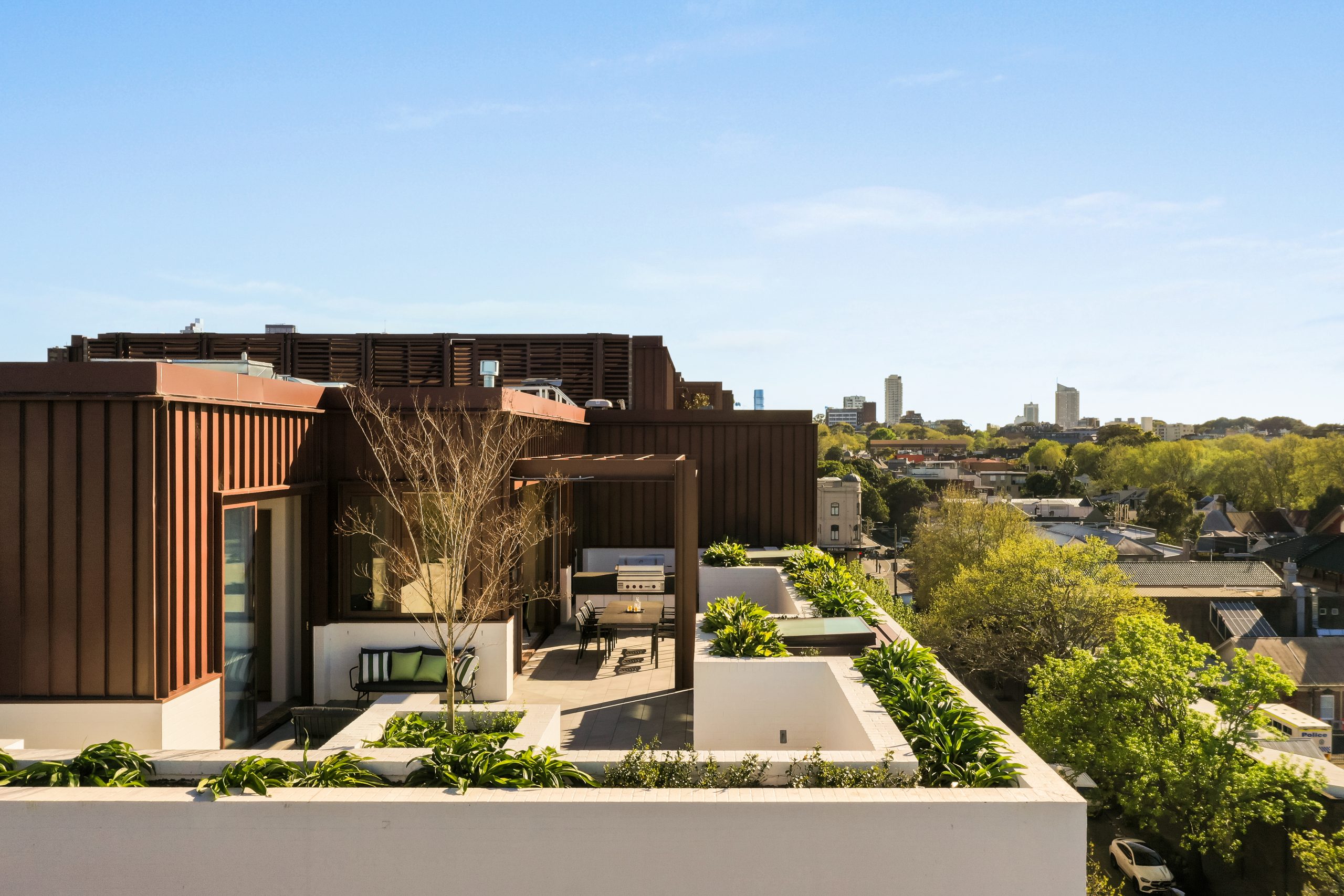
The crowning feature of the 122-apartment project is the three-bedroom penthouse, fully completed and just released to market with a $7.5 million price guide.
Measuring 211sqm of internal space, with a 136sqm terrace complete with landscaping, the penthouse is the brand new brainchild of Surry Hills local Adam Haddow, director of architecture at award-winning firm SJB.
Victoria Judge, senior associate and co-interior design lead at SJB says Surry Hills Village sets a new residential benchmark for the southern end of Surry Hills.
“The residential offering is well-appointed, confident, luxe and bohemian. Smart enough to know what makes good living, and cool enough to hold its own amongst design-centric Surry Hills.”
Allan Vidor, managing director of Toga Group, adds that the penthouse is the quintessential jewel in the crown of Surry Hills Village.
“Bringing together a distinct design that draws on the beauty and vibrancy of Sydney; grand spaces and the finest finishes across a significant footprint, located only a stone’s throw away from the exciting cultural hub of Crown St and Surry Hills.”
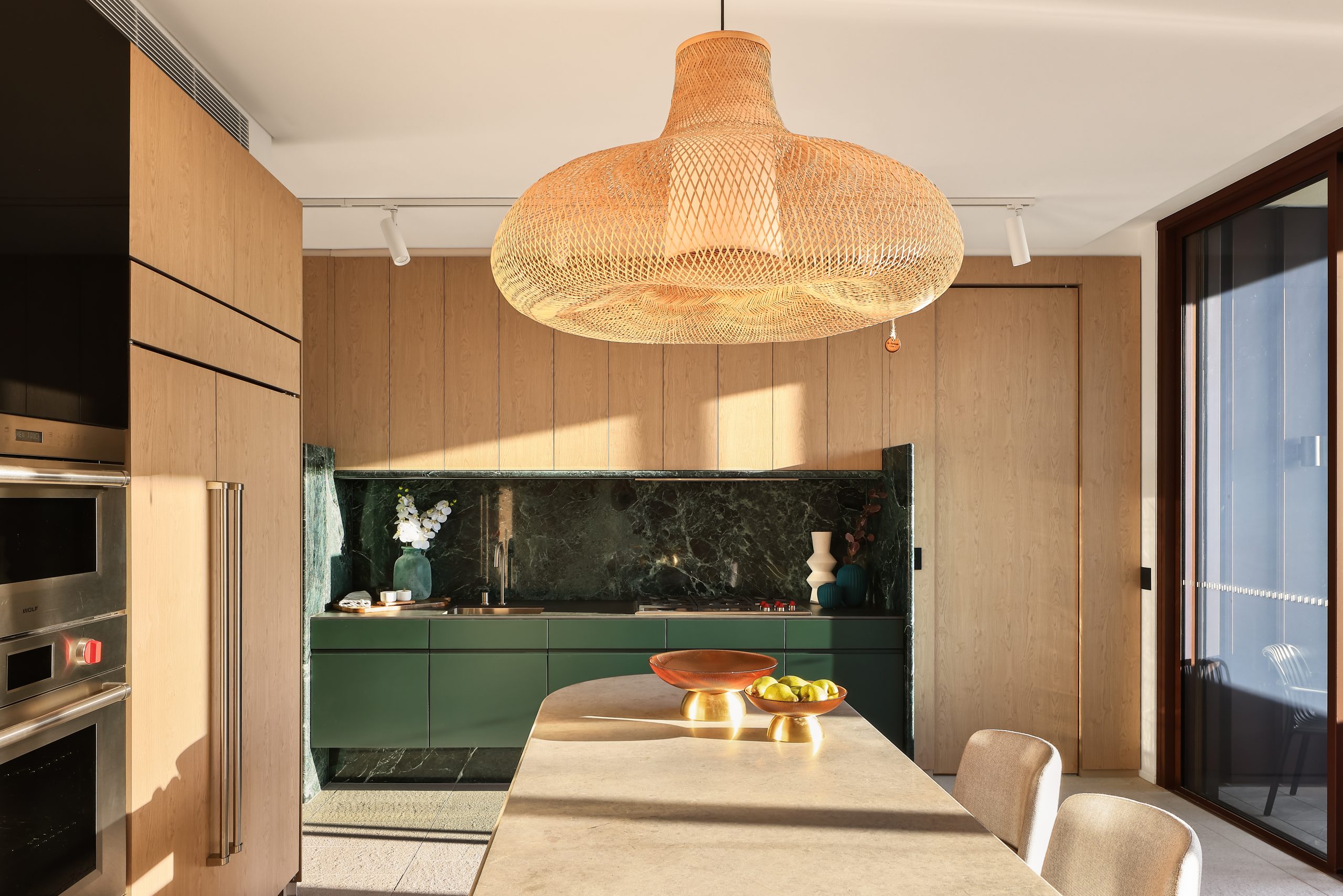
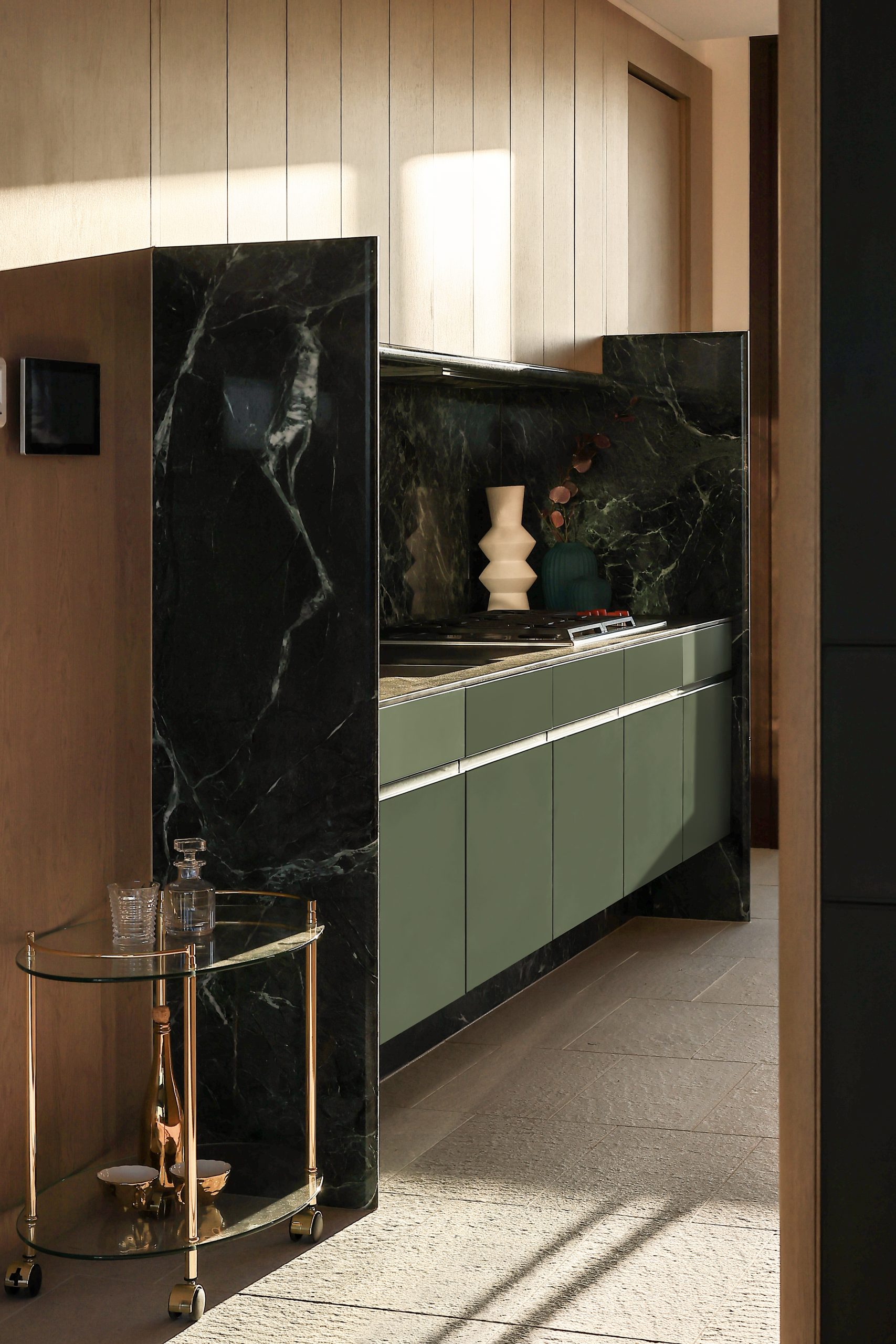
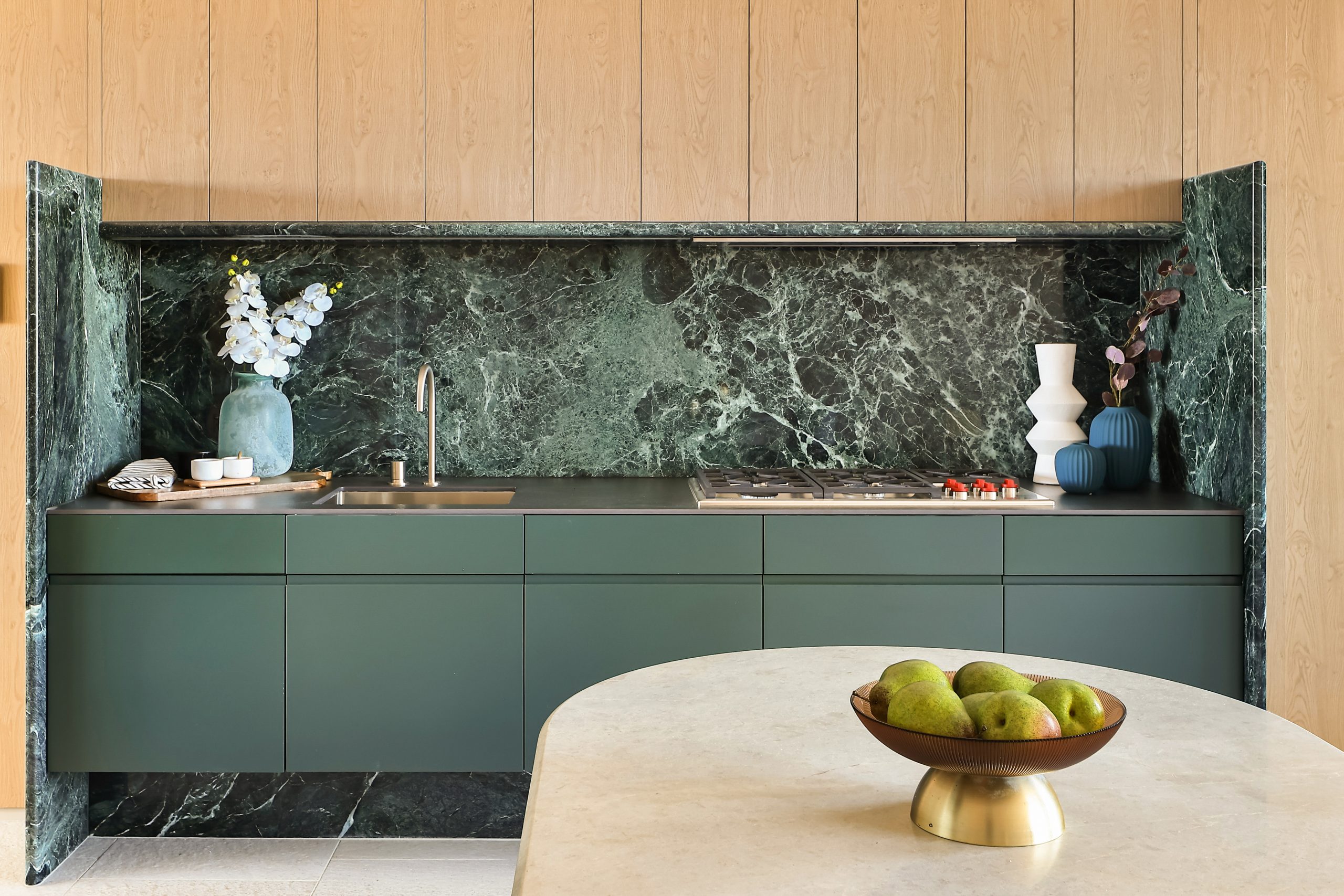
Created to maximise views of the city skyline and parkland, the top floor apartment has a practical layout including a wide private lobby leading to the main living room, a sleek kitchen featuring Pietra Verde marble and a concealed butler’s pantry Sub-Zero Wolf appliances, full-height Aspen elm joinery panels hiding storage throughout, flamed Saville stone flooring, a powder room, and two car spaces with a personal EV.
All three bedrooms have large wardrobes and ensuites with bathrooms fittings such as freestanding baths, artisan penny tiles, emerald marble surfaces and brushed-nickel accents.
Additional features of the entertainer’s home include leather-bound joinery doors opening to a full wet bar with Sub-Zero wine fridge and Sub-Zero Wolf barbecue.
The Surry Hills Village precinct will open in stages until autumn next year and once complete, Wunderlich Lane will be home to a collection of 25 restaurants and bars plus wellness and boutique retail. The EVE Hotel Sydney will open later in 2024, offering guests an immersive experience in the precinct’s art, culture, and culinary offerings.
The Surry Hills Village penthouse on Baptist is now finished and ready to move into with marketing through Toga Group and inquiries to 1800 554 556.
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.



























