As Americans Work From Home, Europeans and Asians Head Back to the Office
Return-to-office rates in Paris and Tokyo have climbed to over 75%, while U.S. often sits around half
While U.S. offices are half empty three years into the Covid-19 pandemic, workplaces in Europe and Asia are bustling again.
Americans have embraced remote work and turned their backs on offices with greater regularity than their counterparts overseas. U.S. office occupancy stands at 40% to 60% of prepandemic levels, varying within that range by month and by city. That compares with a 70%-to-90% rate in Europe and the Middle East, according to JLL, a property-services firm that manages 4.6 billion square feet of real estate globally.
Return to office was even more common in Asia, JLL said, where rates ranged from 80% to 110%—meaning that in some cities more people are in the office nowadays than before the pandemic.
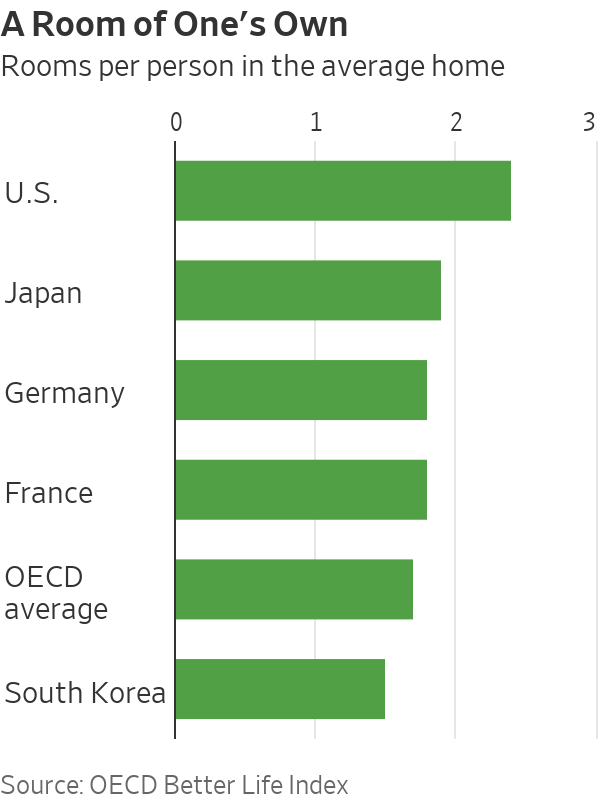
Bigger homes, longer commutes and a tighter labor market help explain why Americans spend less time in the office than Europeans and Asians, workplace consultants say.
This divergence in return-to-office habits not only benefits overseas landlords more than their U.S. peers. It has a direct impact on how quickly metro areas rebound from the pandemic’s economic shock. Cities in Europe and Asia have bounced back relatively well. But empty office buildings and missing commuters have undermined recoveries in U.S. cities such as New York and San Francisco, where local restaurants, shops and other businesses that rely on office workers as their primary customers have suffered.
The number of unemployed in New York City increased by 83,500 between early 2020 and the third quarter of 2022 as the city’s unemployment rate surged far above the national average, according to a report by the New School Center for New York City Affairs. Many of those who lost their jobs worked in Manhattan in face-to-face industries such as retail, accommodation and food services.
While Manhattan has been particularly hard hit because of its dependence on office commuters, other U.S. central business districts are also struggling. Falling office values are threatening to hit city budgets that depend on property taxes. Lower transit ridership is weighing on the finances of public-transportation authorities. Adding more apartments can help revitalise central business districts, but that will take time.
Several overseas capitals experienced periods where more than 75% of their workers were back at their desks in 2021 and 2022, JLL said. That includes Tokyo, Seoul and Singapore in Asia. Paris regularly topped the list of workers back in the office in Europe. Stockholm wasn’t far behind with several months at a more-than-75% return-to-office rate.
No major U.S. city tracked by JLL achieved that high a return rate during the period.
“The U.S. has borne the brunt of this,” said Phil Ryan, director of city futures at JLL.
Living arrangements are one reason for the difference in work habits. Americans are more likely to live in spacious suburban houses. That makes it easier to set up a home office away from distractions. Hong Kong’s small apartments, for example, often house multiple generations, making working from home less appealing.
Suburban sprawl means many Americans have longer, more tedious commutes plagued by worsening traffic jams—another reason to stay home. While a number of European cities also have long average commutes, New York and Chicago are unmatched, according to mobility-services company Moovit Inc. Public-transit systems in Europe and Asia are often more reliable and less prone to delays, making it easier to get to work.
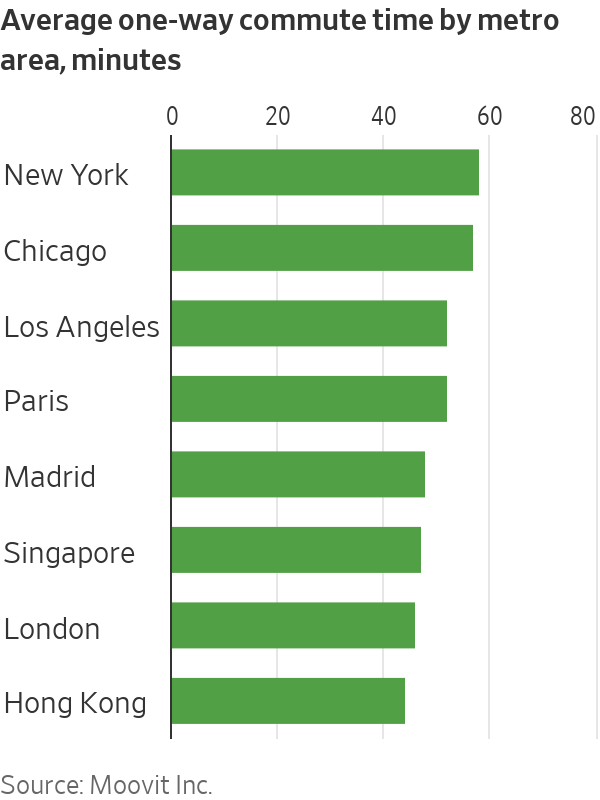
“We have high-density cities with effective public-transport systems,” said Caroline Pontifex, London-based director of workplace experience at consulting firm KKS Savills. “That makes a difference.”
Another explanation for America’s office exceptionalism is its labor market. At 3.4%, the U.S. unemployment rate is barely more than half the European Union’s unemployment rate of 6.1%. While Europe is also facing labor shortages, U.S. companies have been particularly hard hit, said JLL’s Mr. Ryan.
That has forced them to look farther afield for employees and hire remotely. Tech firms, which account for a particularly high share of employment in some big U.S. cities, have long been more tolerant of remote work.
Co-working companies are also reporting lower occupancy in some U.S. cities. WeWork Inc. said 72% of its desks in New York were leased as of the fourth quarter of 2022, compared with 80% in Paris, 81% in London and 82% in Singapore.
Workplace consultants say they expect the office-use gap between the U.S. and the rest of the world to persist.
It doesn’t help that U.S. offices were emptier long before the pandemic. A construction glut led to high vacancy rates, and even within leased offices companies tended to put fewer people on each floor than their European and Asian peers.
All that empty space is now creating a negative reinforcing cycle, said Phil Kirschner, an associate partner at business consulting company McKinsey & Co. Americans sitting in big, mostly empty offices find the experience depressing, making them more likely to stay at home in the first place. “It feels less energetic,” he said.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
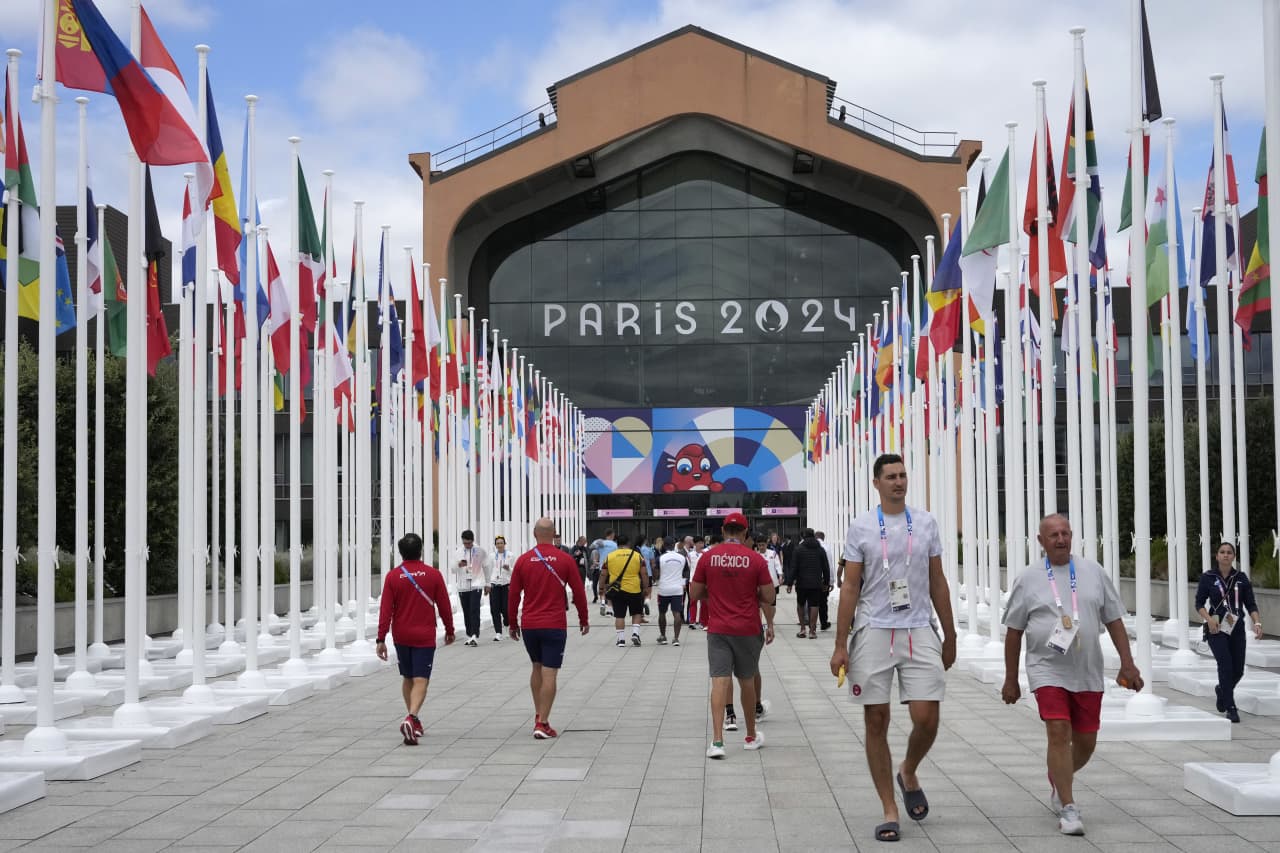
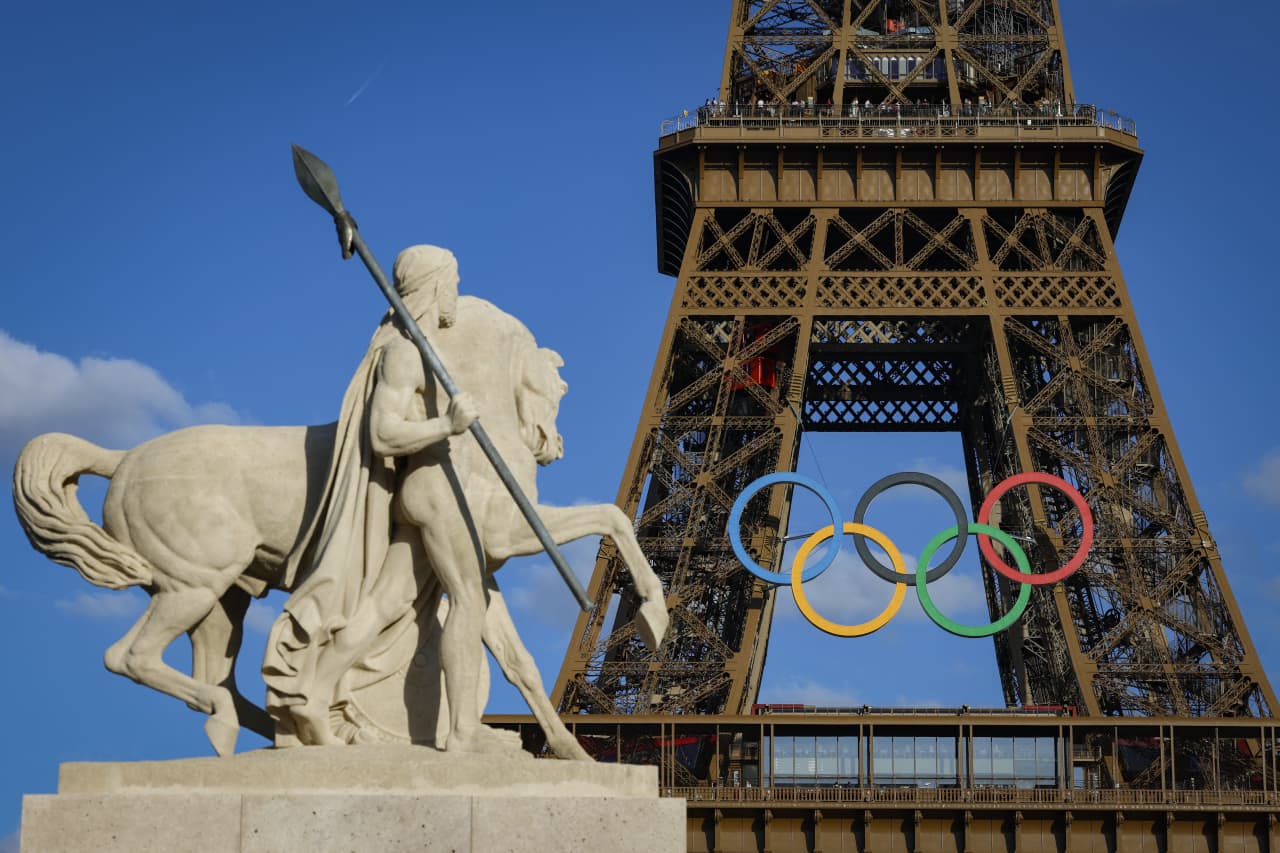
As Paris makes its final preparations for the Olympic games, its residents are busy with their own—packing their suitcases, confirming their reservations, and getting out of town.
Worried about the hordes of crowds and overall chaos the Olympics could bring, Parisians are fleeing the city in droves and inundating resort cities around the country. Hotels and holiday rentals in some of France’s most popular vacation destinations—from the French Riviera in the south to the beaches of Normandy in the north—say they are expecting massive crowds this year in advance of the Olympics. The games will run from July 26-Aug. 1.
“It’s already a major holiday season for us, and beyond that, we have the Olympics,” says Stéphane Personeni, general manager of the Lily of the Valley hotel in Saint Tropez. “People began booking early this year.”
Personeni’s hotel typically has no issues filling its rooms each summer—by May of each year, the luxury hotel typically finds itself completely booked out for the months of July and August. But this year, the 53-room hotel began filling up for summer reservations in February.
“We told our regular guests that everything—hotels, apartments, villas—are going to be hard to find this summer,” Personeni says. His neighbours around Saint Tropez say they’re similarly booked up.
As of March, the online marketplace Gens de Confiance (“Trusted People”), saw a 50% increase in reservations from Parisians seeking vacation rentals outside the capital during the Olympics.
Already, August is a popular vacation time for the French. With a minimum of five weeks of vacation mandated by law, many decide to take the entire month off, renting out villas in beachside destinations for longer periods.
But beyond the typical August travel, the Olympics are having a real impact, says Bertille Marchal, a spokesperson for Gens de Confiance.
“We’ve seen nearly three times more reservations for the dates of the Olympics than the following two weeks,” Marchal says. “The increase is definitely linked to the Olympic Games.”

Getty Images
According to the site, the most sought-out vacation destinations are Morbihan and Loire-Atlantique, a seaside region in the northwest; le Var, a coastal area within the southeast of France along the Côte d’Azur; and the island of Corsica in the Mediterranean.
Meanwhile, the Olympics haven’t necessarily been a boon to foreign tourism in the country. Many tourists who might have otherwise come to France are avoiding it this year in favour of other European capitals. In Paris, demand for stays at high-end hotels has collapsed, with bookings down 50% in July compared to last year, according to UMIH Prestige, which represents hotels charging at least €800 ($865) a night for rooms.
Earlier this year, high-end restaurants and concierges said the Olympics might even be an opportunity to score a hard-get-seat at the city’s fine dining.
In the Occitanie region in southwest France, the overall number of reservations this summer hasn’t changed much from last year, says Vincent Gare, president of the regional tourism committee there.
“But looking further at the numbers, we do see an increase in the clientele coming from the Paris region,” Gare told Le Figaro, noting that the increase in reservations has fallen directly on the dates of the Olympic games.
Michel Barré, a retiree living in Paris’s Le Marais neighbourhood, is one of those opting for the beach rather than the opening ceremony. In January, he booked a stay in Normandy for two weeks.
“Even though it’s a major European capital, Paris is still a small city—it’s a massive effort to host all of these events,” Barré says. “The Olympics are going to be a mess.”
More than anything, he just wants some calm after an event-filled summer in Paris, which just before the Olympics experienced the drama of a snap election called by Macron.
“It’s been a hectic summer here,” he says.

AFP via Getty Images
Parisians—Barré included—feel that the city, by over-catering to its tourists, is driving out many residents.
Parts of the Seine—usually one of the most popular summertime hangout spots —have been closed off for weeks as the city installs bleachers and Olympics signage. In certain neighbourhoods, residents will need to scan a QR code with police to access their own apartments. And from the Olympics to Sept. 8, Paris is nearly doubling the price of transit tickets from €2.15 to €4 per ride.
The city’s clear willingness to capitalise on its tourists has motivated some residents to do the same. In March, the number of active Airbnb listings in Paris reached an all-time high as hosts rushed to list their apartments. Listings grew 40% from the same time last year, according to the company.
With their regular clients taking off, Parisian restaurants and merchants are complaining that business is down.
“Are there any Parisians left in Paris?” Alaine Fontaine, president of the restaurant industry association, told the radio station Franceinfo on Sunday. “For the last three weeks, there haven’t been any here.”
Still, for all the talk of those leaving, there are plenty who have decided to stick around.
Jay Swanson, an American expat and YouTuber, can’t imagine leaving during the Olympics—he secured his tickets to see ping pong and volleyball last year. He’s also less concerned about the crowds and road closures than others, having just put together a series of videos explaining how to navigate Paris during the games.
“It’s been 100 years since the Games came to Paris; when else will we get a chance to host the world like this?” Swanson says. “So many Parisians are leaving and tourism is down, so not only will it be quiet but the only people left will be here for a party.”
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.






















