Here’s a Different Way to Think About Stock Diversification
Everybody knows to spread money across many investments. Fewer think about diversifying over time.
Investors often think of diversification as a free lunch—it allows them to maintain returns while reducing risk. But most people only get part of diversification right, and that can hurt them later in life.
With traditional diversification, people spread money around different kinds of investments to mitigate risk. That approach misses a key opportunity: “diversifying” how you invest over time.
Most people start investing with a small amount of money, because that is all they can afford, and ramp it up as their earnings grow. But investing so much later in life unnecessarily puts people at greater risk when they are close to retirement. They end up with far greater exposure to stock-market risk in their 50s and 60s than in their 20s and 30s, even if they are buying diversified mutual funds.
We propose a different method: People ought to borrow money to make their initial investments larger, so that they can invest closer to the same amount every year over their lifetime. Think of investing $2 a decade steadily for three decades, instead of $1 for the first, $2 for the next and $3 for the third.
The overall amount they invest stays the same—$2 of average market exposure—but when it is a steady amount, instead of an increasing one, the market exposure is larger than otherwise earlier on ($2 versus $1) and then smaller than otherwise in later life ($2 versus $3).
Steady dollars
Both choices—investing $2 each decade instead of $1, $2 and $3—provide the same expected return, since they both have $6 accumulated market exposure over time. But risks associated with the two strategies are different: Our time-diversified path brings lower variance in returns than one with increasing investments.
When investment exposure varies over time, the market’s ups and downs don’t balance out as well. With 2/2/2, an up in the first decade balances out with a down in the third, and vice versa. But with 1/2/3, an up in the first decade is dominated by a down in the third, and a down in the first decade is also dominated by an up in the third. Consequently, the 1/2/3 investment pattern leads to larger swings in lifetime accumulations. The 1/2/3 strategy has too little dependence on the first decade’s stock return and too much on the third. By comparison, the 2/2/2 approach is evenly spread out and thus better diversified.
People might think they can’t follow a 2/2/2 type of strategy because they haven’t saved enough when young: They can’t invest $2 because they only have $1. But that’s not true. Using leverage—that is, borrowing money to buy stocks—people can use $1 of capital to borrow another $1 and thereby get $2 of market exposure in their first decade.
Sound risky? Consider that young people do the same thing with housing when they borrow money to buy a house they live in for decades—and there the leverage often involves borrowing $9 for every $1 of equity. We propose borrowing only $1 for each $1 invested. Limiting ourselves to 2:1 leverage means we don’t hit a perfectly even market exposure over time, but gets us closer to that ideal.
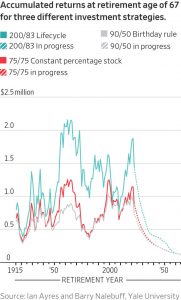
The lessons of history
Using an initial 200% allocation—and gradually reducing the allocation to stocks over time, down to 83% at retirement age—is a winning strategy. In a 2010 book, we found that this “leveraged life cycle” approach produced superior retirement accumulation for each and every cohort retiring from 1914 to 2009. We now have more than a dozen years of post-publication returns where we can evaluate how the strategy actually worked in practice. Leveraged life-cycle returns have continued to provide superior retirement accumulation for each and every cohort through mid-2022.
Average investors using our method—assuming they invested 4% of their annual income, which rose during their careers to $100,000 in their final year of work—accumulated $1,255,000, while a traditional target-date fund investment, starting at 90% stocks and going down to 50%, produced only $675,000, and a constant 75% strategy led to $774,000.
Of course, these higher returns are partly due to more stock exposure and not to the diversifying benefits of the leveraged life-cycle strategy. To focus solely on the diversification benefits, we compared the retirement accumulations of a less-aggressive life-cycle strategy, one that again starts with 200% in stock but ramps down to 50% at retirement. We compared this to a constant 75% of savings in stocks and 25% in bonds. We chose this particular 75% allocation because it produces the same average accumulation ($774,000) across the retiring cohorts. Therefore, any difference in the strategies won’t be because one has more lifetime exposure to the stocks, which on average outperform bonds.
Comparing these two strategies shows that the leveraged life-cycle strategy decreases the standard deviation of retirement accumulation across retiring cohorts by an impressive 19%. Our more time-diversified, leveraged strategy produces higher returns for cohorts that experienced the worst stock returns (the 10th-percentile accumulation increases by 10.9% relative to the constant 75% strategy) and lower returns for cohorts that lived through the best stock returns (the 90th-percentile accumulation also decreases by 10.9% relative to the constant 75% strategy).
Producing the same average return with less risk is compelling evidence of how a leveraged life-cycle strategy can diversify market risk. Of course, ramping down to 50% instead of 83% in stocks at retirement has less market exposure and therefore lower average returns. The investor can choose: the same returns as a constant 75% exposure strategy with less risk, or the same risk but with higher expected return. Time diversification makes either possible.
Avoiding trouble
Our strategy works in theory and in practice. But there are possible objections that might hold people back.
For one, people might say that it is expensive to invest on margin. But competitive margin loans are cheaper than home mortgages (though you may need to consider online brokerages).
A second objection is that leverage is risky. But when you are more evenly exposed to market risk across time, you have less risk. Using leverage to go from 1/2/3 to 2/4/6 would be adding risk and market exposure. But a 2/2/2 strategy doesn’t.
When markets drop, those investors near retirement who have followed 1/2/3 are in trouble. If stocks fall by 25% in their last decade of investing, they would lose 25% of their $3 investment—while a 2/2/2 investor would lose just 25% of $2. That is a 50% greater loss on the $3 investment.
One objection that does have some merit is that our approach requires discipline. Some people can’t bring themselves to borrow money to buy stock or would bail out at the first downturn in the market. We would like to see target-date funds make things easier for investors by automating the process, borrowing at low cost and automatically adjusting a portfolio. People could put in money each month and forget about it.
Meantime, young investors can move to 100% equities. That isn’t 200%, but it is a step in the right direction and doesn’t require the psychological or logistical burdens of borrowing to buy. And even if this advice is coming a bit late for readers in their 50s and 60s, this is advice to pass along to the next generation. They don’t have to repeat our mistakes.
Dr. Ayres is the William Townsend professor at Yale Law School, and Dr. Nalebuff is the Milton Steinbach professor at the Yale School of Management. Together, they are the authors of “Lifecycle Investing.”
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
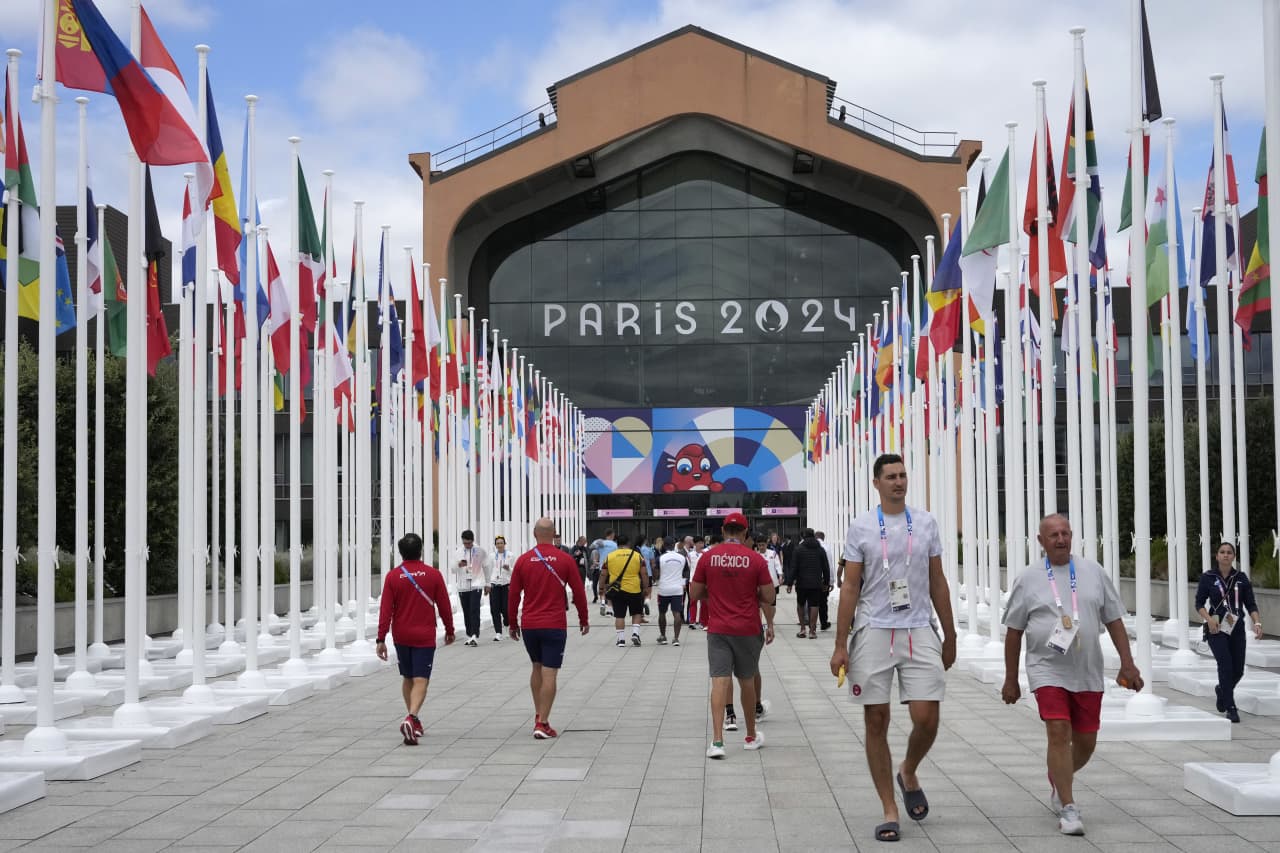
As Paris makes its final preparations for the Olympic games, its residents are busy with their own—packing their suitcases, confirming their reservations, and getting out of town.
Worried about the hordes of crowds and overall chaos the Olympics could bring, Parisians are fleeing the city in droves and inundating resort cities around the country. Hotels and holiday rentals in some of France’s most popular vacation destinations—from the French Riviera in the south to the beaches of Normandy in the north—say they are expecting massive crowds this year in advance of the Olympics. The games will run from July 26-Aug. 1.
“It’s already a major holiday season for us, and beyond that, we have the Olympics,” says Stéphane Personeni, general manager of the Lily of the Valley hotel in Saint Tropez. “People began booking early this year.”
Personeni’s hotel typically has no issues filling its rooms each summer—by May of each year, the luxury hotel typically finds itself completely booked out for the months of July and August. But this year, the 53-room hotel began filling up for summer reservations in February.
“We told our regular guests that everything—hotels, apartments, villas—are going to be hard to find this summer,” Personeni says. His neighbours around Saint Tropez say they’re similarly booked up.
As of March, the online marketplace Gens de Confiance (“Trusted People”), saw a 50% increase in reservations from Parisians seeking vacation rentals outside the capital during the Olympics.
Already, August is a popular vacation time for the French. With a minimum of five weeks of vacation mandated by law, many decide to take the entire month off, renting out villas in beachside destinations for longer periods.
But beyond the typical August travel, the Olympics are having a real impact, says Bertille Marchal, a spokesperson for Gens de Confiance.
“We’ve seen nearly three times more reservations for the dates of the Olympics than the following two weeks,” Marchal says. “The increase is definitely linked to the Olympic Games.”

Getty Images
According to the site, the most sought-out vacation destinations are Morbihan and Loire-Atlantique, a seaside region in the northwest; le Var, a coastal area within the southeast of France along the Côte d’Azur; and the island of Corsica in the Mediterranean.
Meanwhile, the Olympics haven’t necessarily been a boon to foreign tourism in the country. Many tourists who might have otherwise come to France are avoiding it this year in favour of other European capitals. In Paris, demand for stays at high-end hotels has collapsed, with bookings down 50% in July compared to last year, according to UMIH Prestige, which represents hotels charging at least €800 ($865) a night for rooms.
Earlier this year, high-end restaurants and concierges said the Olympics might even be an opportunity to score a hard-get-seat at the city’s fine dining.
In the Occitanie region in southwest France, the overall number of reservations this summer hasn’t changed much from last year, says Vincent Gare, president of the regional tourism committee there.
“But looking further at the numbers, we do see an increase in the clientele coming from the Paris region,” Gare told Le Figaro, noting that the increase in reservations has fallen directly on the dates of the Olympic games.
Michel Barré, a retiree living in Paris’s Le Marais neighbourhood, is one of those opting for the beach rather than the opening ceremony. In January, he booked a stay in Normandy for two weeks.
“Even though it’s a major European capital, Paris is still a small city—it’s a massive effort to host all of these events,” Barré says. “The Olympics are going to be a mess.”
More than anything, he just wants some calm after an event-filled summer in Paris, which just before the Olympics experienced the drama of a snap election called by Macron.
“It’s been a hectic summer here,” he says.

AFP via Getty Images
Parisians—Barré included—feel that the city, by over-catering to its tourists, is driving out many residents.
Parts of the Seine—usually one of the most popular summertime hangout spots —have been closed off for weeks as the city installs bleachers and Olympics signage. In certain neighbourhoods, residents will need to scan a QR code with police to access their own apartments. And from the Olympics to Sept. 8, Paris is nearly doubling the price of transit tickets from €2.15 to €4 per ride.
The city’s clear willingness to capitalise on its tourists has motivated some residents to do the same. In March, the number of active Airbnb listings in Paris reached an all-time high as hosts rushed to list their apartments. Listings grew 40% from the same time last year, according to the company.
With their regular clients taking off, Parisian restaurants and merchants are complaining that business is down.
“Are there any Parisians left in Paris?” Alaine Fontaine, president of the restaurant industry association, told the radio station Franceinfo on Sunday. “For the last three weeks, there haven’t been any here.”
Still, for all the talk of those leaving, there are plenty who have decided to stick around.
Jay Swanson, an American expat and YouTuber, can’t imagine leaving during the Olympics—he secured his tickets to see ping pong and volleyball last year. He’s also less concerned about the crowds and road closures than others, having just put together a series of videos explaining how to navigate Paris during the games.
“It’s been 100 years since the Games came to Paris; when else will we get a chance to host the world like this?” Swanson says. “So many Parisians are leaving and tourism is down, so not only will it be quiet but the only people left will be here for a party.”
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.






















