Hong Kong’s Property Market Is a Mess—and the Fed Is Partly to Blame
U.S. rate increases have tamed inflation at home but caused pain elsewhere
Hong Kong’s notoriously expensive property market is often seen as a barometer of the city’s economy. It isn’t looking good.
Home prices are down. Office vacancy rates have hit a record high. Commercial real-estate investment has plummeted. The shares of some big developers in the city are trading at a 30-year low to their net asset value, a measure of financial health, according to research by analysts at JPMorgan.
A key reason is high interest rates, which have increased the burden on mortgage-paying home buyers, said Cathie Chung, senior director of research at Jones Lang LaSalle, a real-estate services company. The Hong Kong dollar’s peg to the U.S. dollar forces monetary authorities in the city to track U.S. interest-rate decisions, limiting their ability to stimulate the property sector and the wider economy.
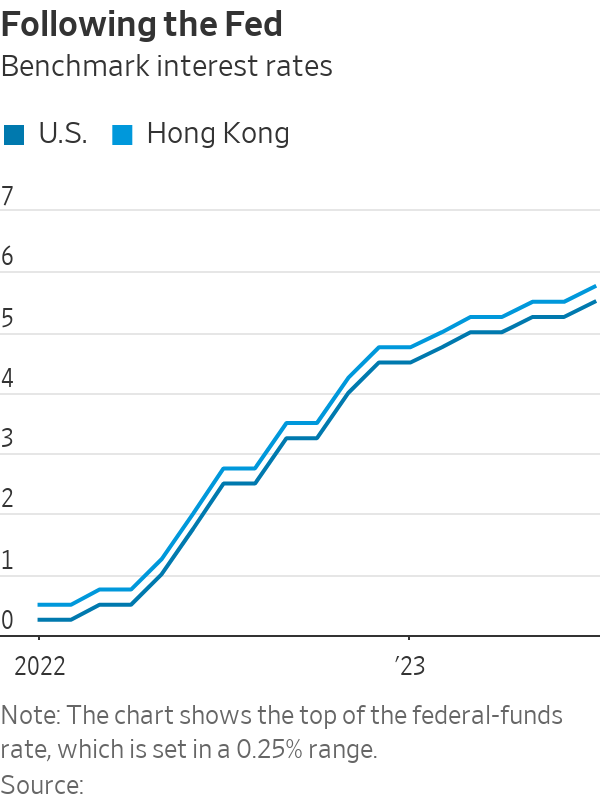
The Federal Reserve has embarked on a historic cycle of interest-rate rises since last March, raising the benchmark federal-funds rate from around zero to 5.25% to 5.50%. The Hong Kong Monetary Authority, the city’s de facto central bank, has followed these hikes, increasing its base rate to 5.75% from 0.75% over the same period.
The full impact of higher interest rates in the city still hasn’t been felt, said Asif Ghafoor, chief executive of online real-estate marketplace Spacious. Asking prices of residential properties listed on the platform have fallen 5% since the start of the year. Sales prices tend to follow suit, and are likely to fall 5% to 10% in the next six months, he said.
To prop up the market, the HKMA relaxed mortgage rules in early July for the first time since 2009, allowing home buyers to pay less upfront and borrow more for some properties if they plan to live in them. But those working in the sector think the pain is far from over.
“We expect that the recovery will be slow and long,” said Chung at Jones Lang LaSalle.
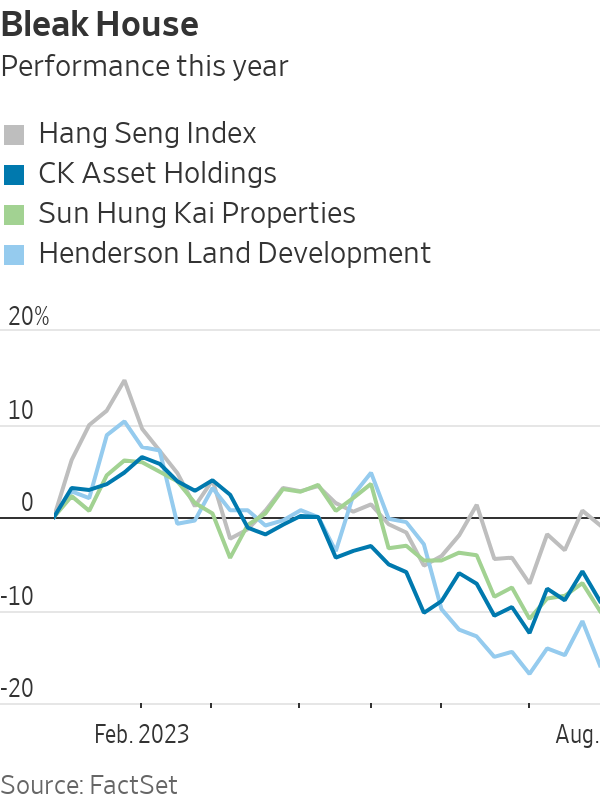
The slump in the property market has hurt the share prices of developers, a major source of wealth for some of the city’s richest families. CK Asset Holdings, Henderson Land Development, Sun Hung Kai Properties and New World Development—all still partly owned by the families of the founders—are performing much worse than the wider stock market this year. New World and Henderson Land have lost more than 15% this year, according to FactSet data.
Hong Kong is one of the world’s leading financial centres and is seen by many foreign businesses as a gateway to mainland China. It is now being hit by a slowdown in investment-banking activity—with several large banks cutting staff this year—and the shaky recovery of China’s economy, which has undermined confidence among businesses and potential home buyers in Hong Kong.
The overall vacancy rate for offices reached a record high of 15.7% in the first half of this year, compared with an average of under 5% in 2018, according to figures by CBRE. In the central business district, there was almost eight times as much empty office space as in 2018, when the area had a vacancy rate of just 1.3%.
The equivalent of $603 million was invested in commercial real estate between April and June, according to CBRE data, just a third of the first-quarter tally and the lowest quarterly figure since the end of 2008, when the global financial crisis caused a huge drop in confidence.
Hong Kong’s border with mainland China was reopened earlier this year, but companies from the mainland haven’t grabbed office space in the numbers many had hoped, said Ada Fung, head of office services at CBRE Hong Kong. Flexible working arrangements and geopolitical tensions that have made many companies pause expansion plans are also crimping demand, she said.
The drop in demand is being exacerbated by a supply glut. Developers bought land and started constructing a number of new buildings before 2019, when widespread protests rocked the city and only ended with the passing of a strict national-security law. Demand for commercial property after that was soon undermined by the spread of Covid-19.
This shift in supply and demand is finally giving potential renters the upper hand, said Fung. “It could be a healthy reset,” she said.
There are some reasons for optimism. Retail businesses have increased their demand for commercial property after the reopening of the border with China, which has brought in tourists looking to spend on luxury goods. There is also hope that a recent rise in residential rents could help home prices.
After an exodus of professionals and other residents in recent years, people have started to move to the city, including foreign students and those coming to Hong Kong through government talent schemes designed to reverse a brain drain. That is helping rents pick up after hitting a bottom in the first quarter, and could lead to more demand for properties as investments, said Cusson Leung, head of property research in Hong Kong at JPMorgan.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.
Ahead of the Games, a breakdown of the city’s most desirable places to live
PARIS —Paris has long been a byword for luxurious living. The traditional components of the upscale home, from parquet floors to elaborate moldings, have their origins here. Yet settling down in just the right address in this low-rise, high-density city may be the greatest luxury of all.
Tradition reigns supreme in Paris real estate, where certain conditions seem set in stone—the western half of the city, on either side of the Seine, has long been more expensive than the east. But in the fashion world’s capital, parts of the housing market are also subject to shifting fads. In the trendy, hilly northeast, a roving cool factor can send prices in this year’s hip neighborhood rising, while last year’s might seem like a sudden bargain.
This week, with the opening of the Olympic Games and the eyes of the world turned toward Paris, The Wall Street Journal looks at the most expensive and desirable areas in the City of Light.
The Most Expensive Arrondissement: the 6th
Known for historic architecture, elegant apartment houses and bohemian street cred, the 6th Arrondissement is Paris’s answer to Manhattan’s West Village. Like its New York counterpart, the 6th’s starving-artist days are long behind it. But the charm that first wooed notable residents like Gertrude Stein and Jean-Paul Sartre is still largely intact, attracting high-minded tourists and deep-pocketed homeowners who can afford its once-edgy, now serene atmosphere.
Le Breton George V Notaires, a Paris notary with an international clientele, says the 6th consistently holds the title of most expensive arrondissement among Paris’s 20 administrative districts, and 2023 was no exception. Last year, average home prices reached $1,428 a square foot—almost 30% higher than the Paris average of $1,100 a square foot.
According to Meilleurs Agents, the Paris real estate appraisal company, the 6th is also home to three of the city’s five most expensive streets. Rue de Furstemberg, a secluded loop between Boulevard Saint-Germain and the Seine, comes in on top, with average prices of $2,454 a square foot as of March 2024.
For more than two decades, Kyle Branum, a 51-year-old attorney, and Kimberly Branum, a 60-year-old retired CEO, have been regular visitors to Paris, opting for apartment rentals and ultimately an ownership interest in an apartment in the city’s 7th Arrondissement, a sedate Left Bank district known for its discreet atmosphere and plutocratic residents.
“The 7th was the only place we stayed,” says Kimberly, “but we spent most of our time in the 6th.”
In 2022, inspired by the strength of the dollar, the Branums decided to fulfil a longstanding dream of buying in Paris. Working with Paris Property Group, they opted for a 1,465-square-foot, three-bedroom in a building dating to the 17th century on a side street in the 6th Arrondissement. They paid $2.7 million for the unit and then spent just over $1 million on the renovation, working with Franco-American visual artist Monte Laster, who also does interiors.
The couple, who live in Santa Barbara, Calif., plan to spend about three months a year in Paris, hosting children and grandchildren, and cooking after forays to local food markets. Their new kitchen, which includes a French stove from luxury appliance brand Lacanche, is Kimberly’s favourite room, she says.
Another American, investor Ashley Maddox, 49, is also considering relocating.
In 2012, the longtime Paris resident bought a dingy, overstuffed 1,765-square-foot apartment in the 6th and started from scratch. She paid $2.5 million and undertook a gut renovation and building improvements for about $800,000. A centrepiece of the home now is the one-time salon, which was turned into an open-plan kitchen and dining area where Maddox and her three children tend to hang out, American-style. Just outside her door are some of the city’s best-known bakeries and cheesemongers, and she is a short walk from the Jardin du Luxembourg, the Left Bank’s premier green space.
“A lot of the majesty of the city is accessible from here,” she says. “It’s so central, it’s bananas.” Now that two of her children are going away to school, she has listed the four-bedroom apartment with Varenne for $5 million.
The Most Expensive Neighbourhoods: Notre-Dame and Invalides
Garrow Kedigian is moving up in the world of Parisian real estate by heading south of the Seine.
During the pandemic, the Canada-born, New York-based interior designer reassessed his life, he says, and decided “I’m not going to wait any longer to have a pied-à-terre in Paris.”
He originally selected a 1,130-square-foot one-bedroom in the trendy 9th Arrondissement, an up-and-coming Right Bank district just below Montmartre. But he soon realised it was too small for his extended stays, not to mention hosting guests from out of town.
After paying about $1.6 million in 2022 and then investing about $55,000 in new decor, he put the unit up for sale in early 2024 and went house-shopping a second time. He ended up in the Invalides quarter of the 7th Arrondissement in the shadow of one Paris’s signature monuments, the golden-domed Hôtel des Invalides, which dates to the 17th century and is fronted by a grand esplanade.
His new neighbourhood vies for Paris’s most expensive with the Notre-Dame quarter in the 4th Arrondissement, centred on a few islands in the Seine behind its namesake cathedral. According to Le Breton, home prices in the Notre-Dame neighbourhood were $1,818 a square foot in 2023, followed by $1,568 a square foot in Invalides.
After breaking even on his Right Bank one-bedroom, Kedigian paid $2.4 million for his new 1,450-square-foot two-bedroom in a late 19th-century building. It has southern exposures, rounded living-room windows and “gorgeous floors,” he says. Kedigian, who bought the new flat through Junot Fine Properties/Knight Frank, plans to spend up to $435,000 on a renovation that will involve restoring the original 12-foot ceiling height in many of the rooms, as well as rescuing the ceilings’ elaborate stucco detailing. He expects to finish in 2025.
Over in the Notre-Dame neighbourhood, Belles demeures de France/Christie’s recently sold a 2,370-square-foot, four-bedroom home for close to the asking price of about $8.6 million, or about $3,630 a square foot. Listing agent Marie-Hélène Lundgreen says this places the unit near the very top of Paris luxury real estate, where prime homes typically sell between $2,530 and $4,040 a square foot.
The Most Expensive Suburb: Neuilly-sur-Seine
The Boulevard Périphérique, the 22-mile ring road that surrounds Paris and its 20 arrondissements, was once a line in the sand for Parisians, who regarded the French capital’s numerous suburbs as something to drive through on their way to and from vacation. The past few decades have seen waves of gentrification beyond the city’s borders, upgrading humble or industrial districts to the north and east into prime residential areas. And it has turned Neuilly-sur-Seine, just northwest of the city, into a luxury compound of first resort.
In 2023, Neuilly’s average home price of $1,092 a square foot made the leafy, stately community Paris’s most expensive suburb.
Longtime residents, Alain and Michèle Bigio, decided this year is the right time to list their 7,730-square-foot, four-bedroom townhouse on a gated Neuilly street.
The couple, now in their mid 70s, completed the home in 1990, two years after they purchased a small parcel of garden from the owners next door for an undisclosed amount. Having relocated from a white-marble château outside Paris, the couple echoed their previous home by using white- and cream-coloured stone in the new four-story build. The Bigios, who will relocate just back over the border in the 16th Arrondissement, have listed the property with Emile Garcin Propriétés for $14.7 million.
The couple raised two adult children here and undertook upgrades in their empty-nester years—most recently, an indoor pool in the basement and a new elevator.
The cool, pale interiors give way to dark and sardonic images in the former staff’s quarters in the basement where Alain works on his hobby—surreal and satirical paintings, whose risqué content means that his wife prefers they stay downstairs. “I’m not a painter,” he says. “But I paint.”
The Trendiest Arrondissement: the 9th
French interior designer Julie Hamon is theatre royalty. Her grandfather was playwright Jean Anouilh, a giant of 20th-century French literature, and her sister is actress Gwendoline Hamon. The 52-year-old, who divides her time between Paris and the U.K., still remembers when the city’s 9th Arrondissement, where she and her husband bought their 1,885-square-foot duplex in 2017, was a place to have fun rather than put down roots. Now, the 9th is the place to do both.
The 9th, a largely 19th-century district, is Paris at its most urban. But what it lacks in parks and other green spaces, it makes up with nightlife and a bustling street life. Among Paris’s gentrifying districts, which have been transformed since 2000 from near-slums to the brink of luxury, the 9th has emerged as the clear winner. According to Le Breton, average 2023 home prices here were $1,062 a square foot, while its nearest competitors for the cool crown, the 10th and the 11th, have yet to break $1,011 a square foot.
A co-principal in the Bobo Design Studio, Hamon—whose gut renovation includes a dramatic skylight, a home cinema and air conditioning—still seems surprised at how far her arrondissement has come. “The 9th used to be well known for all the theatres, nightclubs and strip clubs,” she says. “But it was never a place where you wanted to live—now it’s the place to be.”
With their youngest child about to go to college, she and her husband, 52-year-old entrepreneur Guillaume Clignet, decided to list their Paris home for $3.45 million and live in London full-time. Propriétés Parisiennes/Sotheby’s is handling the listing, which has just gone into contract after about six months on the market.
The 9th’s music venues were a draw for 44-year-old American musician and piano dealer, Ronen Segev, who divides his time between Miami and a 1,725-square-foot, two-bedroom in the lower reaches of the arrondissement. Aided by Paris Property Group, Segev purchased the apartment at auction during the pandemic, sight unseen, for $1.69 million. He spent $270,000 on a renovation, knocking down a wall to make a larger salon suitable for home concerts.
During the Olympics, Segev is renting out the space for about $22,850 a week to attendees of the Games. Otherwise, he prefers longer-term sublets to visiting musicians for $32,700 a month.
Most Exclusive Address: Avenue Junot
Hidden in the hilly expanses of the 18th Arrondissement lies a legendary street that, for those in the know, is the city’s most exclusive address. Avenue Junot, a bucolic tree-lined lane, is a fairy-tale version of the city, separate from the gritty bustle that surrounds it.
Homes here rarely come up for sale, and, when they do, they tend to be off-market, or sold before they can be listed. Martine Kuperfis—whose Paris-based Junot Group real-estate company is named for the street—says the most expensive units here are penthouses with views over the whole of the city.
In 2021, her agency sold a 3,230-square-foot triplex apartment, with a 1,400-square-foot terrace, for $8.5 million. At about $2,630 a square foot, that is three times the current average price in the whole of the 18th.
Among its current Junot listings is a 1930s 1,220-square-foot townhouse on the avenue’s cobblestone extension, with an asking price of $2.8 million.
This stylish family home combines a classic palette and finishes with a flexible floorplan
Just 55 minutes from Sydney, make this your creative getaway located in the majestic Hawkesbury region.






















