Future Returns: Opportunity in Global Healthcare
Strategists at Citi believe the sector is inexpensive and worth a look.
The shares of healthcare companies often aren’t the first to take off when the economy recharges, but strategists at Citi believe the sector is inexpensive and worth a look.
Citi Private Bank shifted a recommendation that investors overweight their stock allocation to global healthcare by 2% to 4% in late April. That means healthcare now represents half of the bank’s recommended 8% overweighting to global stocks, making it a substantial bet.
Typically healthcare “is a more defensive asset,” says David Bailin, chief investment officer and global head of investments at Citi Global Wealth. But the bank is making this bet because “healthcare looks unusually cheap.”
Shares in healthcare companies have risen only by 15% since the end of 2019, including a 5% gain for the year through mid-April—a significant lag to the double-digit gain in the S&P 500 in that time period, according to Cit Private Bank’s April 22 global strategy report. These subdued gains are despite a valuation discount of 25% to the broad S&P 500 index, Citi said.
Also, in the U.S., the sector trades at a 30% forward price-to-earnings ratio discount to the S&P 500, the bank said.
Some of the relative drag on the sector could be related to worries about potential regulation. Proposals mentioned since the Democratic primaries have included regulation of drug prices and an overhaul of the U.S. insurance system, Bailin says.
But, he adds, “talk about actual legislation so far includes increased subsidies to fund long-term care as well as enhancements to the Affordable Care Act subsidy regime—not cutbacks.” There’s also no call for healthcare reform.
“Given that we see the Biden proposal as a ceiling, not a floor, to what can actually be passed in the current Congress, we view the odds of major healthcare regulation that would constrict the growth of healthcare revenues as lower than what the market is currently pricing,” Bailin says.
The reason to tilt to healthcare is to gain exposure to global growth, exposure to stocks with high dividend yields, and exposure to what Citi views as an “unstoppable trend”—the demographic shift within many countries to older populations that have the money to spend on the healthcare they increasingly need.
Penta recently spoke with Bailin about where the opportunities in healthcare are.
Why Is Healthcare Undervalued?
Healthcare historically trades at a lower valuation to the market, but always at a correlated lower valuation. Since the market bottomed in March 2020, however, stocks have been driven to lofty levels by growth sectors, such as technology—a trend that stumbled on Monday as the Dow sank 500 points.
But during this period, over the last 15 months, healthcare stocks “did not inflate,” Bailin says. Their valuations remained “within a channel of normality,” yet relative to everything else, they’re “under-appreciated,” he says.
One interesting note about healthcare is that the sector hasn’t ever had a down year in revenues or earnings—even during the years of the financial crisis, 2008-09—since the late 1980s. “How much would you pay for that consistency? Right now, you’d pay a lot,” Bailin says.
Also, the bank’s strategists note in the April report that the sector has not been a bad place to be when markets slide. “Healthcare has historically fallen the least among market segments during corrections,” the report said.
Which Sectors to Focus On?
In terms of specifically where to invest, Citi wrote that “the long-term case” for spending on healthcare “rests on aging demographics, rising income levels in emerging market countries, and tremendous innovation in vaccines, gene therapy, med-tech, wearables, Alzheimer’s treatments, and much more.”
One company that will benefit from current demographic shifts, for instance, is San Diego-based Dexcom, which develops, makes, and distributes monitoring systems for diabetes.
Biotechnology and biopharmaceutical companies also should benefit, given the important role these companies play in drug discoveries and treatments.
To capture global growth—and high dividend yields—Citi recommends companies such as Chicago-based biopharmaceutical AbbVie (with a 4.5% dividend yield), and companies listed on exchanges outside the U.S., where stocks are slightly less expensive, Bailin says. An example of the latter is Paris-based multinational pharmaceutical company Sanofi, which also has a high dividend yield of 3.7%.
Citi also likes companies creating healthcare delivery systems, such as telehealth—services that allow patients to interact virtually with their health-care practitioners.
“There are a whole bunch of companies that are changing the delivery modality to moving away from the hospital and away from the office,” Bailin says. “We think this will happen with many sectors.”
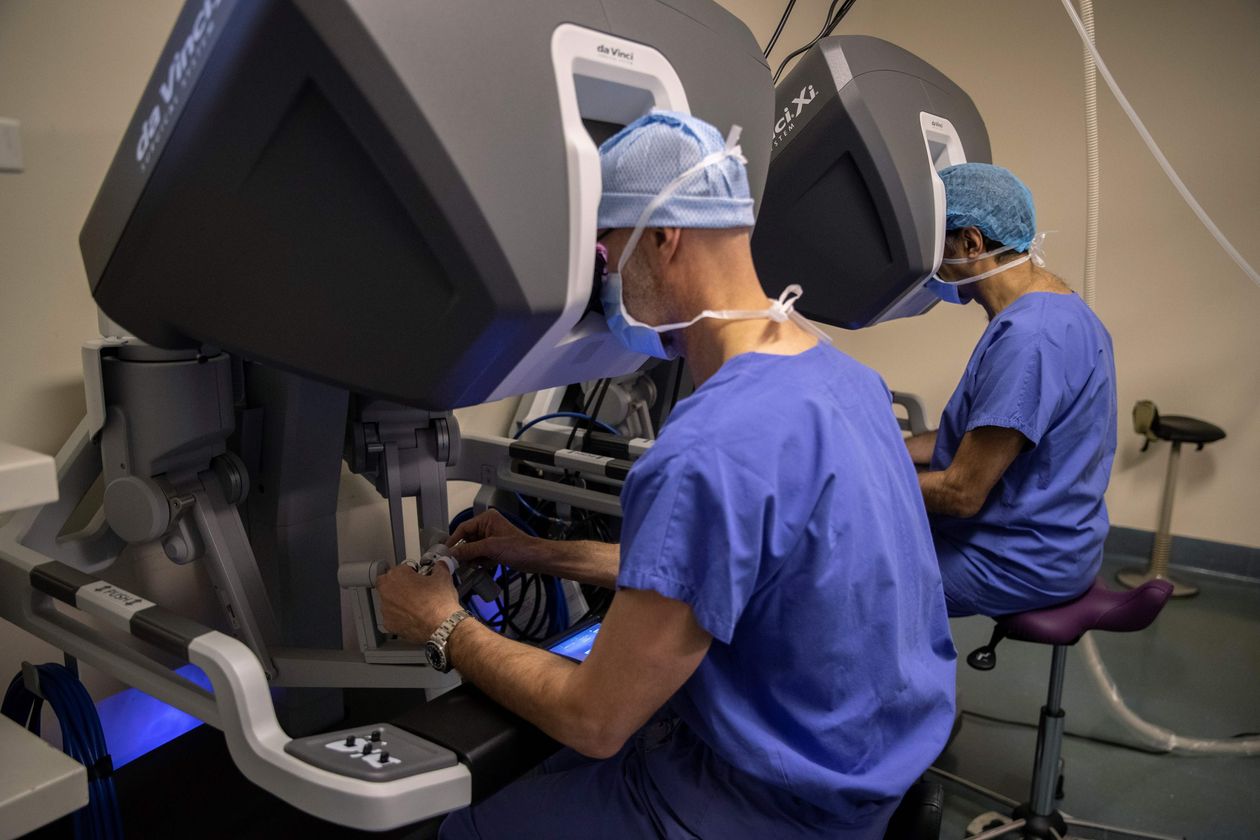
Also worth a look are companies involved in medical devices, robotic surgery, or “anything that creates better decisions,” he says.
Intuitive Surgical, for example, is the leader in robotic-assisted surgeries, Bailin says. It “continues to expand into new surgical indications, and the [total addressable market] is enormous.”
In the wake of the pandemic, Bailin expects some pharmaceutical companies and companies focused on physician-administered therapies and vaccines will get a boost temporarily as people return to the doctor for the first time in more than a year.
“Instances of disease are lower, but it doesn’t mean they actually are lower—they are just not reported,” Bailin says. “We have a bunch of catch-up over the next 12-to-24 months to [get] back to baseline interaction with healthcare providers.”
New Jersey-based Merck, for instance, could benefit “given that its oncology and vaccines are a significant percentage of revenue,” he says.
What About Technology?
While the technology sector had a bad day on Tuesday as the market rotated out of growth stocks, investors may not be ready to abandon hot tech names just yet. In announcing the tactical shift higher in healthcare, Citi noted that investors who followed their recommendation would still have plenty of exposure to technology.
Investors who follow Citi’s recommended 60% allocation to global stocks as defined by the investable MSCI All Country World Index will have 12.6% of their portfolio invested in technology, according to Citi. The recommendation to increase healthcare to a 4% overweight will lead to an 11.2% exposure.
“For decades the sector has carried some modicum of political and headline risk,” Citi wrote. “But that has yet to upend an enviable record of positive revenue growth. Steady revenue growth at a deep valuation discount is the type of script we like.”
Reprinted by permission of Penta. Copyright 2021 Dow Jones & Company. Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. Original date of publication: May 11, 2021
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
As Paris makes its final preparations for the Olympic games, its residents are busy with their own—packing their suitcases, confirming their reservations, and getting out of town.
Worried about the hordes of crowds and overall chaos the Olympics could bring, Parisians are fleeing the city in droves and inundating resort cities around the country. Hotels and holiday rentals in some of France’s most popular vacation destinations—from the French Riviera in the south to the beaches of Normandy in the north—say they are expecting massive crowds this year in advance of the Olympics. The games will run from July 26-Aug. 1.
“It’s already a major holiday season for us, and beyond that, we have the Olympics,” says Stéphane Personeni, general manager of the Lily of the Valley hotel in Saint Tropez. “People began booking early this year.”
Personeni’s hotel typically has no issues filling its rooms each summer—by May of each year, the luxury hotel typically finds itself completely booked out for the months of July and August. But this year, the 53-room hotel began filling up for summer reservations in February.
“We told our regular guests that everything—hotels, apartments, villas—are going to be hard to find this summer,” Personeni says. His neighbours around Saint Tropez say they’re similarly booked up.
As of March, the online marketplace Gens de Confiance (“Trusted People”), saw a 50% increase in reservations from Parisians seeking vacation rentals outside the capital during the Olympics.
Already, August is a popular vacation time for the French. With a minimum of five weeks of vacation mandated by law, many decide to take the entire month off, renting out villas in beachside destinations for longer periods.
But beyond the typical August travel, the Olympics are having a real impact, says Bertille Marchal, a spokesperson for Gens de Confiance.
“We’ve seen nearly three times more reservations for the dates of the Olympics than the following two weeks,” Marchal says. “The increase is definitely linked to the Olympic Games.”

Getty Images
According to the site, the most sought-out vacation destinations are Morbihan and Loire-Atlantique, a seaside region in the northwest; le Var, a coastal area within the southeast of France along the Côte d’Azur; and the island of Corsica in the Mediterranean.
Meanwhile, the Olympics haven’t necessarily been a boon to foreign tourism in the country. Many tourists who might have otherwise come to France are avoiding it this year in favour of other European capitals. In Paris, demand for stays at high-end hotels has collapsed, with bookings down 50% in July compared to last year, according to UMIH Prestige, which represents hotels charging at least €800 ($865) a night for rooms.
Earlier this year, high-end restaurants and concierges said the Olympics might even be an opportunity to score a hard-get-seat at the city’s fine dining.
In the Occitanie region in southwest France, the overall number of reservations this summer hasn’t changed much from last year, says Vincent Gare, president of the regional tourism committee there.
“But looking further at the numbers, we do see an increase in the clientele coming from the Paris region,” Gare told Le Figaro, noting that the increase in reservations has fallen directly on the dates of the Olympic games.
Michel Barré, a retiree living in Paris’s Le Marais neighbourhood, is one of those opting for the beach rather than the opening ceremony. In January, he booked a stay in Normandy for two weeks.
“Even though it’s a major European capital, Paris is still a small city—it’s a massive effort to host all of these events,” Barré says. “The Olympics are going to be a mess.”
More than anything, he just wants some calm after an event-filled summer in Paris, which just before the Olympics experienced the drama of a snap election called by Macron.
“It’s been a hectic summer here,” he says.

AFP via Getty Images
Parisians—Barré included—feel that the city, by over-catering to its tourists, is driving out many residents.
Parts of the Seine—usually one of the most popular summertime hangout spots —have been closed off for weeks as the city installs bleachers and Olympics signage. In certain neighbourhoods, residents will need to scan a QR code with police to access their own apartments. And from the Olympics to Sept. 8, Paris is nearly doubling the price of transit tickets from €2.15 to €4 per ride.
The city’s clear willingness to capitalise on its tourists has motivated some residents to do the same. In March, the number of active Airbnb listings in Paris reached an all-time high as hosts rushed to list their apartments. Listings grew 40% from the same time last year, according to the company.
With their regular clients taking off, Parisian restaurants and merchants are complaining that business is down.
“Are there any Parisians left in Paris?” Alaine Fontaine, president of the restaurant industry association, told the radio station Franceinfo on Sunday. “For the last three weeks, there haven’t been any here.”
Still, for all the talk of those leaving, there are plenty who have decided to stick around.
Jay Swanson, an American expat and YouTuber, can’t imagine leaving during the Olympics—he secured his tickets to see ping pong and volleyball last year. He’s also less concerned about the crowds and road closures than others, having just put together a series of videos explaining how to navigate Paris during the games.
“It’s been 100 years since the Games came to Paris; when else will we get a chance to host the world like this?” Swanson says. “So many Parisians are leaving and tourism is down, so not only will it be quiet but the only people left will be here for a party.”
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.