IKEA’s Latest Climate Target: Glue
The furniture group has spent more than a decade working to replace a fossil-based glue that represents 5% of its global carbon footprint
Swedish furniture brand IKEA is switching to a new glue to help meet its climate goals, underscoring how small changes can make a measurable impact.
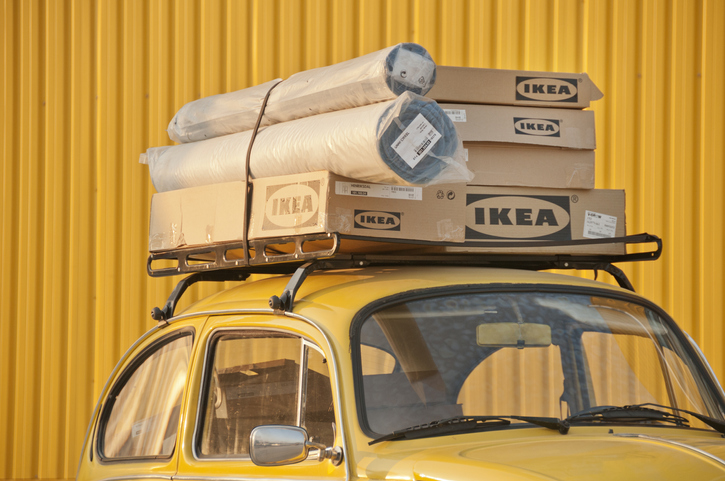
Inter IKEA—which owns the IKEA brand, develops its products and manages its supply chain—said around 5% of its value chain’s carbon footprint comes from fossil-based glue in its particle-and-fiber boards, used in products such as cupboards, wardrobes and shelves. It said Wednesday that it is aiming to eliminate 40% of its fossil-based glue in the boards by fiscal 2030, which could cut its greenhouse-gas emissions by 1.5 percentage points, depending on future business growth.
A factory in Kazlu Ruda, Lithuania will be the first to use a biobased glue made from corn in industrial plants rather than the food chain. IKEA is also trialing other biobased glues. The changes are part of IKEA’s efforts to meet its goal to use only renewable or recycled materials by fiscal 2030.
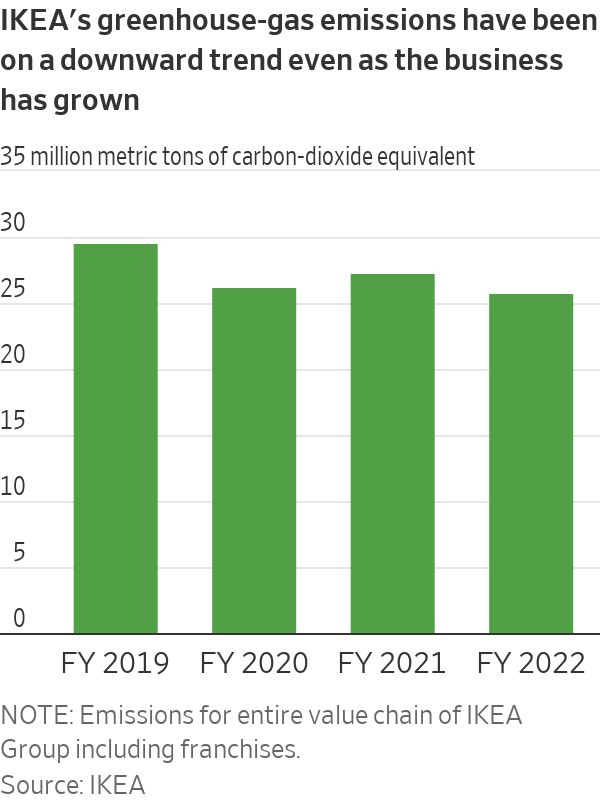
“It’s not an easy transformation. We are talking about the industry using the same glues for 60 years and that glue has been optimized for performance and cost for 60 years,” said Venla Hemmilä, material and technology engineer at IKEA of Sweden.
IKEA began searching for alternatives to fossil-based glue more than a decade ago, but found lower carbon, biobasedoptions were too expensive and the industry wasn’t well prepared to supplythem. Today, there is still a premium for biobased glues but it isn’t expected to be passed onto shoppers and should come down as production scales up.
The company expects biomaterials to become more cost competitive with fossil-based materials in the coming years. IKEA hopes its manufacturing footprint will accelerate that cost reduction of greener alternatives and that other companies will follow its lead. It declined to provide the names of the green glue suppliers for competitive reasons.
Glue became a focus for the group after 2016. That year IKEA examined how its climate goals aligned with the Paris Agreement and charted how they could expand the business while cutting their emissions, said Andreas Rangel Ahrens, head of climate at Inter IKEA Group.
“It is so easy to set goals, but how do you actually understand the impact and what to drive?,” Mr. Rangel Ahrens said.
To address that challenge, Mr. Rangel Ahrens said IKEA carried out a breakdown analysis of the sources of its carbon footprint, including production, materials and food. It also enlisted consultants to conduct life-cycle assessments of certain materials. In the 2022 financial year, IKEA said 52% of its emissions came from the materials in its products, the next highest contribution was 14% from people using its products at home, followed by production, which was responsible for around 8%.
Companies often use spending metrics, such as purchased goods, to calculate the carbon footprint of their materials. Instead, Mr. Rangel Ahrens said IKEA uses weight because it allows them to measure changes in a material, such as recycled and renewable content.
For example, when IKEA looked at its particle-and-fiber boards, it estimated the emissions coming from transport, forestry and energy, among other areas. It discovered around half of the material’s emissions were from the glue used to bind the wood chips and fibers together, meaning that fossil-based glue was responsible for about 5% of IKEA’s carbon footprint, Mr. Rangel Ahrens said.
This detailed approach to break down a product’s footprint allows sustainability teams to identify specific areas for other parts of the business to work on. “We are not just telling them you should reduce emissions from suppliers by 80% and go fish,” Mr. Rangel Ahrens said. We tell them where to focus and then they actually know what to do rather than just getting a very ambitious goal dropped on their laps, he said.
The company has also reduced emissionswith other targeted changes, including plant-based meatballs, a bookcase that uses paper foil instead of veneer, and switching to LED lightbulbs. It is also exploring how to add biobased content into coatings.
“It’s very important for us that sustainability is not a luxury for the few. It needs to be available also for people with thin wallets,” Mr. Rangel Ahrens said.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
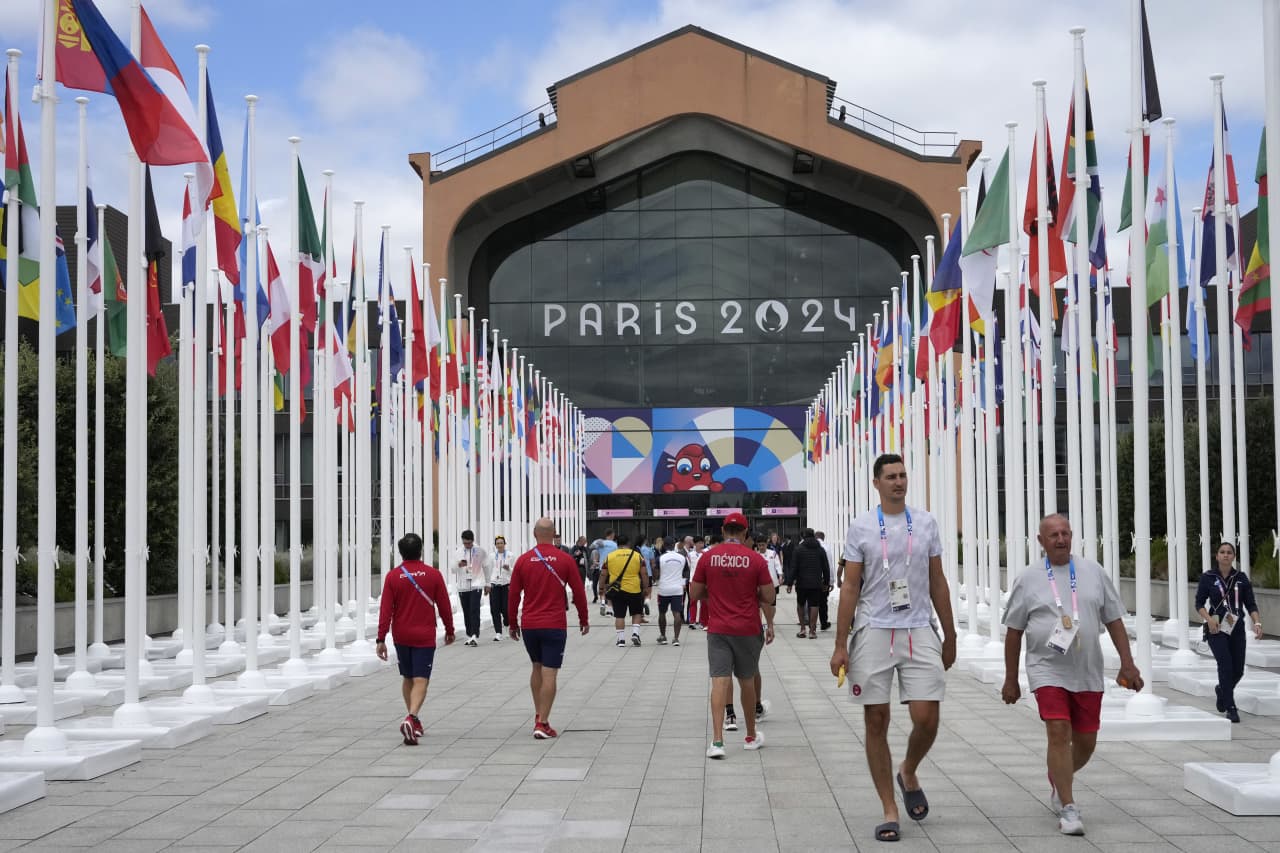
As Paris makes its final preparations for the Olympic games, its residents are busy with their own—packing their suitcases, confirming their reservations, and getting out of town.
Worried about the hordes of crowds and overall chaos the Olympics could bring, Parisians are fleeing the city in droves and inundating resort cities around the country. Hotels and holiday rentals in some of France’s most popular vacation destinations—from the French Riviera in the south to the beaches of Normandy in the north—say they are expecting massive crowds this year in advance of the Olympics. The games will run from July 26-Aug. 1.
“It’s already a major holiday season for us, and beyond that, we have the Olympics,” says Stéphane Personeni, general manager of the Lily of the Valley hotel in Saint Tropez. “People began booking early this year.”
Personeni’s hotel typically has no issues filling its rooms each summer—by May of each year, the luxury hotel typically finds itself completely booked out for the months of July and August. But this year, the 53-room hotel began filling up for summer reservations in February.
“We told our regular guests that everything—hotels, apartments, villas—are going to be hard to find this summer,” Personeni says. His neighbours around Saint Tropez say they’re similarly booked up.
As of March, the online marketplace Gens de Confiance (“Trusted People”), saw a 50% increase in reservations from Parisians seeking vacation rentals outside the capital during the Olympics.
Already, August is a popular vacation time for the French. With a minimum of five weeks of vacation mandated by law, many decide to take the entire month off, renting out villas in beachside destinations for longer periods.
But beyond the typical August travel, the Olympics are having a real impact, says Bertille Marchal, a spokesperson for Gens de Confiance.
“We’ve seen nearly three times more reservations for the dates of the Olympics than the following two weeks,” Marchal says. “The increase is definitely linked to the Olympic Games.”

Getty Images
According to the site, the most sought-out vacation destinations are Morbihan and Loire-Atlantique, a seaside region in the northwest; le Var, a coastal area within the southeast of France along the Côte d’Azur; and the island of Corsica in the Mediterranean.
Meanwhile, the Olympics haven’t necessarily been a boon to foreign tourism in the country. Many tourists who might have otherwise come to France are avoiding it this year in favour of other European capitals. In Paris, demand for stays at high-end hotels has collapsed, with bookings down 50% in July compared to last year, according to UMIH Prestige, which represents hotels charging at least €800 ($865) a night for rooms.
Earlier this year, high-end restaurants and concierges said the Olympics might even be an opportunity to score a hard-get-seat at the city’s fine dining.
In the Occitanie region in southwest France, the overall number of reservations this summer hasn’t changed much from last year, says Vincent Gare, president of the regional tourism committee there.
“But looking further at the numbers, we do see an increase in the clientele coming from the Paris region,” Gare told Le Figaro, noting that the increase in reservations has fallen directly on the dates of the Olympic games.
Michel Barré, a retiree living in Paris’s Le Marais neighbourhood, is one of those opting for the beach rather than the opening ceremony. In January, he booked a stay in Normandy for two weeks.
“Even though it’s a major European capital, Paris is still a small city—it’s a massive effort to host all of these events,” Barré says. “The Olympics are going to be a mess.”
More than anything, he just wants some calm after an event-filled summer in Paris, which just before the Olympics experienced the drama of a snap election called by Macron.
“It’s been a hectic summer here,” he says.

AFP via Getty Images
Parisians—Barré included—feel that the city, by over-catering to its tourists, is driving out many residents.
Parts of the Seine—usually one of the most popular summertime hangout spots —have been closed off for weeks as the city installs bleachers and Olympics signage. In certain neighbourhoods, residents will need to scan a QR code with police to access their own apartments. And from the Olympics to Sept. 8, Paris is nearly doubling the price of transit tickets from €2.15 to €4 per ride.
The city’s clear willingness to capitalise on its tourists has motivated some residents to do the same. In March, the number of active Airbnb listings in Paris reached an all-time high as hosts rushed to list their apartments. Listings grew 40% from the same time last year, according to the company.
With their regular clients taking off, Parisian restaurants and merchants are complaining that business is down.
“Are there any Parisians left in Paris?” Alaine Fontaine, president of the restaurant industry association, told the radio station Franceinfo on Sunday. “For the last three weeks, there haven’t been any here.”
Still, for all the talk of those leaving, there are plenty who have decided to stick around.
Jay Swanson, an American expat and YouTuber, can’t imagine leaving during the Olympics—he secured his tickets to see ping pong and volleyball last year. He’s also less concerned about the crowds and road closures than others, having just put together a series of videos explaining how to navigate Paris during the games.
“It’s been 100 years since the Games came to Paris; when else will we get a chance to host the world like this?” Swanson says. “So many Parisians are leaving and tourism is down, so not only will it be quiet but the only people left will be here for a party.”
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.






















