Big Oil’s Talent Crisis: High Salaries Are No Longer Enough
Energy companies scramble to attract engineers as young workers fret over climate and job security
Good news from the oil patch: Jobs are plentiful and salaries are soaring.
The bad news is that young people still aren’t interested.
Even as oil-and-gas companies post record profits, the industry is facing a worsening talent drought.
At U.S. colleges, the pool of new entrants for petroleum-engineering programs has shrunk to its smallest size since before the fracking boom began more than a decade ago. European universities, which have historically provided many of the engineers for companies with operations across the Middle East and Asia, are seeing similar trends.
Students and high-skilled young workers are concerned about the industry’s role in climate change, as well as long-term job security given that global economies are transitioning away from fossil fuels to other energy sources, according to executives, analysts and professors.
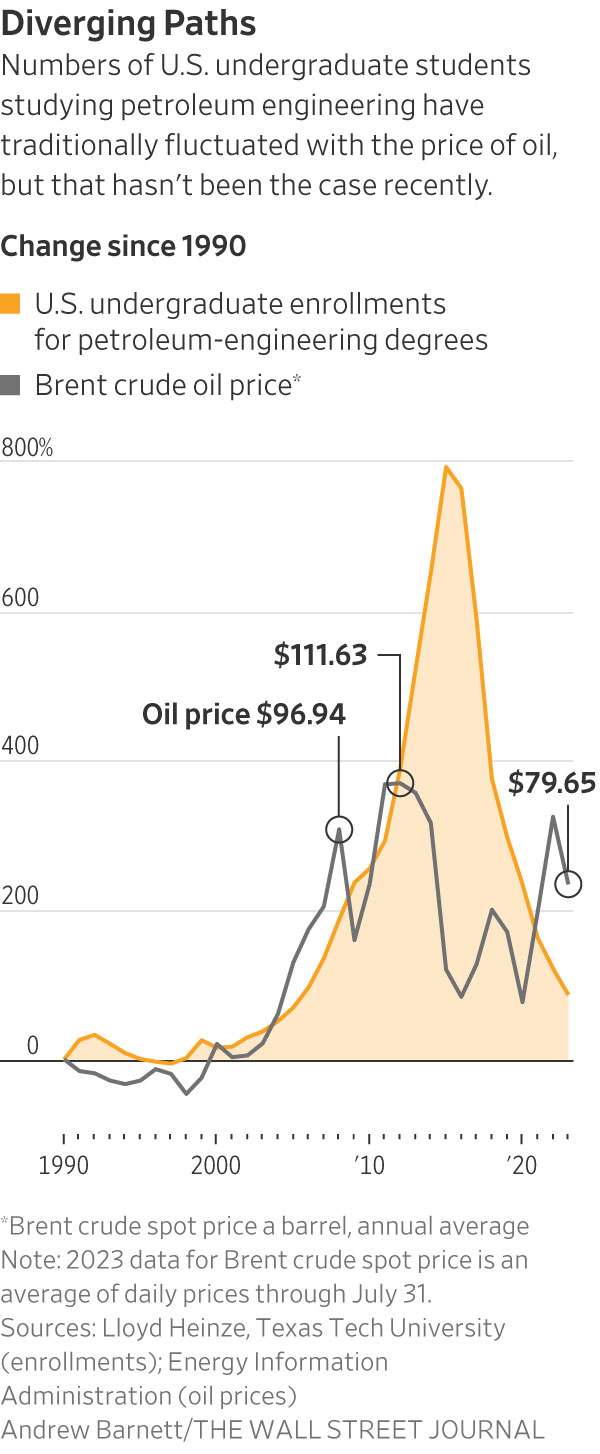
The trend is a stark departure from previous cycles, when the industry’s workforce ebbed and flowed with the rise and fall of oil prices.
Between 2016 and 2021—a period when the Brent crude price nearly doubled—the number of petroleum-engineering graduates more than halved, according to the U.S. Department of Education.
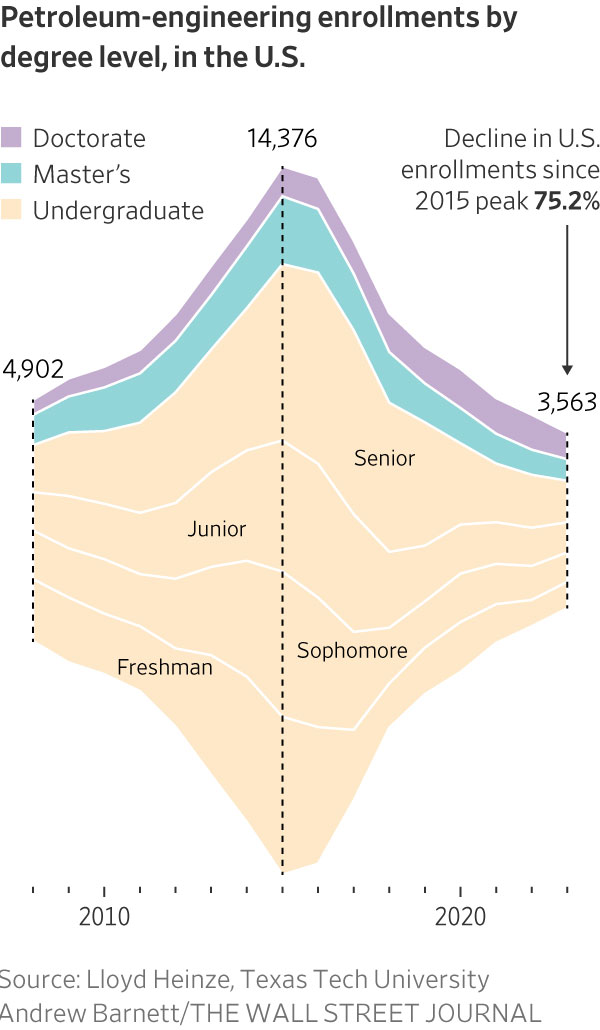
The number of undergraduates pursuing petroleum engineering has dropped 75% since 2014, according to Lloyd Heinze, a Texas Tech University professor.
It is a trend that has continued even as other recent studies have shown that the average graduate earns 40% more than a peer with a computer science degree.
That puts students, including Hayden Gregg, in high demand.
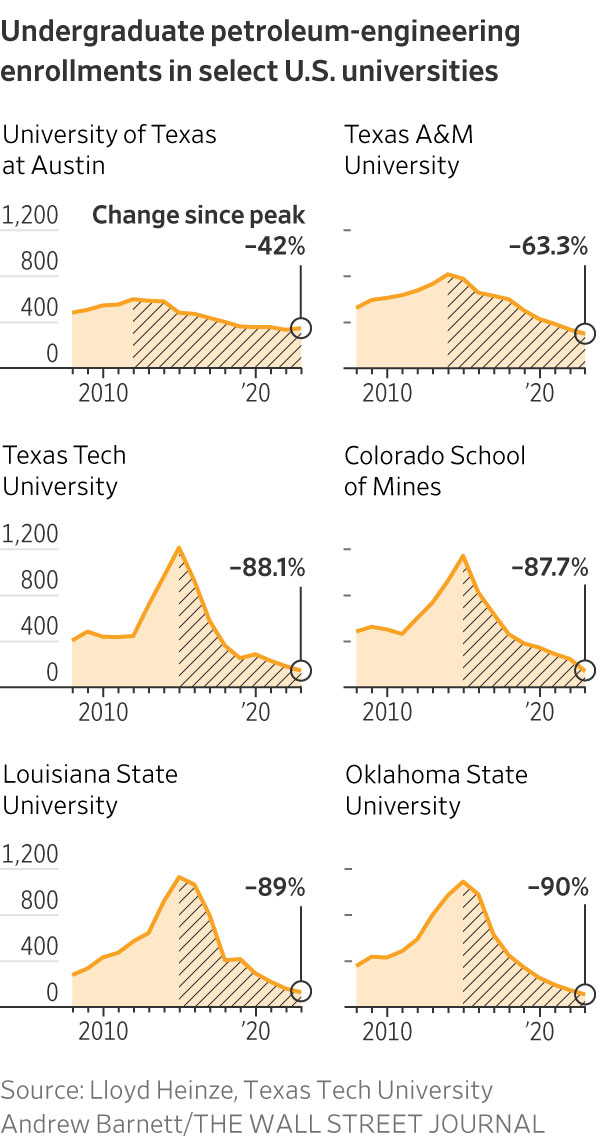
The 21-year-old Kansas City, Mo., native is studying petroleum engineering at Colorado School of Mines. His graduating class of 36 students is down from around 200 in the years before oil prices collapsed in the mid-2010s, according to a college official.
“People are concerned they won’t have a job in 10 to 20 years,” said Gregg.
Encouraged by his roommates and a visit to the oil-and-gas heartland of Texas, he became convinced that the industry offers a range of engineering possibilities as it transitions to a broader mix of energy sources.
“Even if oil and gas is going away, I can deploy my skills in other engineering fields,” he said.
Jennifer Miskimins, head of the petroleum engineering department at Colorado School of Mines, said Gregg’s graduating class is benefiting from a pickup in oil-industry hiring and many have gotten good internships. “They’re a hot commodity,” she said. “I think this class is going to be sitting pretty.”
Oil-and-gas companies are pouring money into fellowships and other programs designed to cultivate a new generation of talent. Much of the focus is on white-collar careers that tend to attract college graduates, but the trend is broadly true among the industry’s blue-collar workers as well.
A big part of the pitch is that the industry is increasingly dynamic and creative, requiring employees who can run carbon capture, hydrogen and geothermal projects, said Barbara Burger, who served in several leadership roles at Chevron and is now a senior adviser at investment bank Lazard.
Part of the challenge, she said, is that there are more startups and fast-growing companies in those fields that don’t carry the same baggage as the giants that earn most of their profits from fossil fuels.
“There’s competition in a way that probably wasn’t there 15 years ago,” she said.
Burger recently attended an event hosted by Fervo Energy, a startup that uses the shale boom’s horizontal drilling and fracking techniques to develop geothermal wells for electricity generation. Around 60% of Fervo’s employees previously worked at oil-and-gas outfits, the company said.
To attract workers, she said, oil-and-gas companies need to better articulate their energy transition strategies, including efforts to carve out new businesses or curb emissions.
“That’s a hook for employees—current and future,” Burger said. “They want to know there’s a future in the actual companies, the industries and the skill sets they have.”
The talent shortage represents a long-term problem at a moment when energy security—largely dependent on fossil fuels for the foreseeable future—is increasingly a global priority. Since Russia’s invasion of Ukraine last year, Europe has become desperate for new supplies of oil and gas, though countries around the world are trying to keep fuel affordable.
Darian Kane-Stolz said that growing up in New York, she was always concerned with climate change. She taught neighbours how to recycle.
When Kane-Stolz, 25, enrolled at the University of Texas at Austin seven years ago, she felt that joining the petroleum-engineering program was consistent with her desire to have a positive impact on the planet.
Now a BP engineer bringing wells online in the Gulf of Mexico, she said the attitude toward the industry has drastically shifted within her cohort. Before she goes out with friends, she sometimes prepares talking points in case someone attacks the industry.
“There’s definitely a negative perception out there,” said Kane-Stolz.
BP this year launched a new $4 million fellowship program with U.S. universities to provide students with exposure to the energy industry. It also said last year that it planned to double the size of its apprenticeship program to 2,000 people this decade.
“To achieve our goal of reimagining energy, we need the brightest talent,” said a BP spokesperson.
Meanwhile, Kane-Stolz’s alma mater, the University of Texas, is working on adding a new master’s degree without the word “petroleum” to capture a broader group of students who still want to work in energy-related engineering, said Jon E. Olson, the department chair of petroleum and geoscience at UT.
Other universities are ending their petroleum engineering degrees or rebranding them. Imperial College London—formerly housing the Royal School of Mines—shut its program last year and replaced it with one in geo-energy with machine learning and data science.
Analysts and company officials say a steady flow of talent is critical to company efforts to build out infrastructure needed to curb emissions and develop clean-energy and low-carbon businesses.
“One of the scarcest resources at the moment seems to be people,” said Aslak Hellestø, a business adviser for Northern Lights, a carbon capture and storage project off the coast of Norway operated by European energy companies Equinor, Shell and TotalEnergies.
“This is groundbreaking technology and we cannot afford to try and fail,” he said. “We need young people with new ideas and bright minds to make it right the first time.”
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Records keep falling in 2025 as harbourfront, beachfront and blue-chip estates crowd the top of the market.
A divide has opened in the tech job market between those with artificial-intelligence skills and everyone else.
Only 25 of the most intricate Rolls-Royce Phantoms ever made will celebrate the nameplate’s 100-year legacy.
A luxury lifestyle might cost more than it used to, but how does it compare with cities around the world?
From mud baths to herbal massages, Fiji’s heat rituals turned one winter escape into a soul-deep reset.
























